underScore专题-源码分析迭代器
下面会用到undefined判断,所以这里先来跟underScore学习一下undefined的处理
在javaScript中我们判断一个变量是否是undefined通常会这样写
var a;
if (a === undefined) {
console.log(1) // 1
}但是在javaScript中undefined并不可靠,因为undefined可以作为变量名使用:
var a;
var undefined = 2
console.log(undefined) // 2
if (a === undefined) {
console.log(1)
}underScore中通过这样的方法来获取undefined:
console.log(void 0) // undefined
console.log(void (0)) //undefined好了,切入正题:
就像数组原型上又map方法,允许对数组处理并返回,underScore中也有map方法,并且比Array.prototype.map更加健全,不能叫健全吧,应该说是健壮。下面从map方法的使用上来分析源码。
function
正常处理
var arr = [4, 6, 1]
_.map(arr, function(item, index) {
console.log(item, index)
})不传递
返回原对象
var arr = [4, 6, 1]
var a = _.map(arr)
console.log(a)obj
var arr = [4, 6, 1]
var obj = [{ name: '麦乐' }, { name: 'maile' }]
var a = _.map(obj, { name: 'maile' })
console.log(a)字符串
var arr = [4, 6, 1]
var obj = [{ name: '麦乐' }, { name: 'maile' }]
var a = _.map(obj, 'name')
console.log(a)数组
var obj = [{ name: '麦乐', age: 18, height: 168 },
{ name: 'maile', age: 16, height: 19 }]
var a = _.map(obj, ['age'])
console.log(a)可以分析出,map可以根据传递的参数不同,返回不同的值,具体分以下几种情况:
- 当迭代器也就是iteratee不传递时,返回第一个参数
- 当iteratee传递为函数时,正常处理
- 当iteratee传递为对象时,返回匹配结果
-
iteratee传递为字符串时,返回匹配到的键值数组
看下源码是怎么实现的?
// Return the results of applying the iteratee to each element.
function map(obj, iteratee, context) {
iteratee = cb(iteratee, context);
var _keys = !isArrayLike(obj) && keys(obj),
length = (_keys || obj).length,
results = Array(length);
for (var index = 0; index < length; index++) {
var currentKey = _keys ? _keys[index] : index;
results[index] = iteratee(obj[currentKey], currentKey, obj);
}
return results;
}函数接受三个参数,对象,迭代器,上下文对象也就是this。
这里将我们传递进去的迭代器做了处理,就是上面出现的几种情况,cb函数是underScore内部的一个函数,就是负责处理不同的迭代器参数的。源码内部多处用到了这个函数。
iteratee = cb(iteratee, context);cb
function cb(value, context, argCount) {
if (_.iteratee !== iteratee) return _.iteratee(value, context);
return baseIteratee(value, context, argCount);
}_.iteratee
_.iteratee = iteratee;
function iteratee(value, context) {
return baseIteratee(value, context, Infinity);
}可以看到一般情况下_.iteratee === iteratee 是true,_.iteratee(value, context);不会执行,但是当我们在外部自定义一个这样的函数,迭代器函数被修改这时返回的下面这个函数的调用结果,也就是说允许我们修改map函数的功能。
_.iteratee = function(value, context) {
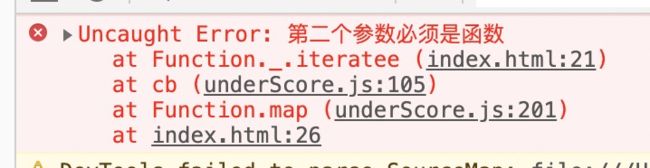
}比如,如果不想考虑那么多,只允许第二个参数是函数,就可以这么写
var arr = [4, 6, 1]
_.iteratee = function(value, context) {
if (typeof value !== 'function') throw Error('第二个参数必须是函数')
return function(...agrs) {
value.call(context, agrs)
}
};
_.map(arr, 'aa')baseIteratee
大多数情况下,不会去修改iteratee,cb函数一般都会走到下面这一步:
return baseIteratee(value, context, argCount);这里调用了baseIteratee函数,源码中这个函数如下:
function baseIteratee(value, context, argCount) {
if (value == null) return identity;
if (isFunction(value)) return optimizeCb(value, context, argCount);
if (isObject(value) && !isArray(value)) return matcher(value);
return property(value);
}可以看到,实在这个函数中对传递进来的第二个参数做了处理:
identity
if (value == null) return identity; function identity(value) {
return value;
}初始化了一个迭代器,返回传递进来的参数。
optimizeCb
if (isFunction(value)) return optimizeCb(value, context, argCount);如果是函数,就交给内部的optimizeCb函数去处理:
function optimizeCb(func, context, argCount) {
if (context === void 0) return func;
switch (argCount == null ? 3 : argCount) {
case 1: return function(value) {
return func.call(context, value);
};
// The 2-argument case is omitted because we’re not using it.
case 3: return function(value, index, collection) {
return func.call(context, value, index, collection);
};
case 4: return function(accumulator, value, index, collection) {
return func.call(context, accumulator, value, index, collection);
};
}
return function() {
return func.apply(context, arguments);
};
}大多数情况下,都不会传递context,直接返回了func,也就是传递进来的迭代器。如果传递了context,只需这样返回就可以满足需求:
var optimizeCb = function(func, context) {
if (context === void 0) return func;
return function() {
return func.apply(context, arguments);
};
};
但是 underScore中却对传递的参数个数进行分类处理。之所以这么做就是为了避免使用arguments。因为使用arguments的要不使用效率低一些。
比如map中,迭代器的调用就传递了三个参数:
results[index] = iteratee(obj[currentKey], currentKey, obj);这里没有传递argCount,optimizeCb中,argCount默认是3。返回
case 3: return function(value, index, collection) {
return func.call(context, value, index, collection);
};正好对应iteratee(obj[currentKey], currentKey, obj);这里传递的3个参数。
matcher
if (isObject(value) && !isArray(value)) return matcher(value);第二个参数是对象,并且不是数组,也就是这样的情况:
var arr = [4, 6, 1]
var obj = [{ name: '麦乐' }, { name: 'maile' }]
var a = _.map(obj, { name: 'maile' })
console.log(a) // [false, true] function matcher(attrs) {
attrs = extendOwn({}, attrs);
return function(obj) {
return isMatch(obj, attrs);
};
}var extendOwn = createAssigner(keys);keys
keys是一个函数, 主要作用是获取对象的key,并以数组的形式返回,类似于Object.keys(obj)。underScore为什么要扩展这样一个方法,不直接使用Objetc.keys()呢?
源码中nativeKeys = Object.keys,因为有的环境中可能没有Object.keys这个方法,IE9以下浏览器会有不同的返回,待会再讲,封装这个函数的目的主要是做兼容性处理,也是设计模式中的外观模式:为一组复杂的子系统接口提供一个更高级的统一接口。
Object.keys找的是对象上可枚举的属性,for in 找的是对象自身和原型链上可枚举的属性。
function keys(obj) {
if (!isObject(obj)) return [];
if (nativeKeys) return nativeKeys(obj);
var _keys = [];
for (var key in obj) if (_has(obj, key)) _keys.push(key);
// Ahem, IE < 9.
if (hasEnumBug) collectNonEnumProps(obj, _keys);
return _keys;
}- 不是对象直接返回空数组
- 支持Object.keys方法直接调用
- 不支持的话调用_has方法,检查对像是否包含key,如果有就放入_keys数组中返回
function _has(obj, path) {
return obj != null && hasOwnProperty.call(obj, path);
}hasOwnProperty = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty;- 最后做IE9以下的兼容处理(这里做下说明,可能大部分ie浏览器已经修复了这样的bug,这里主要是让大家明白这么做的目的)
IE9以下浏览器中,如果在对象中扩展了一个对象原型上的方法,默认是不可枚举的,通过Object.keys方法是拿不到这个key的.
高版本浏览器中:
var obj = { name: '麦乐', toString: function() { } }
console.log(Object.keys(obj)) // ["name", "toString"]低版本浏览器中
var obj = { name: '麦乐', toString: function() { } }
console.log(Object.keys(obj)) // ["name"]propertyIsEnumerable检查一个对象的属性是否是可枚举的
// Keys in IE < 9 that won't be iterated by `for key in ...` and thus missed.
var hasEnumBug = !{ toString: null }.propertyIsEnumerable('toString');hasEnumBug是true说明是不可枚举的,就存在iebug,需要做兼容处理
if (hasEnumBug) collectNonEnumProps(obj, _keys);先来找一下原型上的方法都有哪些?
var nonEnumerableProps = ['valueOf', 'isPrototypeOf', 'toString',
'propertyIsEnumerable', 'hasOwnProperty', 'toLocaleString'];循环遍历看两者是否相等
obj[nonEnumerableProps[i]] === Object.prototype[nonEnumerableProps[i]]如果相等,说明没有被扩展,不相等说明被扩展了。
这里没有constructor,是因为这个属性比较特殊。具体哪里特殊还没有弄明白。。。
collectNonEnumProps
if (hasEnumBug) collectNonEnumProps(obj, _keys);
function collectNonEnumProps(obj, _keys) {
var nonEnumIdx = nonEnumerableProps.length;
var constructor = obj.constructor;
var proto = isFunction(constructor) && constructor.prototype || ObjProto;
// Constructor is a special case.
var prop = 'constructor';
if (_has(obj, prop) && !contains(_keys, prop)) _keys.push(prop);
while (nonEnumIdx--) {
prop = nonEnumerableProps[nonEnumIdx];
if (prop in obj && obj[prop] !== proto[prop] && !contains(_keys, prop)) {
_keys.push(prop);
}
}
}createAssigner
matcher方法中用到了对象的扩展,extendOwn中keys是获取对象自身可枚举的属性。extend中的allkeys是获取对象自身和原型上都可枚举的属性,这里做了颗粒度解藕。
var extendOwn = createAssigner(keys);
var extend = createAssigner(allkeys);合并对象,这里是浅拷贝,jQuery的extend方法是深拷贝:
function createAssigner(keysFunc, defaults) {
return function(obj) {
var length = arguments.length;
if (defaults) obj = Object(obj);
if (length < 2 || obj == null) return obj;
for (var index = 1; index < length; index++) {
var source = arguments[index],
_keys = keysFunc(source),
l = _keys.length;
for (var i = 0; i < l; i++) {
var key = _keys[i];
if (!defaults || obj[key] === void 0) obj[key] = source[key];
}
}
return obj;
};
}isMatch
第一参数是map函数的第一个参数的元素,第二个参数是map函数的第二个参数,两个对象只要有key 或者value任何一个不同,都会返回false,匹配不到值。
// Returns whether an object has a given set of `key:value` pairs.
function isMatch(object, attrs) {
var _keys = keys(attrs), length = _keys.length;
if (object == null) return !length;
var obj = Object(object);
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {
var key = _keys[i];
if (attrs[key] !== obj[key] || !(key in obj)) return false;
}
return true;
}property
最后,就是处理是map的第二个参数是数组或者是字符串的情况了:
return property(value); function property(path) {
if (!isArray(path)) {
return shallowProperty(path);
}
return function(obj) {
return deepGet(obj, path);
};
}字符串
shallowProperty
获取对象的属性值,返回null或者对象的value值
function shallowProperty(key) {
return function(obj) {
return obj == null ? void 0 : obj[key];
};
}数组
返回null,undefined,或者返回处理后的obj这个obj是键值。
deepGet
是为了获取对象深层次的值
function deepGet(obj, path) {
var length = path.length;
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (obj == null) return void 0;
obj = obj[path[i]];
}
return length ? obj : void 0;
}
var obj = [{ name: '麦乐', age: 18, height: 168 },
{ name: 'maile', age: 16, height: 19 }]
var a = _.map(obj, ['age', 'name'])
console.log(a) // [undefined, undefined] var obj = [{
name: {
age: 18
}
},
{
name: {
age: 16
}
}]
var a = _.map(obj, ['name', 'age'])
console.log(a) // [18, 16]使用这个函数,可以避免深层次取值时,因为没有其中的一个属性,导致的报错。