android 自定义控件--用viewGroup实现流式布局
java布局中有一个流式布局,但是android布局中并没有。手机上用到流式布局大概就是热门标签的添加吧。流式布局就是控件一个一个的自动往右添加,如果超出宽度,则自动到下一行。
步骤分析
1.对于本布局,我们需要能得到margin属性的LayoutParams,即MarginLayoutParams.
2.在onMeasure()方法中计算所有子view的高度和宽度,以便得到FlowLayout 的宽高(流式布局为warp_content模式)。
3.在onLayout()方法中放置所有子view的位置。
解决问题
1.得到MarginLayoutParams
只需要我们重写generateLayoutParams()方法
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)
{
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}2.onMeasure()计算宽高
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//如果为warp_content模式下测量的宽高
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
//记录每一行的宽高
int lineW = 0;
int lineH = 0;
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);//获取每一个子view
measureChild(child,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);//测量子view
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childW = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;//得到子view的宽高
int childH = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//如果放入该view是超过父布局宽度,需要换行,那么高度累加,宽度取当前行与该子view最大的为父布局宽度
if (childW + lineW > widthSize - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()){
width = Math.max(lineW,childW);
height +=lineH;//高度累加
//开启新行
lineW = childW;
lineH = childH;
}else {//如果不换行,则宽度累加,高度取最大值
lineW += childW;
lineH = Math.max(lineH,childH);
}
if (i == childCount -1){//最后一个子view
width = Math.max(width, lineW);
height += lineH;
}
}
Log.i("FLOW",width+" "+height);
setMeasuredDimension((widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? widthSize : width +getPaddingLeft()+getPaddingRight(),
(heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? heightSize : height +getPaddingTop()+getPaddingBottom()));
}首先得到父布局的测量模式和宽高,然后遍历所有的子view,得到子view的宽高,计算父布局wrap_content模式下的宽高,最后根据模式设置父布局的宽高。但是在测量时应注意一点,在遍历到最后一个子view时,可能会换行,会走换行的if语句,但是并没有将在view的高度进行累加,所以要单独写一个判断进行累加。
3.onLayout()为子view布局
List> allViews = new ArrayList<>();
List lineH = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
allViews.clear();
lineH.clear();
int width = getWidth();//父布局的宽度
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
//存放每一行的子view
List lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);//得到view实例
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
//得到子view的宽高
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin +lp.rightMargin;
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.bottomMargin +lp.topMargin;
if (lineWidth + childWidth > (width -getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight())){//如果需要换行
lineH.add(lineHeight);//保存这一行的view以及最大高度
allViews.add(lineViews);
//重置宽高
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = 0;
lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
}
//如果不换行,则行高等于最高的,行宽累加
lineWidth = lineWidth + childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight,childHeight);
lineViews.add(child);
}
lineH.add(lineHeight);
allViews.add(lineViews);
int lineNums = allViews.size();
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
for (int i =0; i < lineNums; i++) {
lineViews = allViews.get(i);
lineHeight = lineH.get(i);
//遍历每一行的view
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
View child = lineViews.get(j);
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE){
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//计算子view的坐标
int lc = left +lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top +lp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
child.layout(lc,tc,rc,bc);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.rightMargin
+ lp.leftMargin;
}
//重置left和top 为下一行的计算坐准备
left = getPaddingLeft();
top +=lineHeight;
}
} 代码分析:
allViews 存放所有的子view,lineH 存放每一行的最大高度,lineView 存放每一行的view。
然后遍历所有子view,设置每一行的高度,和每一行的子view,最后遍历每一行的子view。设置每一个view的left,top,right,bottom.
测试
我用几个textView来测试,看一看效果
在res/values/styles.xml中:
frag_01.xml
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<solid android:color="#7690A5" >
solid>
<corners android:radius="5dp"/>
<padding
android:bottom="2dp"
android:left="10dp"
android:right="10dp"
android:top="2dp" />
shape> item_flow.xml
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
style="@style/text_flag_01"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
TextView>代码动态添加textview
FlowLayout flow;
String[] str = new String[]{"hallo world1","text","FlowLayout Image3","hallo world1",
"textView2","FlowLayout Image3","hallo world1",
"textView2","FlowLayout Image3"};
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
TextView tv = (TextView) inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_flow,flow,false);
tv.setText(str[i]);
flow.addView(tv);
}
最后效果如图
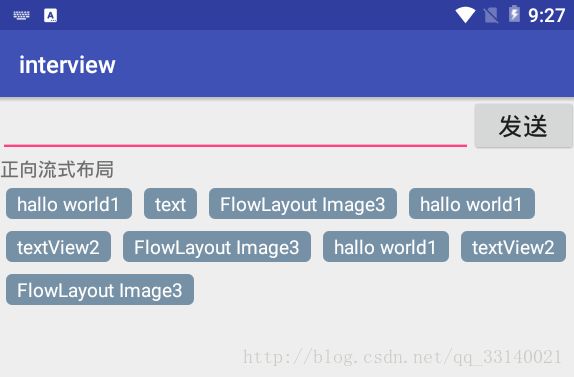
到这里,流式布局基本上就实现了,如果想动态添加,可以自己定义一个接口实现单个添加标签。
优化
上面的方法实现了流式布局,但是我们可以看到,在onMeasure()和onLayout()方法中都计算了子view的宽高。如此,我们可不可以只计算一次呢,在onMeasure()中就将view的坐标计算好呢?
要解决这个问题,就需要有一个数组或列表来保存每一个view的坐标。
比如定义一个类,记录坐标点
public class ViewPosition{
int left;
int top;
int right;
int bottom;
public ViewPosition(int left,int top,int right,int bottom){
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
}在onMeasure()中实现坐标计算
List<ViewPos> vPos = new ArrayList<>();
if (childW + lineW > widthSize - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()){//如果放入该view是超过父布局宽度,换行
width = Math.max(lineW,childW);//取最大行宽为父布局行宽
height +=lineH;//高度累加
//开启新行
lineW = childW;
lineH = childH;
vPos.add(new ViewPos(getPaddingLeft()+lp.leftMargin,
getPaddingTop()+lp.topMargin+height,
getPaddingLeft() + childW - lp.rightMargin,
getPaddingTop() + height + childH - lp.bottomMargin));
}else {//如果不换行,则宽度累加,高度取最大值
vPos.add(new ViewPos(getPaddingLeft() + lineW + lp.leftMargin,
getPaddingTop() + height + lp.topMargin,
getPaddingLeft() + lineW + childW - lp.rightMargin,
getPaddingTop() + height + childH - lp.bottomMargin));
lineW += childW;
lineH = Math.max(lineH,childH);
}最后在onLayout()中就简单了
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
ViewPos pos = vPos.get(i);
//设置View的左边、上边、右边底边位置
child.layout(pos.left, pos.top, pos.right, pos.bottom);
}
}参考博客:Android 自定义ViewGroup 实战篇 -> 实现FlowLayout