2019杭电多校训练七 hdu 6653 Halt Hater
学大佬的暴力打表找规律,大佬打的表看不懂,自己打了一份。先看看表
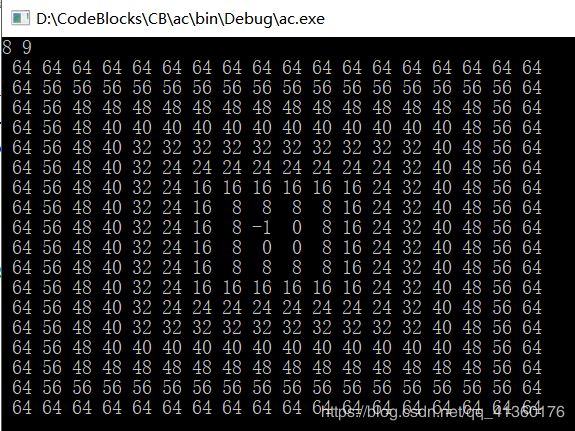
当a=8 b=9的时候,规律很明显了
当a=8 b=8的时候规律是一样的
经过测试当a<=b的时候,规律相同
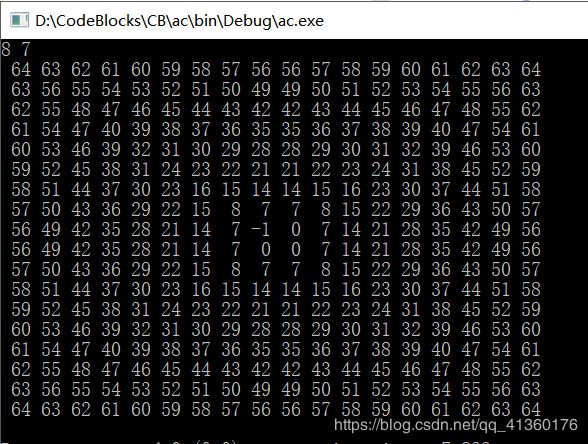
当a>b的时候规律发生变化,经过测试,当a>b && a<2*b 的时候规律相同
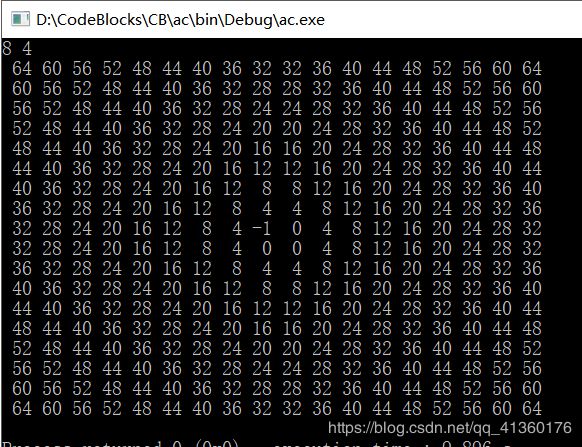
当 a>= 2b 的时候,又一个规律
把坐标轴分成四个部分,用那四个零点当原点,判断终点应该对应哪个原点
现在规律总结一下:
1.当a<=b的时候,答案就是终点到原点的水平距离和垂直距离中最大的那个值乘a
2.当a>b && a<=2b 答案是终点到原点的水平距离和垂直距离中最大的值乘b加上最小的值乘b-a
3.当a>=2b 答案是终点到原点的水平距离和垂直距离之和乘b
接下来是我的打表代码,是用bfs打的
#include
for(int i=492;i<=509;i++){
for(int j=492;j<=509;j++){
if(i==500 && j==500)printf("%3d",-1);
else
printf("%3d",min(min(mp[i][j][0],mp[i][j][1]),min(mp[i][j][2],mp[i][j][3])));
}cout<<endl;
}
}
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
bfs();
return 0;
}
接下来是我的ac代码,写的有点麻烦,但是当时为了找规律没管他
#include