Android软键盘挡住输入框问题的终极解决方案
前言
开发做得久了,总免不了会遇到各种坑。
而在Android开发的路上,『软键盘挡住了输入框』这个坑,可谓是一个旷日持久的巨坑——来来来,我们慢慢看。
入门篇
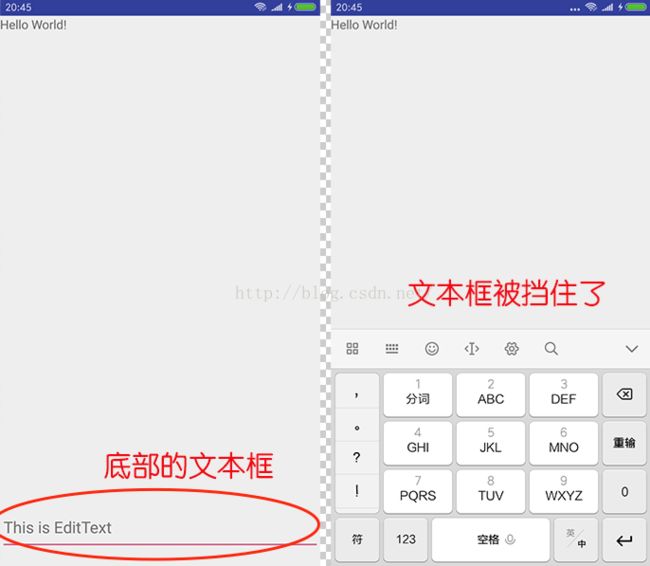
最基本的情况,如图所示:在页面底部有一个EditText,如果不做任何处理,那么在软键盘弹出的时候,就有可能会挡住EditText。
对于这种情况的处理其实很简单,只需要在AndroidManifest文件中对activity设置:android:windowSoftInputMode的值adjustPan或者adjustResize即可,像这样:
对于这种情况的处理其实很简单,只需要在AndroidManifest文件中对activity设置:android:windowSoftInputMode的值adjustPan或者adjustResize即可,像这样:
...
adjustPan是把整个界面向上平移,使输入框露出,不会改变界面的布局;
adjustResize则是重新计算弹出软键盘之后的界面大小,相当于是用更少的界面区域去显示内容,输入框一般自然也就在内了。
**********************************************************华丽分割线**********************************************************
OK,这只是入门,基本上地球上所有的Android工程师都能搞定。
**********************************************************华丽分割线**********************************************************
加上WebView试试看?坑来了……
上面的入门篇中,软键盘是由原生的EditText触发弹出的。而在H5、Hybrid几乎已经成为App标配的时候,我们经常还会碰到的情况是:软键盘是由WebView中的网页元素所触发弹出的。
情况描述
这时候,情况就会变得复杂了:
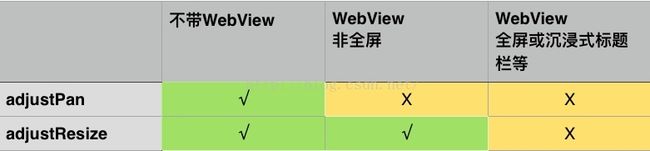
首先,页面是非全屏模式的情况下,给activity设置adjustPan会失效。
其次,页面是全屏模式的情况,adjustPan跟adjustResize都会失效。
解释一下,这里的全屏模式即是页面是全屏的,包括Application或activity使用了Fullscreen主题、使用了『状态色着色』、『沉浸式状态栏』、『Immersive Mode』等等——总之,基本上只要是App自己接管了状态栏的控制,就会产生这种问题。
下面这个表格可以简单列举了具体的情况。
首先,页面是非全屏模式的情况下,给activity设置adjustPan会失效。
其次,页面是全屏模式的情况,adjustPan跟adjustResize都会失效。
解释一下,这里的全屏模式即是页面是全屏的,包括Application或activity使用了Fullscreen主题、使用了『状态色着色』、『沉浸式状态栏』、『Immersive Mode』等等——总之,基本上只要是App自己接管了状态栏的控制,就会产生这种问题。
下面这个表格可以简单列举了具体的情况。
上面表格的这种情况并非是Google所期望的,理想的情况当然是它们都能正常生效才对——所以这其实是Android系统本身的一个BUG(issue 5497)。
为什么文章开头说这是个坑呢?
——因为这个BUG从Android1.x时代(2009年)就被报告了,而一直到了如今的Android7.0(2016年)还是没有修复……/(ㄒoㄒ)/
可以说这不仅是个坑,而且还是个官方挖的坑~
为什么文章开头说这是个坑呢?
——因为这个BUG从Android1.x时代(2009年)就被报告了,而一直到了如今的Android7.0(2016年)还是没有修复……/(ㄒoㄒ)/
可以说这不仅是个坑,而且还是个官方挖的坑~
为什么说它是个坑?”issue 5497″
“issue 5497″,详情传送门 ☞ Issue 5497 – android -WebView adjustResize windowSoftInputMode breaks when activity is fullscreen – Android Open Source Project – Issue Tracker – Google Project Hosting
当然了,不管坑是谁挖的,最终还是要开发者来解决。
遇到坑之后,有两种方法可以过去:躲,或者填。
遇到坑之后,有两种方法可以过去:躲,或者填。
躲坑姿势
如前文所示,出现坑的条件是:带有WebView的activity使用了全屏模式或者adjustPan模式。那么躲坑的姿势就很简单了——
如果activity中有WebView,就不要使用全屏模式,并且把它的windowSoftInputMode值设为adjustResize就好了嘛
怎么样,是不是很简单?
填坑姿势
但总有些时候,是需要全屏模式跟WebView兼得的,这时候,躲坑就不行了,我们需要一个新的填坑的姿势。幸好,开发者的智慧是无穷的,这个坑出现了这么多年,还是有人找到了一些解决方案的。Android Bug 5497 Workaround
我个人认为最好的解决方案是这个:AndroidBug5497Workaround,只需要一个神奇的AndroidBug5497Workaround类。
看名字就知道,它是专门用来对付”5497″问题的,使用步骤也是超级简单:
把AndroidBug5497Workaround类复制到项目中
在需要填坑的activity的onCreate方法中添加一句AndroidBug5497Workaround.assistActivity(this)即可。
经过测试,基本在各个Android版本上都可用,效果基本与设置了adjustResize相当。
看一个对比图:
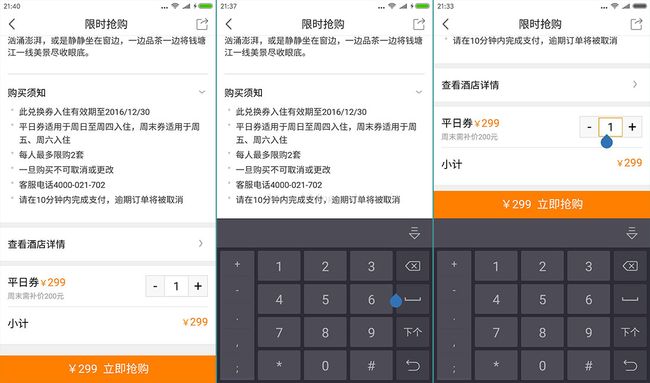
来自我厂App的某个使用WebView的全屏模式Activity页面,从左到右分别是:没有软键盘的样式、软键盘挡住输入框的效果、以及使用AndroidBug5497Workaround之后的最终效果。
它的原理是什么?
这个炫酷AndroidBug5497Workaround类,其实并不是很复杂,只有几十行代码,先贴在这里:
public class AndroidBug5497Workaround {
// For more information, see https://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=5497
// To use this class, simply invoke assistActivity() on an Activity that already has its content view set.
public static void assistActivity (Activity activity) {
new AndroidBug5497Workaround(activity);
}
private View mChildOfContent;
private int usableHeightPrevious;
private FrameLayout.LayoutParams frameLayoutParams;
private AndroidBug5497Workaround(Activity activity) {
FrameLayout content = (FrameLayout) activity.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
mChildOfContent = content.getChildAt(0);
mChildOfContent.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
public void onGlobalLayout() {
possiblyResizeChildOfContent();
}
});
frameLayoutParams = (FrameLayout.LayoutParams) mChildOfContent.getLayoutParams();
}
private void possiblyResizeChildOfContent() {
int usableHeightNow = computeUsableHeight();
if (usableHeightNow != usableHeightPrevious) {
int usableHeightSansKeyboard = mChildOfContent.getRootView().getHeight();
int heightDifference = usableHeightSansKeyboard - usableHeightNow;
if (heightDifference > (usableHeightSansKeyboard/4)) {
// keyboard probably just became visible
frameLayoutParams.height = usableHeightSansKeyboard - heightDifference;
} else {
// keyboard probably just became hidden
frameLayoutParams.height = usableHeightSansKeyboard;
}
mChildOfContent.requestLayout();
usableHeightPrevious = usableHeightNow;
}
}
private int computeUsableHeight() {
Rect r = new Rect();
mChildOfContent.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(r);
return (r.bottom - r.top);// 全屏模式下: return r.bottom
}
}代码大致是做了这么几件事:
1.找到activity的根View
看一下入口的代码:FrameLayout content = (FrameLayout) activity.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
mChildOfContent = content.getChildAt(0);如果Activity是全屏模式,那么android.R.id.content就是占满全部屏幕区域的。
如果Activity是普通的非全屏模式,那么android.R.id.content就是占满除状态栏之外的所有区域。
其他情况,如Activity是弹窗、或者7.0以后的分屏样式等,android.R.id.content也是弹窗的范围或者分屏所在的半个屏幕——这些情况较少,就暂且不考虑了。
我们经常用的setContentView(View view)/setContent(int layRes)其实就是把我们指定的View或者layRes放到android.R.id.content里面,成为它的子View。
所以,然后,第二行content.getChildAt(0)获取到的mChildOfContent,其实也就是用以获取到我们用setContentView放进去的View。
2.设置一个Listener监听View树变化
mChildOfContent.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener({ //简化了写法
possiblyResizeChildOfContent();
});——『软键盘弹出』,则是会触发这个事件的一个源。 (软键盘弹出会使GlobalLayout发生变化)
也就是说,现在能监听到『软键盘弹出』的事件了。
3.界面变化之后,获取”可用高度”
当软键盘弹出了之后,接下来的事情是获取改变之后的界面的可用高度(可以被开发者用以显示内容的高度)。直接看代码:
private int computeUsableHeight() {
Rect rect = new Rect();
mChildOfContent.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(rect);
// rect.top其实是状态栏的高度,如果是全屏主题,直接 return rect.bottom就可以了
return (rect.bottom - rect.top);
}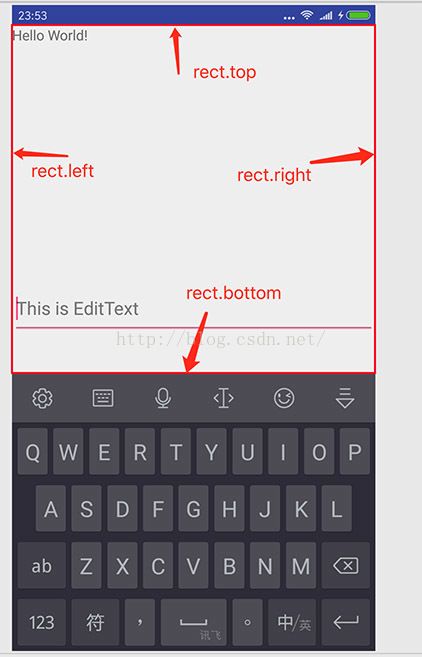
↑也可以看出:
rect.top值,其实就是标题栏的高度。(实际上,这也常常被用作为获取标题栏高度的方法)
屏幕高度-rect.bottom,是软键盘的高度。(获取软键盘高度的方法也出现了)
这时,就有:
全屏模式下,可用高度 = rect.bottom
非全屏模式,可用高度 = rect.bottom – rect.top
所以,最后一步,就是把界面高度置为可用高度——大功告成。
普通Activity(不带WebView),直接使用adjustpan或者adjustResize
如果带WebView:
a) 如果非全屏模式,可以使用adjustResize
b) 如果是全屏模式,则使用AndroidBug5497Workaround进行处理。
OK,以上就是一段关于『软键盘挡住输入框』的爬坑之旅。
rect.top值,其实就是标题栏的高度。(实际上,这也常常被用作为获取标题栏高度的方法)
屏幕高度-rect.bottom,是软键盘的高度。(获取软键盘高度的方法也出现了)
这时,就有:
全屏模式下,可用高度 = rect.bottom
非全屏模式,可用高度 = rect.bottom – rect.top
4.最后一步,重设高度
我们计算出的可用高度,是目前在视觉效果上能看到的界面高度。但当前界面的实际高度是比可用高度要多出一个软键盘的距离的。所以,最后一步,就是把界面高度置为可用高度——大功告成。
private void possiblyResizeChildOfContent() {
int usableHeightNow = computeUsableHeight();
if (usableHeightNow != usableHeightPrevious) {
int usableHeightSansKeyboard = mChildOfContent.getRootView().getHeight();
int heightDifference = usableHeightSansKeyboard - usableHeightNow;
if (heightDifference > (usableHeightSansKeyboard/4)) {
// keyboard probably just became visible
frameLayoutParams.height = usableHeightSansKeyboard - heightDifference;
} else {
// keyboard probably just became hidden
frameLayoutParams.height = usableHeightSansKeyboard;
}
mChildOfContent.requestLayout();
usableHeightPrevious = usableHeightNow;
}
}总结
总结起来,就是这样:普通Activity(不带WebView),直接使用adjustpan或者adjustResize
如果带WebView:
a) 如果非全屏模式,可以使用adjustResize
b) 如果是全屏模式,则使用AndroidBug5497Workaround进行处理。
OK,以上就是一段关于『软键盘挡住输入框』的爬坑之旅。
继续填坑中。。。
就算使用此类,有虚拟键的手机上显示不全的。。。。。。。。。