行为型模式
行为型模式关注于应用运行过程中算法的提供和通信关系的梳理。
相比于创建型模式和结构型模式,行为型模式包含了最多的设计模式种类,包括:
- 职责链模式
- 模板方法模式
- 解释器模式
- 命令模式
- 迭代器模式
- 中介者模式
- 备忘录模式
- 观察者模式
- 状态模式
- 策略模式
- 访问者模式
职责链模式
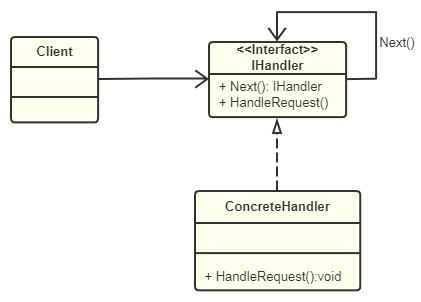
职责链模式为了避免请求发送者与接收者耦合在一起,让多个对象都有可能接收请求,会将这些对象连接成一条链,并且沿着这条链传递请求,直到有对象处理它为止。
GOF对外观模式的描述为:
Avoid coupling the sender of a request to its receiver by giving morethan one object a chance to handle the request. Chain the receivingobjects and pass the request along the chain until an object handles it.
— Design Patterns : Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software
在日常生活中,也会遇到类似的具有一系列“工序”的场景,比如用洗衣机洗衣服,需要经过注水、洗涤、漂洗、排水等过程,但作为使用者,我们并不需要关注这些步骤,需要做的只是把衣服放到洗衣机、加入洗涤剂、等结束后取出而已。
职责链模式的使用场景
- 输入对象需要经过一系列处理,而每个处理环节也只针对这个对象进行修改,但产出的是同一个对象,比如洗衣服要经过多个步骤,但每个步骤产出的都是衣服本身。
- 对象本身要经过哪些处理需要在运行态动态决定,决定的因素可能取决于对象当前的某些属性或外部策略,但为了把输入方和输出方从与每个具体的处理环节的耦合关系中解脱出来,可以考虑把它们做成一条链,按照每个节点的后继依次遍历,酌情处理。
- 需要向多个操作发送处理请求时,可以用链表的形式组织它们。
- 在对象处理经常发生动态变化的情况下,借助链表来动态维护处理对象。
代码示例
假设商品的价格分成内部认购价、折扣价、平价,以及邮购价格,用职责链模式来进行价格的计算:
public enum PurchaseType
{
Internal, //内部认购价格
Discount, //折扣价
Regular, //平价
Mail //邮购价
}
//请求对象
public class Request
{
public double Price { get; set; }
public PurchaseType Type { get; set; }
public Request(double price, PurchaseType type)
{
this.Price = price;
this.Type = type;
}
}
//抽象的操作对象
public interface IHandler
{
void HandleRequest(Request request);
IHandler Next { get; set; }
PurchaseType Type { get; set; }
}
public abstract class HandlerBase : IHandler
{
public IHandler Successor { get; set; }
public PurchaseType Type { get; set; }
public HandlerBase(PurchaseType type, IHandler successor)
{
this.Type = type;
this.Successor = successor;
}
public HandlerBase(PurchaseType type) : this(type, null) { }
//需要具体IHandler类型处理的内容
public abstract void Process(Request request);
//在当前结点处理,还是传递给下一个结点
public virtual void HandleRequest(Request request)
{
if (request == null) return;
if (request.Type == Type)
{
Process(request);
}
else if (Successor != null)
{
Successor.HandleRequest(request);
}
}
public class InternalHandler : HandlerBase
{
public InternalHandler() : base(PurchaseType.Internal) { }
public override void Process(Request request)
{
request.Price *= 0.6;
}
}
public class MailHandler : HandlerBase
{
public MailHandler() : base(PurchaseType.Mail) { }
public override void Process(Request request)
{
request.Price *= 1.3;
}
}
public class DiscountHandler : HandlerBase
{
public DiscountHandler() : base(PurchaseType.Discount) { }
public override void Process(Request request)
{
request.Price *= 0.9;
}
}
public class RegularHandler : HandlerBase
{
public RegularHandler() : base(PurchaseType.Regular) { }
public override void Process(Request request) { }
}
}
组装职责链并调用
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IHandler handler1 = new InternalHandler();
IHandler handler2 = new DiscountHandler();
IHandler handler3 = new MailHandler();
IHandler handler4 = new RegularHandler();
handler1.Next = handler3;
handler3.Next = handler2;
handler2.Next = handler4;
IHandler head = handler1;
Request request = new Request(20, PurchaseType.Mail);
head.HandleRequest(request);
Console.Write(request.Price); //26
//将MailHandler短路
handler1.Next = handler1.Next.Next;
request = new Request(20, PurchaseType.Mail);
head.HandleRequest(request);
Console.Write(request.Price); //20
}
在实际应用中,组装职责链的过程可以交给创建型模式,或者从配置读取。
职责链模式的特点
优势
从上面的示例可以发现这种模式的一些优势:
- 降低了请求发送者和接收者之间的耦合,请求发送者只需要拿到调用链的头部,就可以触发链式处理。
- 可以动态地改变链内节点的次序,也可以方便地动态增加、删除节点,并即刻生效。
缺点
- 不能保证请求一定被接收。
- 系统性能将受到一定影响,而且在进行代码调试时不太方便。
- 如果调用链组装不合理,可能会造成循环调用。
参考书籍:
王翔著 《设计模式——基于C#的工程化实现及扩展》