Hanlder的使用及其Looper,MessageQueue原理
Handler是Android中的消息处理机制,多用于线程之间传递消息。
一.使用方法
final Handler mHandler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
Log.v(TAG,"handleMessage is running:"+msg.what);
}
};
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
Log.v(TAG, "new a Thread");
for(int i = 0; i < 10;i ++){
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(i);
}
}
}.start(); 或者
Runnable mRunnable = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
Log.v(TAG, "new a Thread:");
for(int i = 0; i < 10;i ++){
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(i);
}
}
};
new Handler().post(mRunnable);使用Handler 存在的问题
内存方面
Handler 被作为 Activity 引用,如果为非静态内部类,则会引用外部类对象。当 Activity finish 时,Handler可能并未执行完,从而引起 Activity 的内存泄漏。故而在所有调用 Handler 的地方,都用静态内部类。
异常方面
当 Activity finish 时,在 onDestroy 方法中释放了一些资源。此时 Handler 执行到 handlerMessage 方法,但相关资源已经被释放,从而引起空指针的异常。为解决这个问题,如果是使用 handlerMessage,则在方法中加try catch。如果是用 post 方法,则在Runnable方法中加try catch。
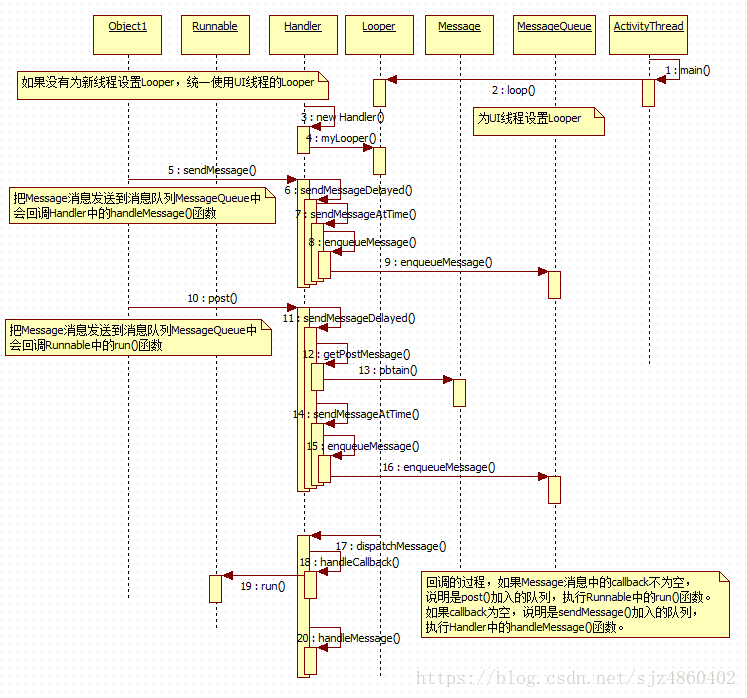
二. Looper,MessageQueue,Hanlder
MessageQueue: 消息队列,把加入的Message消息互相链接起来组成一个单链表。
Handler:负责把Message消息加入MessageQueue队列中
Looper:负责循环读取MessageQueue消息队列中的消息,并把消息派发给相应的类处理(Handler,Runnable )
ActivityThread:
public static void main(String[] args) {
......
Looper.prepareMainLooper();//为UI线程设置Looper
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();//循环读取MessageQueue队列,取出Message做处理
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}Looper
public final class Looper {
//静态
static final ThreadLocal sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
//构建Looper对象
public static void prepare() {
prepare(true);
}
//构建Looper对象,并把新构建的Looper对象保存到sThreadLocal 中
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
//构建UI线程的Looper对象
public static void prepareMainLooper() {
prepare(false);
synchronized (Looper.class) {
if (sMainLooper != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared.");
}
sMainLooper = myLooper();
}
}
//循环读取MessageQueue队列,取出Message并回调msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)。target就是Handler对象的引用
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
//死循环读取MessageQueue并取出Message
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
......
try {
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);//回调Handler中的dispatchMessage()函数
end = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
} finally {
if (traceTag != 0) {
Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);
}
}
.......
}
}
//取出保存在sThreadLocal中的Looper对象
public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() {
return sThreadLocal.get();
} MessageQueue
public final class MessageQueue {
......
//Message加入队列的操作
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {......}
......
}
Handler
public class Handler {
//如果Message中的callback为空,调用handleCallback(),否则调用handleMessage()
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
//回调callback中的run()方法,一般都是Runnable中的run()
private static void handleCallback(Message message) {
message.callback.run();
}
//把Message消息加入到队列中
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
} 关于Looper:
每个线程都绑定一个唯一Looper,不能构建多个。如果新构建的线程没有绑定新的Looper,那这个线程不能使用Handler,否则会报java.lang.RuntimeException: Can’t create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()错误。我们需要调用prepare()创建Looper对象,并循环取出MessageQueue中的数据,Looper.java源码中的案例如下:
*
* class LooperThread extends Thread {
* public Handler mHandler;
*
* public void run() {
* Looper.prepare();
*
* mHandler = new Handler() {
* public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
* // process incoming messages here
* }
* };
*
* Looper.loop();
* }
* }