2、字节跳动-数组与排序
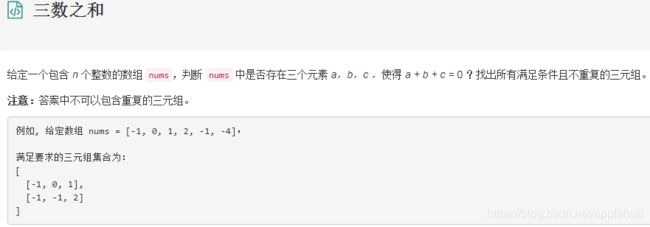
1、三数之和
class Solution {
public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List> result = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0) break;
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;
int j = nums.length - 1;
int target = 0 - nums[i];
int k = i + 1;
while (k < j) {
if (nums[k] + nums[j] == target) {
List item = Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[k], nums[j]);
result.add(item);
while (k < j && nums[k] == nums[k + 1]) k++;
while (k < j && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) j--;
k++;j--;
} else if (nums[k] + nums[j] < target) {
k++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35170267/article/details/81031368
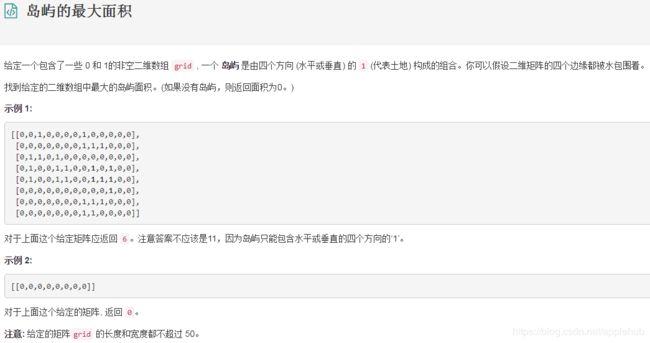
2、岛屿的最大面积
class Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int i,j,temp,result=0;
for(i=0;i=grid.length||j>=grid[0].length||grid[i][j]!=1) return 0;
grid[i][j]=0;
return 1+countArea(grid,i+1,j)+countArea(grid,i-1,j)+countArea(grid,i,j+1)+countArea(grid,i,j-1);
}
} 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38959715/article/details/80937405
3、搜索旋转排序数组
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums==null||nums.length<1) return -1;
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) return mid;
//条件1
if (nums[mid] >= nums[left]) {
if (target < nums[mid] && target >= nums[left]) {
right = mid - 1;
}else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
//条件2
if (nums[mid] <= nums[right]) {
if (target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
}else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/keeya/p/9689927.html
4、最长连续递增序列
public class Test48 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int[] res=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i A[i - 1]) {
current++;
} else {
if (current > res) {
res = current;
}
current = 1;
}
}
return res;
}
} 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/boguesfei/article/details/82901414
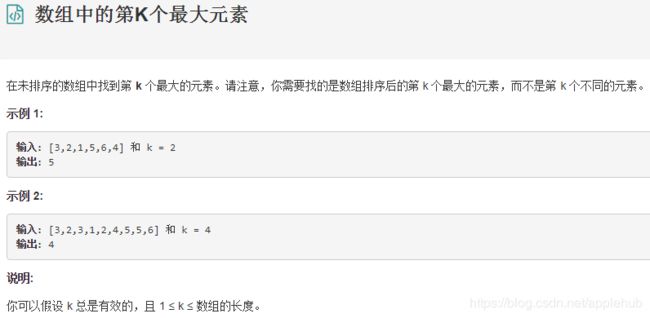
5、数组中的第K个最大元素
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length - k];
}参考:https://blog.csdn.net/ccccc1997/article/details/81673753
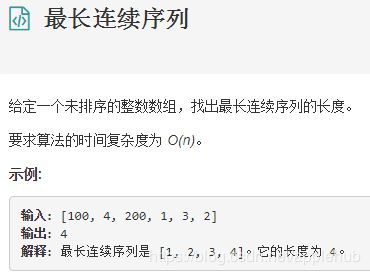
6、最长连续序列
public int longestcontinueArrays(int arr[])
{
if(arr==null||arr.length==0)
return 0;
int longest=0;
int len=1;
Arrays.sort(arr);
//对数组进行排序
for(int i=0;i原文:https://blog.csdn.net/u013309870/article/details/70242770
7、第k个排列
public class Solution {
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
k--;
List list = new ArrayList();//注意存储1-n
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
int times = n-1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
list.add(i);
}
int factorail = 1;//阶乘
for(int i=2;i=0){
int indexList = k/factorail;
s.append(list.get(indexList));
list.remove(indexList);
k=k%factorail;
if(times!=0){
factorail/=times;
}
times--;
}
return s.toString();
}
}
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/Lynn_Baby/article/details/80948414
8、朋友圈
public class Solution {
public void dfs(int[][] M, int[] visited, int i) {
for (int j = 0; j < M.length; j++) {
if (M[i][j] == 1 && visited[j] == 0) {
visited[j] = 1;
dfs(M, visited, j);
}
}
}
public int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
int[] visited = new int[M.length];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
dfs(M, visited, i);
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}原文:https://blog.csdn.net/mine_song/article/details/70195463
9、合并区间
public class Solution {
public List merge(List intervals) {
List result = new LinkedList<>();
if (intervals == null || intervals.size() < 1) {
return result;
}
// 先对区间进行排序,使用一个匿名内部类
Collections.sort(intervals, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Interval o1, Interval o2) {
return o1.start - o2.start;
}
});
// 排序后,后一个元素(记为next)的start一定是不小于前一个(记为prev)start的,
// 对于新加入的区间,假设next.start大于prev.end就说明这两个区间是分开的,要添
// 加一个新的区间。否则说明next.start在[prev.start, prev.end]内。则仅仅要看
// next.end是否是大于prev.end,假设大于就要合并区间(扩大)
Interval prev = null;
for (Interval item : intervals) {
if (prev == null || prev.end < item.start) {
result.add(item);
prev = item;
} else if (prev.end < item.end) {
prev.end = item.end;
}
}
return result;
}
} 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/gccbuaa/p/7088508.html
10、接雨水
public class Solution {
/**
* @param heights: an array of integers
* @return: a integer
*/
public int trapRainWater(int[] heights) {
// write your code here
int left = 0, right = heights.length - 1;
int res = 0;
if(left >= right)
return res;
int leftheight = heights[left];
int rightheight = heights[right];
while(left < right) {
if(leftheight < rightheight) {
left ++;
if(leftheight > heights[left]) {
res += (leftheight - heights[left]);
} else {
leftheight = heights[left];
}
} else {
right --;
if(rightheight > heights[right]) {
res += (rightheight - heights[right]);
} else {
rightheight = heights[right];
}
}
}
return res;
}
}原文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_14927217/article/details/72861208