MDK5 keil 下动态内存分配以及使用事例
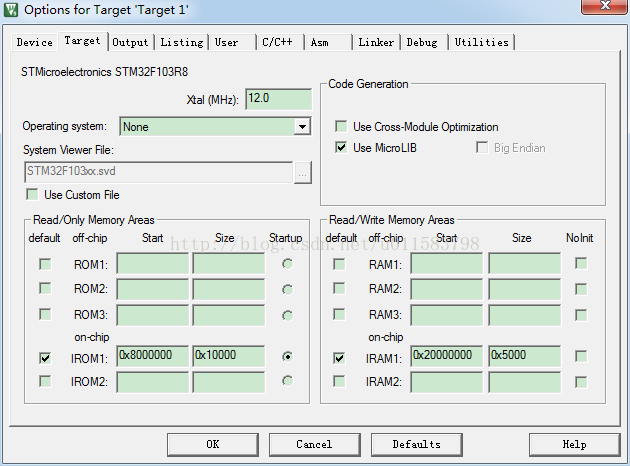
1.打开mdk的Operation选项,在target栏目里选中Use MicroLIB选项以便支持malloc-free函数原型
2.打开stm32工程源码,找到start_stm32f10x_md.s文件修改:Heap_Size EQU 0x00001000
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: /mnt/hgfs/I/PROJECT/Charger/RegrahcOOP/USER/xlist.h
> Author: XXDK
> Email: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2016年12月26日 星期一 19时04分35秒
************************************************************************/
#ifndef _XLIST_H
#define _XLIST_H
#include "string.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "usart.h"
/*
* Simple doubly linked list implementation.
*
*/
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
struct hlist_head {
struct hlist_node *first;
};
struct hlist_node {
struct hlist_node *next, **pprev;
};
/*
* 自定义数据结构示例:
*/
struct message
{
int id;
int data;
struct list_head list;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
/*
* 定义链表类型变量name, 并且初始化其prev 和next
* 成员变量指向自身
* */
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
/*
* 遍历由head所领导的所有数据结构节点
* */
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/*
* 获取链表所在的数据结构的地址
* @ptr: 指向数据结构的某成员的指针
* @type: 该数据结构的类型
* @member: 数据结构的某数据成员变量
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
((type*)((char*)(ptr) - (unsigned long)(&((type*)0)->member)))
// 示例函数
struct message* create_node(void);
void dynamic_memory_allocate_example(void);
/*
* 初始化一个空链表
* */
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head* list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
/*
* Insert a new entry between two know consecutive entries.
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we
* know the prev/next entries already.
* */
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
/**
* Add a new entry
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
* */
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
/**
* Add a new entry
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queue.
* **/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
/**
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we
* know the prev/next entries already.
* */
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
/**
* deletes entry from list.
* */
static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head* entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
}
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = 0;
entry->prev = 0;
}
/*
* Replace old entry by new one
*
* */
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}
static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head* old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}
static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head* entry)
{
__list_del_entry(entry);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}
/*
* Delete from one list and add as another's head.
* */
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head* head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add(list, head);
}
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
return list->next == head;
}
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
#endif // _XLIST_H
#include "xlist.h"
struct message* create_node(void)
{
struct message *pmsg = (struct message*)malloc(sizeof(struct message));
if (0 == pmsg) {
printk(KERN_ALERT"allocate memory error.\r\n");
return 0;
}
memset(pmsg, 0, sizeof(struct message));
return pmsg;
}
void dynamic_memory_allocate_example(void)
{
struct message *tmp;
struct list_head *pos;
LIST_HEAD(msg_head);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
struct message *pmsg = create_node();
if(pmsg == 0)
printk(KERN_ALERT"create node error\r\n");
pmsg->id = i;
pmsg->data = i*10;
list_add(&pmsg->list, &msg_head);
}
//for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
list_for_each(pos, &msg_head) {
tmp = list_entry(pos, struct message, list);
printk(KERN_ALERT"message id: %d, data: %d\r\n", tmp->id, tmp->data);
}
}