AndroidUI系列 - ViewGroup实现瀑布流
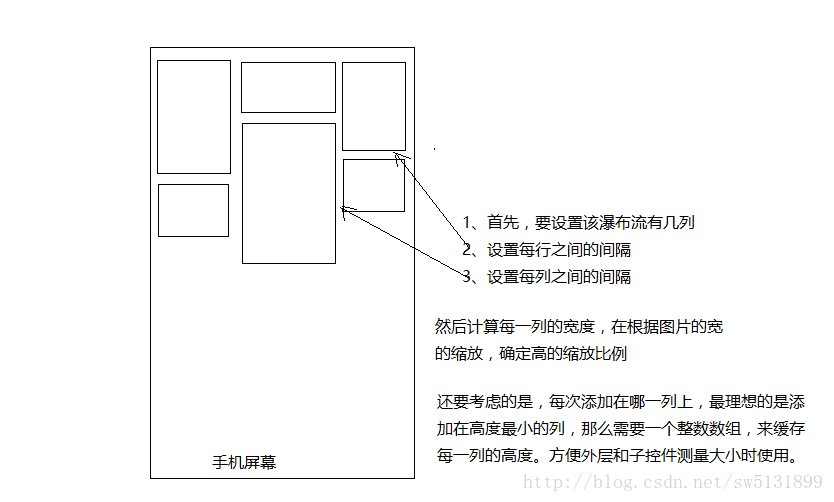
其实瀑布流现在用的越来越少了,更多的是使用MD的风格了。风靡一时的瀑布流现在渐渐地开始退居后幕了。不过,瀑布流也是个不错的自定义控件练习方式。相对简单的实现逻辑,可以帮助更好的更快的上手ViewGroup的自定义,以及onMeasure和onLayout等方法的理解和学习。先看看效果。
很简单的逻辑,外围能滑动,因为加了一层ScollView,当然也可以不加,为了方便就加了。
直接贴代码。
package com.example.administrator.myapplication.flow;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import com.example.administrator.myapplication.R;
/**
* Created by ShuWen on 2017/6/9.
*/
public class WaterFallLayout extends ViewGroup {
private int mTop[];
private int mColNumber = 3;//默认3列
private int mHorozontalSpace = 20;//每列间隔20px
private int mVerticalSpace = 20;//每行之间
private int childWidth = 0;
private int maxHeight = 0;
private int minColNumber = 0;
public WaterFallLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
init(context,null);
}
public WaterFallLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context,attrs);
}
public WaterFallLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context,attrs);
}
private void init(Context context, AttributeSet attrs){
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.WaterFallLayout);
mColNumber = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.WaterFallLayout_mColNumber,3);
mHorozontalSpace = DensityUtil.dip2px(context,typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.WaterFallLayout_mHorozontalSpace,20));
mVerticalSpace = DensityUtil.dip2px(context,typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.WaterFallLayout_mVerticalSpace,20));
mTop = new int[mColNumber];
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//测量模式
int widthMeasureMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMeasureMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//默认大小
int widthMeasureSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMeasureSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//测量之后的宽高
int measuredWidth = 0;
int measuredHeight = 0;
//测量所有子控件
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(view,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
}
//计算每列的宽
childWidth = (widthMeasureSize - mColNumber * mHorozontalSpace) / 3;
//计算控件的宽 若设置了确定的大小,就采用设置大小
if (widthMeasureMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measuredWidth = widthMeasureSize;
} else {
if (getChildCount() > mColNumber) {
measuredWidth = widthMeasureSize;
} else {
measuredWidth = childWidth * getChildCount() + (getChildCount() - 1) * mHorozontalSpace;
}
}
//计算控件的高 若设置了确定的大小,就采用设置大小
if (heightMeasureMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measuredHeight = heightMeasureSize;
} else {
measuredHeight = getMaxHeight();
}
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int left, top, right, bottom;
//再次布局时,清除上次缓存数据
clearTop();
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View viewChild = getChildAt(i);
int measuredHeight = viewChild.getMeasuredHeight();
int measuredWidth = viewChild.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = measuredHeight * childWidth / measuredWidth;
//找到最小高度列
int minColNum = getMinColNumber();
left = minColNum*(mHorozontalSpace + childWidth);
top = mTop[minColNum];
right = left+childWidth;
bottom = top + childHeight;
viewChild.layout(left,top,right,bottom);
//记录每一行的高
mTop[minColNum] += childHeight + mVerticalSpace;
}
}
private void clearTop() {
for (int i = 0; i < mTop.length; i++) {
mTop[i] = 0;
}
}
public int getMaxHeight() {
for (int i = 0; i < mTop.length; i++) {
if (mTop[i] > maxHeight){
maxHeight = mTop[i];
}
}
return maxHeight;
}
public int getMinColNumber() {
for (int i = 0; i < mTop.length; i++) {
if (mTop[minColNumber] > mTop[i]){
minColNumber = i;
}
}
return minColNumber;
}
}
该控件对应的一些属性值。
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="WaterFallLayout">
<attr name="mColNumber" format="integer"/>
<attr name="mHorozontalSpace" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="mVerticalSpace" format="dimension"/>
declare-styleable>
resources>还有一个方法类,将dp转px。
package com.example.administrator.myapplication.flow;
import android.content.Context;
/**
* Created by ShuWen on 2017/6/9.
*/
public class DensityUtil {
/**
* 根据手机的分辨率从 dp 的单位 转成为 px(像素)
*
* @param context
* @param dpValue
* @return
* @date 2015年10月28日
*/
public static int dip2px(Context context, float dpValue) {
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f);
}
/**
* 根据手机的分辨率从 px(像素) 的单位 转成为 dp
*
* @param context
* @param pxValue
* @return
* @date 2015年10月28日
*/
public static int px2dip(Context context, float pxValue) {
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (pxValue / scale + 0.5f);
}
}
然后看看MainActivity
package com.example.administrator.myapplication;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import com.example.administrator.myapplication.flow.WaterFallLayout;
import java.util.Random;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
WaterFallLayout waterfall;
private static int IMG_COUNT = 5;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
waterfall = (WaterFallLayout) findViewById(R.id.waterfall);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(this);
imageView.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));
Random random = new Random();
Integer num = Math.abs(random.nextInt());
if (num % IMG_COUNT == 0) {
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.a0);
} else if (num % IMG_COUNT == 1) {
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.a1);
} else if (num % IMG_COUNT == 2) {
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.a2);
} else if (num % IMG_COUNT == 3) {
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.a3);
} else if (num % IMG_COUNT == 4) {
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.a4);
}else if (num % IMG_COUNT == 5) {
imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.a5);
}
waterfall.addView(imageView);
}
}
}
看看布局。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
tools:context="com.example.administrator.myapplication.MainActivity">
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.example.administrator.myapplication.flow.WaterFallLayout
android:id="@+id/waterfall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:mColNumber="3"
app:mHorozontalSpace="5dp"
app:mVerticalSpace="5dp">
com.example.administrator.myapplication.flow.WaterFallLayout>
ScrollView>
RelativeLayout>简单粗暴,这个例子有利于理解ViewGroup的一些计算逻辑,为其他复杂自定义控件打下基础。