插入、快排、堆排、归并、计数和桶排序详解以及测试
==> 学习汇总(持续更新)
==> 从零搭建后端基础设施系列(一)-- 背景介绍
-
代码
核心思想
测试结果
总结
一、代码
package com.example.sort;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Random;
public class Sort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1000000;
int BUCKET_COUNT = 1000;
int bound = n;
int[] array1 = genRandArray(n, bound);
int[] array2 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array2, 0, n);
int[] array3 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array3, 0, n);
int[] array4 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array4, 0, n);
int[] array5 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array5, 0, n);
int[] array6 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array6, 0, n);
int[] array7 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array7, 0, n);
int[] array8 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array8, 0, n);
int[] array9 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array9, 0, n);
int[] array10 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array10, 0, n);
int[] array11 = new int[n];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array11, 0, n);
long b , e;
//printArray(array1);
System.out.println("数据量: " + n + ", 桶个数:" + BUCKET_COUNT + ", 数据范围:[0, " + bound + "]\n---------------------");
// b = System.currentTimeMillis();
// insertSort(array1);
// e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
// System.out.println("插入:" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
quickSort(array2);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("普通快排:" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
quickSort2(array3);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("基准数随机快排:" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
quickSort3(array4);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("基准数三取中快排:" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
heapSort1(array5);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("递归堆排序:" + e + " ms");
// b = System.currentTimeMillis();
// heapSort2(array2);
// e = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println(e - b);
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
heapSort3(array6);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("循环堆排序:" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
mergeSort(array7);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("归并排序:" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
countSort(array8);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("计数排序:" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
bucketSort(array9, BUCKET_COUNT);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("桶排序(使用TimSort排序桶):" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
bucketSort2(array10, BUCKET_COUNT);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("桶排序(使用插入排序桶):" + e + " ms");
b = System.currentTimeMillis();
bucketSort3(array11, BUCKET_COUNT);
e = System.currentTimeMillis() - b;
System.out.println("桶排序(使用插入和归并排序桶--自定义数组结构):" + e + " ms");
if(checkResult(array2, array3, array4, array5, array6, array7, array8, array9, array10, array11)) {
System.out.println("结果校验一致");
} else {
System.out.println("结果校验错误");
}
// printArray(array1);
// printArray(array2);
// printArray(array3);
// printArray(array4);
// printArray(array5);
// printArray(array6);
// printArray(array7);
}
/**
* 插入排序
* @param array
*/
public static void insertSort(int[] array){
/**
* 假设排序5 7 2 3 4 1 8 6 9 10
* 我们可以依次从序列的第一个拿出来,从后往前插
* 第一次:[5] 7 2 3 4 1 8 6 9 10
* 第二次:[5 7] 2 3 4 1 8 6 9 10
* 第三次:[2 5 7] 3 4 1 8 6 9 10
* 第四次:[2 3 5 7] 4 1 8 6 9 10
* 第五次:[2 3 4 5 7] 1 8 6 9 10
* 第六次:[1 2 3 4 5 7] 8 6 9 10
* 第七次:[1 2 3 4 5 7 8] 6 9 10
* 第八次:[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8] 9 10
* 第九次:[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] 10
* 第十次:[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
*
*/
int pre, cur;
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
cur = array[i]; //从数组中拿出第一个未排序的出来
pre = i -1; //默认第一个是已经排好序的
while (pre >=0 && cur < array[pre]){
array[pre + 1] = array[pre--]; //后移
}
//插入
//就算没有进循环,例如7 > 5,保持原地不动,那么pre+1就是7的位置
array[pre + 1] = cur;
}
}
public static void insertSort2(int[] array, int len){
int pre, cur;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
cur = array[i]; //从数组中拿出第一个未排序的出来
pre = i -1; //默认第一个是已经排好序的
while (pre >=0 && cur < array[pre]){
array[pre + 1] = array[pre--]; //后移
}
//插入
//就算没有进循环,例如7 > 5,保持原地不动,那么pre+1就是7的位置
array[pre + 1] = cur;
}
}
/**
* 快速排序算法
* 核心思想:选取数组中的一个值为基准值,将比它小的放到左边,比它大的放到右边,
* 分成两个子数组,然后子数组按照同样的步骤递归下去即可
* 例如:5 7 2 3 4 1 8 6 9 10
* 选取5作为基准数,从后找小于5的数交换,从前找大于5的数交换
* 第一次:[1] 7 2 3 4 [5] 8 6 9 10
* 第二次:1 [5] 2 3 4 [7] 8 6 9 10
* 第三次:1 [4] 2 3 [5] 7 8 6 9 10
* 经过三次,将数组分为两个子数组[1 4 2 3] 和 [7 8 6 9 10]
* 选取1作为基准数
* 第四次:[1] 和 [4 2 3]
* 选取4作为基准数
* 第五次:[3 2] 和 [4]
* 选取3作为基准数
* 第六次:[2 3]
* 选取7作为基准数
* 第七次:[6 8] 和 [9 10]
* 结束
* @param array
*/
public static void quickSort(int[] array){
quickSort(array, 0, array.length);
}
public static void quickSort(int[] array, int left, int right){
if(left < right) {
int mid = partition(array, left, right);
quickSort(array, left, mid);
quickSort(array, mid + 1, right);
}
}
public static void quickSort2(int[] array){
quickSort2(array, 0, array.length);
}
public static void quickSort2(int[] array, int left, int right){
if(left < right) {
//从区间[lef, right)随机取一个基准值,并且和left交换
swap(array, left, (getRandNum(right) % (right - left)) + left);
int mid = partition(array, left, right);
quickSort2(array, left, mid);
quickSort2(array, mid + 1, right);
}
}
public static void quickSort3(int[] array){
quickSort3(array, 0, array.length);
}
public static void quickSort3(int[] array, int left, int right){
if(left < right) {
//取区间[left,right),left,中间,right-1的中间数作为基准值
swap(array, left, getMidNum(array, left, (left + right) / 2, right-1));
int mid = partition(array, left, right);
quickSort3(array, left, mid);
quickSort3(array, mid + 1, right);
}
}
public static int partition(int[] array, int left, int right){
int mid = left;
int i = left, j = right - 1;
while (i < j) {
//从后往前找第一个小于基准数的
while (i < j && array[j] >= array[mid]){
--j;
}
//防止自己和自己交换
if(i < j){
mid = swap(array, mid, j);
}
//从前往后找第一个大于基准数的
while (i < j && array[i] <= array[mid]) {
++i;
}
if(i < j){
mid = swap(array, mid, i);
}
}
return mid;
}
//递归下沉式构建堆
public static void heapSort1(int[] array){
//构造大顶堆
for (int i = array.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
buildHeadDown(array, array.length, i);
}
//堆排序,每循环一次,将root放到数组后面
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
swap(array, 0, array.length - 1 - i);
buildHeadDown(array, array.length - 1 - i, 0);
}
}
//递归上浮+下沉构建堆
public static void heapSort2(int[] array){
//构造大顶堆
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
buildHeadUp(array, i + 1, 0);
}
//堆排序,每循环一次,将root放到数组后面
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
swap(array, 0, array.length - 1 - i);
buildHeadDown(array, array.length - 1 - i, 0);
}
}
//for循环下沉式构建堆
public static void heapSort3(int[] array){
//构造大顶堆
for (int i = array.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
buildHeadDown2(array, array.length, i);
}
//堆排序,每循环一次,将root放到数组后面
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
swap(array, 0, array.length - 1 - i);
buildHeadDown2(array, array.length - 1 - i, 0);
}
}
//构建堆,上浮法,效率极差(知道有这么个方法就行了)
public static void buildHeadUp(int[] array, int end, int root) {
int lChild = 2 * root + 1, rChild = 2 * root + 2;
if (root < end && (lChild < end || rChild < end)) {
if(lChild < end && (2 * lChild + 1) < end){
buildHeadUp(array, end, lChild);
}
if(rChild < end && (rChild < end || rChild < end)){
buildHeadUp(array, end, rChild);
}
if(lChild < end && rChild < end){
if(array[root] < array[lChild] && array[root] < array[rChild]){
swap(array, root, array[lChild] < array[rChild] ? rChild : lChild);
} else if(array[root] < array[lChild]){
swap(array, root, lChild);
} else if(array[root] < array[rChild]){
swap(array, root, rChild);
}
} else if(lChild < end){
if(array[root] < array[lChild]){
swap(array, root, lChild);
}
} else if(rChild < end) {
if(array[root] < array[rChild]){
swap(array, root, rChild);
}
}
}
}
//递归构建堆,下沉法
public static void buildHeadDown(int[] array, int end, int root) {
int lChild = 2 * root + 1, rChild = 2 * root + 2;
//此根节点不是叶节点、并且左右孩子也不是叶节点就可以继续递归下去
//如果是叶子节点,递归进去,还是什么都不做,直接返回
if (root < end && (lChild < end || rChild < end)) {
//该节点有左右孩子
if(lChild < end && rChild < end && (array[root] < array[lChild] || array[root] < array[rChild])){
buildHeadDown(array, end, swap(array, root, array[lChild] < array[rChild] ? rChild : lChild));
} else if(lChild < end && array[root] < array[lChild]){
//该节点只有左孩子
buildHeadDown(array, end, swap(array, root, lChild));
} else if(rChild < end && array[root] < array[rChild]) {
//该节点只有右孩子
buildHeadDown(array, end, swap(array, root, rChild));
}
}
}
//for循环构建堆,下沉法
public static void buildHeadDown2(int[] array, int end, int root) {
int lChild = 0, rChild = 0;
//i一直跟着传进来的root节点
for (int i = root; i < end && (lChild < end || rChild < end); ) {
lChild = 2 * i + 1;
rChild = 2 * i + 2;
//该节点有左右孩子
if(lChild < end && rChild < end && (array[i] < array[lChild] || array[i] < array[rChild])){
i = swap(array, i, array[lChild] < array[rChild] ? rChild : lChild);
} else if(lChild < end && array[i] < array[lChild]){
//该节点只有左孩子
i = swap(array, i, lChild);
} else if(rChild < end && array[i] < array[rChild]){
//该节点只有右孩子
i = swap(array, i, rChild);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
//归并排序
public static void mergeSort(int[] array){
if(array == null || array.length == 1){
return;
}
//直接在最外面创建一个大小一样的临时数组,避免递归创建临时数组带来的空间时间损耗
int[] tmp = new int[array.length];
mergeSort(array, tmp, 0, array.length - 1);
tmp = null;
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] array, int[] tmp, int left, int right){
if(left < right){
//计算拆分中间位置
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
mergeSort(array, tmp, left, mid);
mergeSort(array, tmp, mid + 1, right);
merge(array, tmp, left, mid, right);
}
}
public static void merge(int[] array, int[] tmp, int left, int mid, int right) {
int i = mid + 1,j = 0 , k = left;
//两个有序子数组合并
while (k <= mid && i <= right) {
tmp[j++] = array[k] < array[i] ? array[k++] : array[i++];
}
//如果左子数组有剩余元素,直接加到临时数组即可
while (k <= mid) {
tmp[j++] = array[k++];
}
//如果左右子数组有剩余元素,直接加到临时数组即可
while (i <= right) {
tmp[j++] = array[i++];
}
//将排好序的元素,覆盖回去
for (i = left, j = 0; i <= right; i++) {
array[i] = tmp[j++];
}
}
//计数排序
public static void countSort(int[] array){
//找范围[min, max]
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
max = array[i] > max ? array[i] : max;
min = array[i] < min ? array[i] : min;
}
//创建桶,个数为max - min + 1
int[] buckets = new int[max - min + 1];
//将数放入桶中
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
//如果数字重复,那么计数累加就好
buckets[array[i] - min]++;
}
//顺序遍历桶则为从小到大排序,逆序遍历则为从大到小排序
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
while (buckets[i]-- != 0) {
array[j++] = i + min;
}
}
}
//桶排序
public static void bucketSort(int[] array, int bucketCount){
//找范围[min, max]
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
max = array[i] > max ? array[i] : max;
min = array[i] < min ? array[i] : min;
}
//计算桶间间隔
double size = (max - min + 1) / (double)bucketCount;
ArrayList[] arrayList = new ArrayList[bucketCount];
//将数放入桶中
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
index = (int)Math.floor((array[i] - min) / size);
if(arrayList[index] == null) {
arrayList[index] = new ArrayList<>();
}
arrayList[index].add(array[i]);
}
//将桶中的数据排序
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) {
if(arrayList[i] == null || arrayList[i].isEmpty()){
continue;
}
if(arrayList[i].size() == 1){
array[j++] = arrayList[i].get(0);
} else {
arrayList[i].sort(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
});
int len = arrayList[i].size();
for (int k = 0; k < len; k++) {
array[j++] = arrayList[i].get(k);
}
}
}
}
public static void bucketSort2(int[] array, int bucketCount){
//找范围[min, max]
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
max = array[i] > max ? array[i] : max;
min = array[i] < min ? array[i] : min;
}
//计算桶间间隔
double size = (max - min + 1) / (double)bucketCount;
ListNode[] arrayList = new ListNode[bucketCount];
//将数放入桶中
//使用链表作为桶,插入的时候即时排序
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
index = (int)Math.floor((array[i] - min) / size);
if(arrayList[index] == null) {
arrayList[index] = new ListNode(array[i]);
} else {
ListNode pre = arrayList[index], cur = arrayList[index];
if(array[i] == cur.val){
arrayList[index].count++;
continue;
}
if(array[i] < cur.val){
ListNode node = new ListNode(array[i]);
node.next = pre;
arrayList[index] = node;
continue;
}
while (cur != null){
if(array[i] == cur.val){
cur.count++;
break;
}
if(array[i] < cur.val || cur.next == null){
ListNode node = new ListNode(array[i]);
if(array[i] < cur.val){
node.next = pre.next;
pre.next = node;
} else {
cur.next = node;
}
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
//遍历
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < arrayList.length; i++) {
while (arrayList[i] != null){
while (arrayList[i].count-- > 0){
array[j++] = arrayList[i].val;
}
arrayList[i] = arrayList[i].next;
}
}
}
public static void bucketSort3(int[] array, int bucketCount){
//找范围[min, max]
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
max = array[i] > max ? array[i] : max;
min = array[i] < min ? array[i] : min;
}
//计算桶间间隔
double size = (max - min + 1) / (double)bucketCount;
Array[] arrayList = new Array[bucketCount];
//将数放入桶中
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
index = (int)Math.floor((array[i] - min) / size);
if(arrayList[index] == null) {
arrayList[index] = new Array();
}
arrayList[index].add(array[i]);
}
//将桶中的数据排序
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) {
if(arrayList[i] == null || arrayList[i].isEmpty()){
continue;
}
if(arrayList[i].size() == 1){
array[j++] = arrayList[i].get(0);
} else {
arrayList[i].sort();
int len = arrayList[i].size();
for (int k = 0; k < len; k++) {
array[j++] = arrayList[i].get(k);
}
}
}
}
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public int count;
public ListNode next = null;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.count = 1;
}
}
public static int swap(int[] array, int pos1, int pos2) {
if(pos1 < 0 || pos2 < 0 || pos1 >= array.length || pos2 >= array.length){
throw new RuntimeException("数组越界");
}
if(pos1 == pos2) {
return pos1;
}
array[pos1] = array[pos1] ^ array[pos2];
array[pos2] = array[pos1] ^ array[pos2];
array[pos1] = array[pos1] ^ array[pos2];
return pos2;
}
public static void printArray(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static int[] genRandArray(int n, int bound){
int[] array = new int[n];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(bound);
}
return array;
}
public static boolean checkResult(int[] ... arrs){
for (int i = 1; i < arrs.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrs[0].length; j++) {
if(arrs[0][j] != arrs[i][j]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public static int getMidNum(int[] array, int a, int b, int c){
if((array[b] - array[a] >= 0 && array[c] - array[a] <= 0 ) || (array[b] - array[a] <= 0 && array[c] - array[a] >= 0 )) {
return a;
} else if((array[a] - array[b] >= 0 && array[c] - array[b] <= 0 ) || (array[a] - array[b] <= 0 && array[c] - array[b] >= 0 )){
return b;
} else {
return c;
}
}
private static Random random = new Random();
public static int getRandNum(int n){
return random.nextInt(n);
}
static class Array {
int[] array;
int size;
int cap;
public Array(){
array = new int[16];
size = 0;
this.cap = 16;
}
public Array(int cap){
array = new int[cap];
size = 0;
this.cap = cap;
}
public void add(int e){
if(size >= cap){
reAlloc();
}
array[size++] = e;
}
public int get(int index){
return array[index];
}
private void reAlloc(){
if(size >= cap) {
int[] tmp = new int[cap];
System.arraycopy(array, 0, tmp, 0, size);
cap = 2 * cap;
array = new int[cap];
System.arraycopy(tmp, 0, array, 0, size);
tmp = null;
}
}
public void sort(){
if(size < 10) {
insertSort2(array, size);
} else {
int[] tmp = new int[size];
mergeSort(array, tmp, 0, size - 1);
}
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size < 1 ;
}
}
}
二、核心思想
1.插入排序- 从后往前比较
- 比较的同时将元素往后移
- 找到要插入的位置时,直接array[i]=val即可
例如:5 7 2 3 4 1 8 6 9 10
第一个元素肯定是已排序的
第一步:从7开始,从后往前比较,7比5大,位置不变
5 7
第二步:2比7小,7往后移(2这个值是已经被拿出来的了,所以可以覆盖2的位置)
5 x 7
x 5 7
2 5 7
第三步:和第二步类似
2 5 x 7
2 x 5 7
2 3 5 7
第四步:同理
……
2.快速排序
- 找基准值,将数组一分为2,比基准值小的在左边,大的在右边
- 基准值一般要么在最左边,要么在最右边,假设在左边,那么从右往左找比基准值小的,交换,从左往右找比基准值大的,交换,直到首尾指针相遇
- 对划分出来的子数组执行同样的操作,直到数组不能划分为止
快速排序可以说是非常简单的一种排序了,就是选择排序的升级版而已。
例如:5 7 2 3 4 1 8 6 9 10
第一步:
选取5为基准值,从右往左找比5小的,交换
[1] 7 2 3 4 [5] 8 6 9 10
从左往右找比5大的,交换
1 [5] 2 3 4 [7] 8 6 9 10
从右往左找比5小的,交换
1 [4] 2 3 [5] 7 8 6 9 10
划分后的两个数组[1 4 2 3 5]和[7 8 6 9 10]
第二步:
选取1为基准值,从右往左找比1小的,找不到,结束
划分后的两个数组[1]和[4 2 3 5],1不可划分了
第三步:
选取4为基准值,从右往左找比4小的,交换
[3] 2 [4] [5]
从左往右找比4大的,找不到,结束
划分后的两个数组[3 2 4]和[5], 5不可划分了
第四步:
选取3为基准值,从右往左找比3小的,交换
[2] [3] 4
划分后的两个数组[2 3]和[4], 4不可划分了
第五步:
选取2为基准值,从右往左找比2小的,找不到,结束
划分后的两个数组[2]和[3], 2和3都不可划分了
第六步:对[7 8 6 9 10]执行同样的操作
……
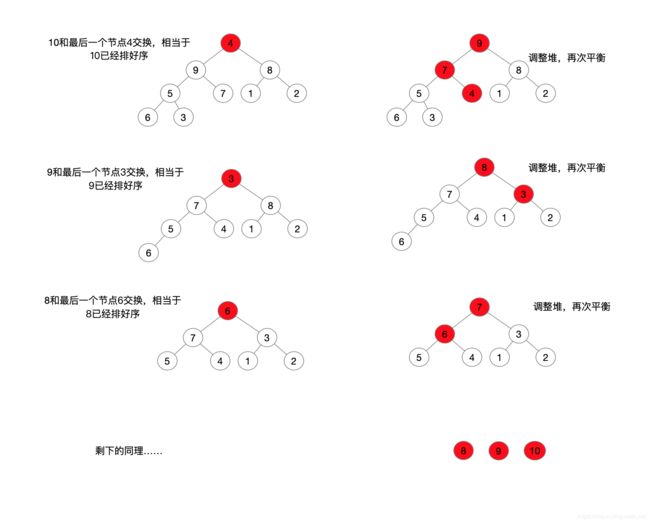
3.堆排序
- 构建堆
- 将小的数字往下沉,即从根节点开始往下一层层比较
- 从堆顶拿到最大的元素,放到数组最后
- 调整堆,重复上述步骤即可

排序就是不断从堆顶拿元素,然后再调整的过程,如图
4.归并排序
- 将数组一分为二
- 重复上述步骤,直到数组不可分割
- 排序、合并
5.计数排序
- 找到数组最小和最大的值(为了节约空间)
- 创建数组,大小为max - min + 1
- 将数放入到对应的位置,重复数字个数累加即可,buckets[array[i] - min]++
6.桶排序
- 找到数组最小和最大的值(为了节约空间)
- 计算桶间间隔(桶的个数需要人为指定)
- 将数放入到对应的桶
三、测试结果
时间单位:ms
1.随机数组测试,范围[0, n]
| 排序算法 | n = 1000 | n = 10000 | n = 100000 | n = 1000000 | n = 10000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 插入排序 | 2 | 17 | 1144 | 108900 | – |
| 普通快速排序 | 1 | 3 | 26 | 139 | 1577 |
| 基准值随机快速排序 | 1 | 5 | 13 | 152 | 1695 |
| 基准值三数取中快速排序 | 0 | 3 | 12 | 134 | 1501 |
| 递归堆排序 | 2 | 4 | 20 | 207 | 3110 |
| for循环堆排序 | 1 | 5 | 26 | 202 | 3150 |
| 归并排序 | 1 | 3 | 17 | 151 | 1597 |
| 计数排序 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 23 | 223 |
2.随机+重复数组测试,范围[0, bound], n = 10000000 固定
当bound <= 1000 时,使用JVM默认的栈大小会栈溢出,需要调大 -Xss10m
| 排序算法 | bound = 1000000 | bound = 100000 | bound = 10000 | bound = 1000 | bound = 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 普通快速排序 | 1434 | 1269 | 2162 | 14236 | 117685 |
| 基准值随机快速排序 | 1582 | 1538 | 2525 | 14322 | 143182 |
| 基准值三数取中快速排序 | 1486 | 1392 | 2221 | 13937 | 128836 |
| 递归堆排序 | 3029 | 2942 | 2701 | 2001 | 1443 |
| for循环堆排序 | 3056 | 3024 | 2520 | 2022 | 1590 |
| 归并排序 | 1571 | 1518 | 1385 | 1215 | 1060 |
| 计数排序 | 92 | 64 | 46 | 41 | 42 |
3.随机+重复+部分有序数组测试,范围[0, bound], n = 10000000 固定,有序序列长度 = bound
| 排序算法 | bound = 10000000 | bound = 1000000 | bound = 100000 | bound = 10000 | bound = 1000 | bound = 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 普通快速排序 | - | 1240 | 1248 | 2218 | 15401 | 146420 |
| 基准值随机快速排序 | 665 | 1258 | 1296 | 2341 | 16071 | 151542 |
| 基准值三数取中快速排序 | 275 | 1166 | 1095 | 2123 | 15011 | 154526 |
| 递归堆排序 | 1272 | 1819 | 2266 | 2091 | 2020 | 1467 |
| for循环堆排序 | 1180 | 1762 | 2059 | 2343 | 1949 | 1525 |
| 归并排序 | 446 | 519 | 488 | 476 | 586 | 678 |
| 计数排序 | 74 | 49 | 44 | 41 | 41 | 43 |
4.桶排序测试
计数排序的变量只有n
随机数组测试,范围[0, n],n = 10000000,桶个数bc为变量
| 排序算法 | bc = 10 | bc = 100 | bc = 1000 | bc = 10000 | bc = 100000 | bc = 1000000 | bc = 10000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数排序 | 247 | 296 | 231 | 222 | 224 | 237 | 218 |
| 桶排序(使用TimSort排序桶) | 4756 | 3930 | 2731 | 2784 | 3207 | 4183 | 8250 |
| 桶排序(使用插入排序桶) | - | - | - | - | 11606 | 3793 | 1440 |
| 桶排序(使用插入和归并排序桶–自定义数组结构) | 1730 | 1516 | 1343 | 1310 | 1950 | 2387 | 3701 |
随机+重复数组测试,范围[0, bound], n = 10000000 固定,桶个数bc为变量
bound = 1000000
| 排序算法 | bc = 10 | bc = 100 | bc = 1000 | bc = 10000 | bc = 100000 | bc = 1000000 | bc = 10000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数排序 | 82 | 82 | 77 | 89 | 78 | 79 | 81 |
| 桶排序(使用TimSort排序桶) | 4779 | 3753 | 2802 | 2837 | 3231 | 3918 | 4375 |
| 桶排序(使用插入排序桶) | - | - | - | 33850 | 4207 | 1009 | 1927 |
| 桶排序(使用插入和归并排序桶–自定义数组结构) | 1806 | 1460 | 1308 | 1211 | 1683 | 2129 | 2543 |
bound = 100000
| 排序算法 | bc = 10 | bc = 100 | bc = 1000 | bc = 10000 | bc = 100000 | bc = 1000000 | bc = 10000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数排序 | 63 | 65 | 65 | 63 | 63 | 65 | 75 |
| 桶排序(使用TimSort排序桶) | 4208 | 3477 | 2550 | 2510 | 2493 | 3047 | 3730 |
| 桶排序(使用插入排序桶) | - | - | 8145 | 1126 | 209 | 415 | 1167 |
| 桶排序(使用插入和归并排序桶–自定义数组结构) | 1527 | 1340 | 1134 | 1001 | 1634 | 2095 | 2749 |
bound = 10000
| 排序算法 | bc = 10 | bc = 100 | bc = 1000 | bc = 10000 | bc = 100000 | bc = 1000000 | bc = 10000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数排序 | 44 | 43 | 43 | 44 | 44 | 45 | 42 |
| 桶排序(使用TimSort排序桶) | 3304 | 2957 | 2401 | 1609 | 1814 | 2157 | 2345 |
| 桶排序(使用插入排序桶) | 25442 | 2842 | 607 | 116 | 160 | 147 | 369 |
| 桶排序(使用插入和归并排序桶–自定义数组结构) | 1342 | 1270 | 990 | 943 | 845 | 970 | 1537 |
bound = 1000
| 排序算法 | bc = 10 | bc = 100 | bc = 1000 | bc = 10000 | bc = 100000 | bc = 1000000 | bc = 10000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数排序 | 43 | 42 | 42 | 43 | 43 | 42 | 43 |
| 桶排序(使用TimSort排序桶) | 2912 | 2459 | 1355 | 1388 | 1432 | 1705 | 1737 |
| 桶排序(使用插入排序桶) | 1262 | 387 | 86 | 111 | 111 | 231 | 201 |
| 桶排序(使用插入和归并排序桶–自定义数组结构) | 1198 | 1118 | 857 | 834 | 849 | 935 | 1020 |
bound = 100
| 排序算法 | bc = 10 | bc = 100 | bc = 1000 | bc = 10000 | bc = 100000 | bc = 1000000 | bc = 10000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数排序 | 44 | 44 | 44 | 46 | 43 | 45 | 46 |
| 桶排序(使用TimSort排序桶) | 1477 | 405 | 426 | 443 | 441 | 457 | 622 |
| 桶排序(使用插入排序桶) | 443 | 110 | 137 | 137 | 141 | 143 | 239 |
| 桶排序(使用插入和归并排序桶–自定义数组结构) | 1091 | 953 | 832 | 769 | 778 | 803 | 920 |
bound = 10
| 排序算法 | bc = 10 | bc = 100 | bc = 1000 | bc = 10000 | bc = 100000 | bc = 1000000 | bc = 10000000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数排序 | 46 | 44 | 47 | 48 | 48 | 53 | 45 |
| 桶排序(使用TimSort排序桶) | 650 | 599 | 512 | 474 | 681 | 519 | 738 |
| 桶排序(使用插入排序桶) | 117 | 134 | 151 | 150 | 135 | 208 | 166 |
| 桶排序(使用插入和归并排序桶–自定义数组结构) | 915 | 807 | 866 | 804 | 885 | 859 | 822 |
四、总结
- 插入排序核心思想,从后往前插入已排序序列。插入排序适合数据量小的(5 ~ 20)排序,如果该序列是已排序序列,那么使用 插入排序的时间复杂度是O(n)
- 快速排序的核心思想,基于基准值,划分数组,直到不能划分为止。普通的快速排序 适合元素重复度不高,且随机的序列。关于快排的各种优化,可以参考该博客三种快速排序以及快速排序的优化
- 堆排序的核心思想,构建堆和调整堆,弄明白堆的构建就明白了如何利用堆来排序。 堆排序一般适合用来求topN问题,因为快速和稳定性和归并排序都比不了。
- 归并排序的核心思想,递归分割、回溯合并。它几乎适合所有类型的序列,很稳定,唯一 的缺点只是空间复杂度恒定在O(n)。
- 计数排序的核心思想,利用数组下标计数,例如10这个数,放入数组中,那么a[10]计数+1。它适合元素均匀分布的序列,如果分布太极端,例如10个元素的数组,最小的是0,最大的是10000000,那么就会创建10000000大小的数组,来排序这10个数。
- 桶排序的核心思想,分桶排序,即将每个数放入到对应范围的桶中,最后每个桶再单独排序,最后遍历数组输出即可。


