Go学习之go-ethereum【以太坊】源码分析 - rlp(二)
接上一篇的源码中的rlp 继续......
- 回顾
- 解码(类型判断,stream结构,数据长度)
- 编码(encbuf)
- 下期
1、回顾
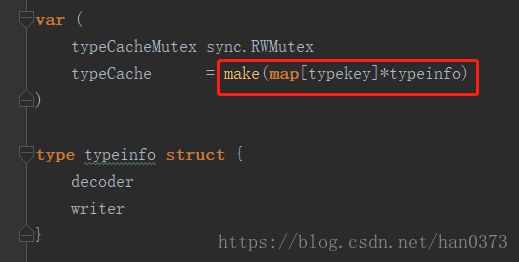
上一文当中讲到了以太坊的基本定义和认识,同时讲解了部分源码中rlp包中的编解码内容。其中,用Go实现的typecache为快速定位查找定义的编解码函数的核心数据结构。
Map中的Key则为类型,Value为对应的编码器和解码器
通过Key得到的类型,使用genTypeInfo生成对应类型的编解码器函数。
接下来,就是具体Decoder和Writer的处理逻辑了。
2、解码判断
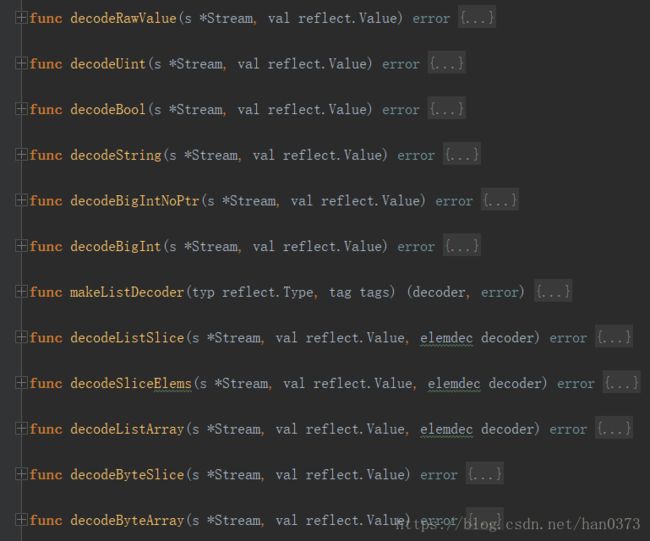
通过定义makeDecoder函数,根据类型来分配不同的处理函数。
func makeDecoder(typ reflect.Type, tags tags) (dec decoder, err error) {
kind := typ.Kind() // 获取当前需要解析的类型和长度
switch {
case typ == rawValueType:
return decodeRawValue, nil
case typ.Implements(decoderInterface):
return decodeDecoder, nil
case kind != reflect.Ptr && reflect.PtrTo(typ).Implements(decoderInterface):
return decodeDecoderNoPtr, nil
case typ.AssignableTo(reflect.PtrTo(bigInt)):
return decodeBigInt, nil
case typ.AssignableTo(bigInt):
return decodeBigIntNoPtr, nil
case isUint(kind):
return decodeUint, nil
case kind == reflect.Bool:
return decodeBool, nil
case kind == reflect.String:
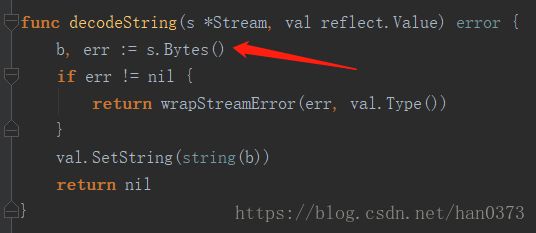
return decodeString, nil
case kind == reflect.Slice || kind == reflect.Array:
return makeListDecoder(typ, tags)
case kind == reflect.Struct:
return makeStructDecoder(typ) //对于不同的结构体类型进行处理
case kind == reflect.Ptr:
if tags.nilOK {
return makeOptionalPtrDecoder(typ)
}
return makePtrDecoder(typ)
case kind == reflect.Interface:
return decodeInterface, nil
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("rlp: type %v is not RLP-serializable", typ)
}
}判断类型时的所有解码方法:
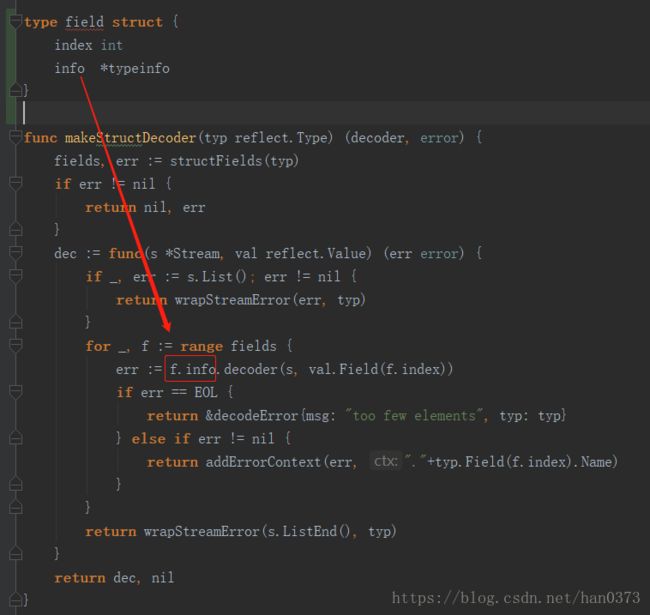
通过反射的方法,遍历fields,调用字段的解码器方法
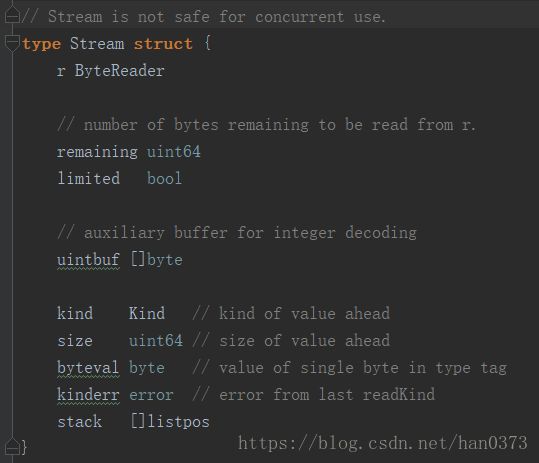
3、Stream
先来看一下它的结构。
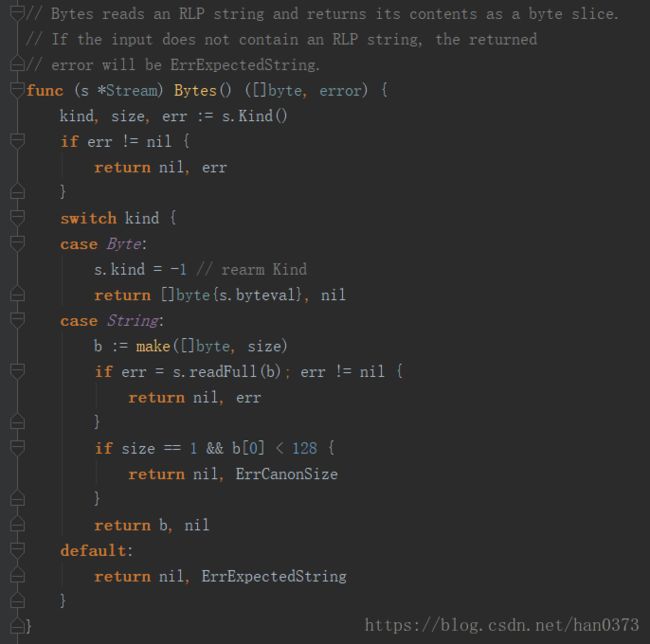
编码中的stream,是用来读取以流方式解码RLP的一个辅助类。在解码过程中,根据Kind()方法获取需要解码的对象的类型和长度,然后根据长度和类型进行数据的解码。
判断类型:如果是Byte类型,直接返回;如果是string类型,读取指定长度值后返回。
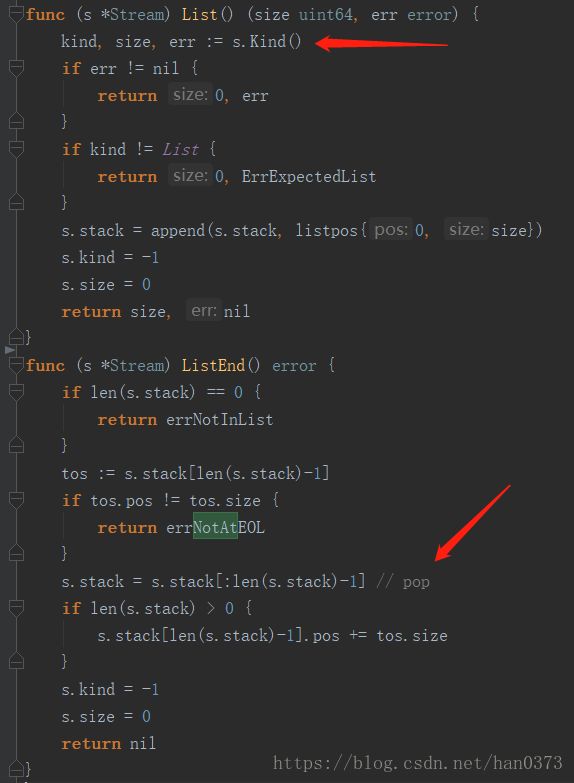
Stream的List()方法:
1、调用Kind方法获取类型和长度,如果类型不匹配那么就抛出错误;
2、把一个listpos对象压入到堆栈;
3、pos:记录当前这个list已经读取了多少字节的数据(初始为0);
4、size:记录这个list对象一共需要读取多少字节数据;
5、比对pos字段和size字段是否相等,不相等则抛异常;
Stream的ListEnd()方法:
1、stack长度为0,抛异常(没有数据);
2、当前读取的数据数量pos不等于声明的数据长度size,抛异常(“call of ListEnd not positioned at EOL”);
3、进行“pop”操作,如果当前stack不为空,pos再加上处理完的数据长度;
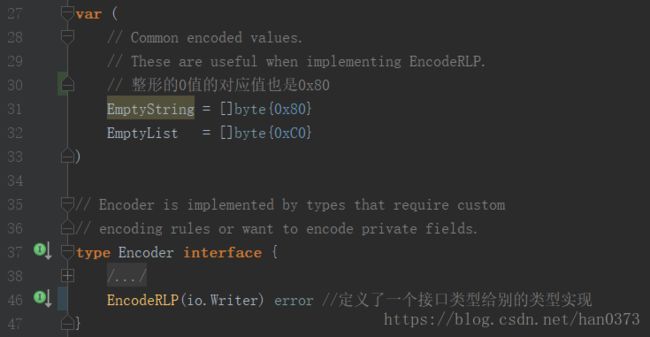
4、编码encode.go
编码的过程与解码大致类似。
(1)定义空字符串和空List值,定义接口EncodeRLP
(2)makeWriter与makeDecoder类似
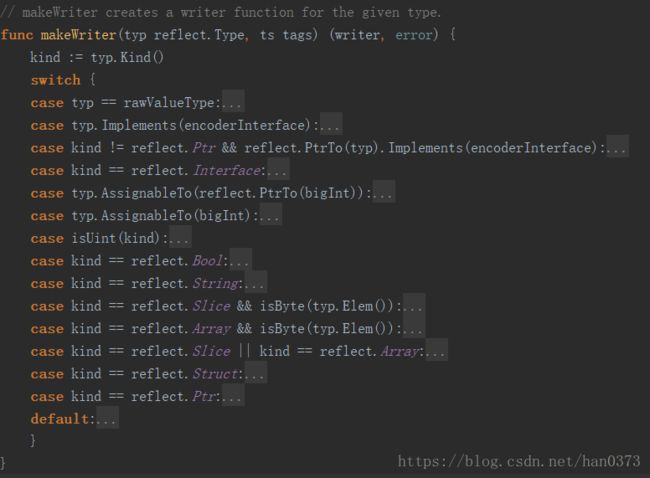
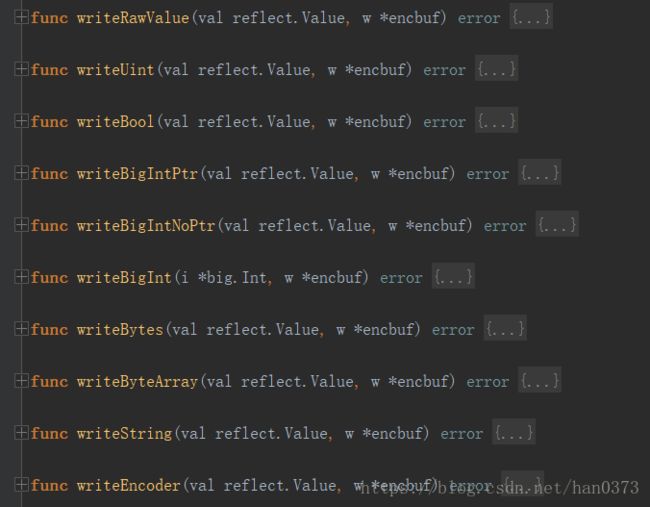
(3)数据填充
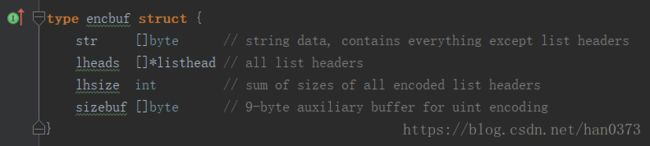
填充过程中使用了一个缓冲buf对象,encbuf:
下期文章将进入以太坊p2p 进行源码分析。
---------------------
另外,文章部分内容和图片来自ZtesoftCS的github,在此鸣谢。
有任何建议或问题,欢迎加微信一起学习交流,欢迎从事IT,热爱IT,喜欢深挖源代码的行业大牛加入,一起探讨。
个人微信号:bboyHan