dlib 13 dlib自带demo DNN狗脸检测
01 dlib的基于DNN的狗脸检测资源
代码:dlib\examples\dnn_mmod_dog_hipsterizer.cpp
工程名:dnn_mmod_dog_hipsterizer
测试图像文件:
dlib\examples\faces\bald_guys.jpg
从代码注释中可以获得model数据文件:
http://dlib.net/files/mmod_dog_hipsterizer.dat.bz2
把上面获得的压缩包内容分别解压到data目录下:
\dlib\data\mmod_dog_hipsterizer.dat
02 项目设置
把examples解决方案中的dnn_mmod_dog_hipsterizer工程设置为启动项。
如需调试,使用debug。使用release运行速度会快一些。
配置属性==>调试==>命令参数==>..\..\..\data\mmod_dog_hipsterizer.dat ..\..\..\examples\faces\dogs.jpg
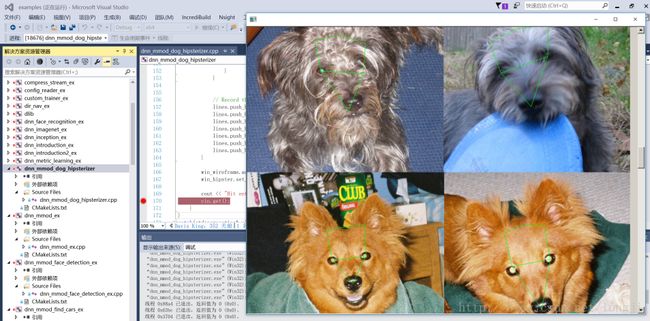
配置属性==>调试==>工作目录==>$(OutDir)03 运行结果
04 代码
dlib\examples\dnn_mmod_dog_hipsterizer.cpp
// The contents of this file are in the public domain. See LICENSE_FOR_EXAMPLE_PROGRAMS.txt
/*
This example shows how to run a CNN based dog face detector using dlib. The
example loads a pretrained model and uses it to find dog faces in images.
We also use the dlib::shape_predictor to find the location of the eyes and
nose and then draw glasses and a mustache onto each dog found :)
Users who are just learning about dlib's deep learning API should read the
dnn_introduction_ex.cpp and dnn_introduction2_ex.cpp examples to learn how
the API works. For an introduction to the object detection method you
should read dnn_mmod_ex.cpp
TRAINING THE MODEL
Finally, users interested in how the dog face detector was trained should
read the dnn_mmod_ex.cpp example program. It should be noted that the
dog face detector used in this example uses a bigger training dataset and
larger CNN architecture than what is shown in dnn_mmod_ex.cpp, but
otherwise training is the same. If you compare the net_type statements
in this file and dnn_mmod_ex.cpp you will see that they are very similar
except that the number of parameters has been increased.
Additionally, the following training parameters were different during
training: The following lines in dnn_mmod_ex.cpp were changed from
mmod_options options(face_boxes_train, 40*40);
trainer.set_iterations_without_progress_threshold(300);
to the following when training the model used in this example:
mmod_options options(face_boxes_train, 80*80);
trainer.set_iterations_without_progress_threshold(8000);
Also, the random_cropper was left at its default settings, So we didn't
call these functions:
cropper.set_chip_dims(200, 200);
cropper.set_min_object_height(0.2);
The training data used to create the model is also available at
http://dlib.net/files/data/CU_dogs_fully_labeled.tar.gz
Lastly, the shape_predictor was trained with default settings except we
used the following non-default settings: cascade depth=20, tree
depth=5, padding=0.2
*/
#include 5,5,2,2,SUBNET>;
template <long num_filters, typename SUBNET> using con5 = con5,5,1,1,SUBNET>;
template <typename SUBNET> using downsampler = relu32, relu32, relu16,SUBNET>>>>>>>>>;
template <typename SUBNET> using rcon5 = relu45,SUBNET>>>;
using net_type = loss_mmod1,9,9,1,1,rcon56>>>>>>>>;
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char** argv) try
{
if (argc < 3)
{
cout << "Call this program like this:" << endl;
cout << "./dnn_mmod_dog_hipsterizer mmod_dog_hipsterizer.dat faces/dogs.jpg" << endl;
cout << "\nYou can get the mmod_dog_hipsterizer.dat file from:\n";
cout << "http://dlib.net/files/mmod_dog_hipsterizer.dat.bz2" << endl;
return 0;
}
// load the models as well as glasses and mustache.
net_type net;
shape_predictor sp;
matrix glasses, mustache;
deserialize(argv[1]) >> net >> sp >> glasses >> mustache;
pyramid_up(glasses);
pyramid_up(mustache);
image_window win1(glasses);
image_window win2(mustache);
image_window win_wireframe, win_hipster;
// Now process each image, find dogs, and hipsterize them by drawing glasses and a
// mustache on each dog :)
for (int i = 2; i < argc; ++i)
{
matrix img;
load_image(img, argv[i]);
// Upsampling the image will allow us to find smaller dog faces but will use more
// computational resources.
//pyramid_up(img);
auto dets = net(img);
win_wireframe.clear_overlay();
win_wireframe.set_image(img);
// We will also draw a wireframe on each dog's face so you can see where the
// shape_predictor is identifying face landmarks.
std::vector