本文将从零开始搭建一个现代化的PHP框架,该框架会拥有现代框架的一切特征,如单入口,路由,依赖注入,composer类自动加载机制等等,如同时下最流行的Laravel框架一样。
一、开发环境搭建
1、开发环境搭建
这里我们使用 Homestead 来作为我们的集成开发环境,里边集成了PHP、MySQL我们需要的软件环境,或者也可以用Xampp集成环境来开发,只要你安装PHP、MySQL即可,我这里用Homestead做为开发环境。
homestead.yaml配置:
atom ~/.homestead/Homestead.yaml---
ip: "192.168.10.10"
memory: 2048
cpus: 1
provider: virtualbox
authorize: ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
keys:
- ~/.ssh/id_rsa
folders:
- map: ~/Code
to: /home/vagrant/Code
sites:
- map: framework.app # <--- 这里,第五个项目,框架学习开发
to: /home/vagrant/Code/php-framework # <--- 这里
databases:
- php-framework
variables:
- key: APP_ENV
value: local
# blackfire:
# - id: foo
# token: bar
# client-id: foo
# client-token: bar
# ports:
# - send: 50000
# to: 5000
# - send: 7777
# to: 777
# protocol: udp
重启vagrant
修改完 Homestead.yaml 文件后,需要重新加载配置文件信息才能生效。
➜ ~ cd Homestead
➜ Homestead git:(7924ab4) vagrant reload --provision修改hosts配置文件
Hosts配置域名在mac的位置: /etc/hosts
192.168.10.10 digtime.app2、开发工具
我们可以选择 Sublime,Atom,PHPStorm 这些IDE。
二、第一版-实现最基本的功能
现在,我们先创建一个简单的框架,实现MySQLPDO的连接,查询,创建引导文件,创建项目的配置文件(包括连接数据库的用户名和密码等)
第一版本GitHub地址
三、第二版本-单一入口和mvc架构
我们对目录进行重构,按照MVC功能划分:
├── index.php
├── config.php
├── controllers
├── core
│ ├── bootstrap.php
│ └── database
│ ├── Connection.php
│ └── QueryBuilder.php
├── models
│ └── Task.php
└── views现在我们再来添加两张页面about.php和contact.php, 按照之前我们说的逻辑层和视图层分离的原则,我们还需要建立about.view.php和contact.view.php, 并在about.php和contact.php中引入它们的视图文件。然后我们可以通过http://framework.app/about.php 或 http://framework.app/contact.php 之类的 uri 来访问这些页面, 像这种方式我们称为多入口方式,这种方式对于小型项目还能管理,项目过大了,管理起来就会比较麻烦了。
现在的框架基本都是采用单一入口的模式,什么是单一入口,其实就是整个站点只有 index.php 这一个入口,我们访问的任何 uri 都是先经过 index.php 页面,然后在index.php中根据输入的 uri 找到对应的文件或者代码运行,然后返回数据。
单一入口思路:
1.访问http://framework.app/about.php这条路径时,先进入到 index.php 中
2.然后在 index.php 中会通过一些方法去找到与这条路由对应需要执行的文件,一般我们会把这些文件放到控制器中。
3、执行控制器文件中的逻辑代码,最终将数据通过对应的视图层显示出来。
事实上,我们访问 http://framework.app/about.php 这个路由时,它真正的路由是 http://framework.app/index.ph...然后通过Apache或者是Nginx做路由跳转,就可以实现成类式 http://framework.app/about.php 这样的路由了。
重写Nginx服务器路由(Homestead 下重写):
nginx配置url重写
// Homestead 对每个域名都分配不同的配置
我们对framework.app的Nginx配置进行路由重写:
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available
vagrant@homestead:/etc/nginx/sites-available$ sudo vim framework.app
重写:
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name framework.app;
root "/home/vagrant/Code/php-framework";
## 重写路由
rewrite ^(.*) /index.php?action=$1 last;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
charset utf-8;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location = /favicon.ico { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
location = /robots.txt { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
access_log off;
error_log /var/log/nginx/framework.app-error.log error;
sendfile off;
client_max_body_size 100m;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_intercept_errors off;
fastcgi_buffer_size 16k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 16k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/framework.app.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/framework.app.key;
}重启服务器:
sudo service nginx restart;重写路由地址后,我们可以直接用 http://framework.app/about 来访问了:
Nginx 服务器会将访问的路径http://framework.app/about 重写为:http://framework.app/index.php?action=about
如果你的服务器是Apache,则可以在根目录下增加.htaccess 文件即可:
RewriteEngine On
#如果文件存在就直接访问目录不进行RewriteRule
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
#如果目录存在就直接访问目录不进行RewriteRule
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
#将所有其他URL重写到 index.php/URL
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php?action=$1 [PT,L]
编写路由类 Router
Router.php
[],
'POST' => []
];
public function get($uri, $controller)
{
$this->routes['GET'][$uri] = $controller;
}
// 当定义POST路由时候,把对应的$uri和$controller以健值对的形式保存在$this->routes['POST']数组中
public function post($uri, $controller)
{
$this->routes['POST'][$uri] = $controller;
}
/**
* 赋值路由关联数组
* @param $routes
*/
public function define($routes)
{
$this->routes = $routes;
}
/**
* 分配控制器路径
* 通过用户输入的 uri 返回对应的控制器类的路径
* @param $uri
* 这里的 $requestType 是请求方式,GET 或者是 POST
* 通过请求方式和 $uri 查询对应请求方式的数组中是否定义了路由
* 如果定义了,则返回对应的值,没有定义则抛出异常。
* @return mixed
* @throws \Exception
*/
public function direct($uri, $requestType)
{
if(array_key_exists($uri, $this->routes[$requestType]))
{
return $this->routes[$requestType][$uri];
}
// 不存在,抛出异常,以后关于异常的可以自己定义一些,比如404异常,可以使用NotFoundException
throw new Exception('No route defined for this URI');
}
public static function load($file)
{
$router = new static;
// 调用 $router->define([]);
require ROOT . DS . $file;
// 注意这里,静态方法中没有 $this 变量,不能 return $this;
return $router;
}
}routes.php 路由文件
get('', 'controllers/index.php');
$router->get('about', 'controllers/about.php');
$router->get('contact', 'controllers/contact.php');
$router->post('tasks', 'controllers/add-task.php');index.php 入口文件
direct(Request::uri(), Request::method());我们来看一下入口文件index.php,先加载路由文件routes.php,该文件是不是和我们Laravel的一样呢,根据请求类型进行控制器分配,先把所有请求的路径根据类型划分到不同的请求类型属性(GET,POST)中,然后,再根据请求的路径来加载对应的控制器。
加载过程详解:http://framework.app/about通过GET请求访问页面:
1:
Router::load('routes.php'),加载所有路由
routes.php
$router->get('', 'controllers/index.php');
$router->get('about', 'controllers/about.php');
$router->get('contact', 'controllers/contact.php');
$router->post('tasks', 'controllers/add-task.php');路由类Router.php
public static function load($file)
{
$router = new static;
// 调用 $router->define([]);
require ROOT . DS . $file;
// 注意这里,静态方法中没有 $this 变量,不能 return $this;
return $router;
}
此方法等价于:
public static function load($file)
{
$router = new static;
// 调用 $router->define([]);
// require ROOT . DS . $file;
// 这里调用get,post方法进行$routes属性赋值
$router->get('', 'controllers/index.php');
$router->get('about', 'controllers/about.php');
$router->get('contact', 'controllers/contact.php');
$router->post('tasks', 'controllers/add-task.php');
// 注意这里,静态方法中没有 $this 变量,不能 return $this;
return $router;
}加载路由文件routes.php之后Router.php的$routes属性结果为:
protected $routes = [
'GET' => [
'' => 'controllers/index.php',
'about' => 'controllers/about.php',
'contact' => 'controllers/contact.php',
],
'POST' => ['tasks' => 'controllers/add-task.php']
];然后再根据 direct($uri, $requestType)方法获取对应路径的控制器路径,然后 require controllers/about.php.
四、使用composer进行类自动加载
我们现在的项目中使用了一堆的require语句, 这样的方式对项目管理并不是很好,现在有人为 php 开发了一个叫做 composer 的依赖包管理工具,非常好用,我们将其集成进来,composer 官方地址 https://getcomposer.org/ 按照提示进行全局安装即可。
我们先将 bootstrap.php 中的下面4句类引入代码注销
// require 'core/Router.php';
// require 'core/Request.php';
// require 'core/database/Connection.php';
// require 'core/database/QueryBuilder.php';然后在根目录下建立 coomposer.json 的配置文件,输入以下内容:
{
"autoload": {
"classmap": [
"./"
]
}
}上面的意思是将根目录下的所有的类文件都加载进来, 在命令行执行 composer install 后,在根目录会生成出一个vendor的文件夹,我们以后通过 composer 安装的任何第三方代码都会被生成在这里。
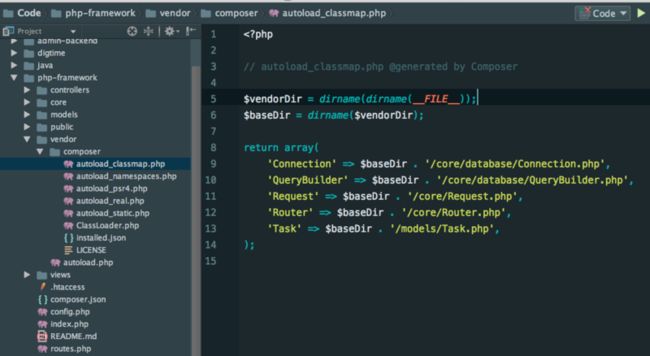
下面在bootstrap.php添加require 'vendor/autoload.php'; 即可。我们可以在vendor/composer/autoload_classmap.php文件中查看生成的文件对应关系。
$baseDir . '/core/database/Connection.php',
'QueryBuilder' => $baseDir . '/core/database/QueryBuilder.php',
'Request' => $baseDir . '/core/Request.php',
'Router' => $baseDir . '/core/Router.php',
'Task' => $baseDir . '/models/Task.php',
);
这里的核心思想是使用了一个 spl_autoload_register() 函数,进行类按需加载,懒加载,即创建对象,然后再加载对象所需要的类文件,而不是之前那种将所有的类文件全部引入,具体请看 详解spl_autoload_register()函数。
如果新添加了类文件,我们需要运行下面命令进行类自动重新加载:
composer dump-autoload注意:以上方法只能将类文件自动加载,其他文件不会进行引入的,如 function.php不会被引入,如果需要,则仍需要使用手动 require 引入。
五、实现依赖注入容器 DI Container
什么是依赖注入容器 DI Container? 一个听上去非常高大上的东西,先不要去纠结字面的意思,你可以这么想,把我们的 APP 想象成一个很大的盒子,把我们所写的一些功能,比如说配置,数据库操作等都扔到这个盒子里,在扔进去的时候你要给它们贴一个标签,以后可以通过这个标签把它们取出来用。大体就是这个意思。
我们来看bootstrap.php 中的代码, 其实 $app 这个数组就可以看成是一个容器,我们把配置文件扔到数组中,贴上config的标签(也就是健),把QueryBuilder也扔进去了,贴上标签database。之后我们可以通过$app['config']这样拿出我们需要的值。
我们为何不把$app数组做成一个对象呢! 这样我们以后可以为其添加很多的属性和方法,会方便很多,需要对象就必须要有类,我们马上就可以在core文件夹内建立一个 App.php 的文件,当中包含App类。
下面看看我们需要哪些方法,先看 $app['config'] = require 'config.php'; 这一句是把config.php放进到App的容器中,现在常用的说法是 注册config 到App, 或者是绑定config 到App, 那我们需要的方法可能是这样的。
$app->bind('config', require 'config.php');
// 或者
$app->register('config', require 'config.php');
// 或者
App::bind(config', require 'config.php');
// 或者
App::register('config', require 'config.php');在我们写类的时候,可能不知道怎么动手,可以先尝试着调用假定存在的方法,再回头去完善类,之前我们也都是这么做的,这样相对会容易些,上面的几种方法个人感觉App::bind(config', require 'config.php');更好些,然后要取出config可以使用 App::get('config') 方法,下面去实现这两个方法。在core/App.php 中
class App
{
protected static $registries = [];
public static function bind($key, $value)
{
static::$registries[$key] = $value;
}
public static function get($key)
{
if (! array_key_exists($key, static::$registries)) {
throw new Exception("No {$key} is bound in the container.");
}
return static::$registries[$key];
}
}bootstrap.php 中目前代码如下:
require 'vendor/autoload.php';
App::bind('config', require 'config.php');
App::bind('database', new QueryBuilder(
Connection::make(App::get('config')['database'])
));将所有使用到$app['config']和$app['database']的地方全部用App::get('config')和App::get('database')替换过来,毫无疑问的会提示“找不到APP的错误”,原因是在我们的autoload_classmap.php文件中并没有导入App.php文件,我们需要在命令行执行 composer dump-autoload 来重新生成autoload_classmap.php文件。
六、重构控制器
1.新建控制器类
现在我们的控制器中的代码还都是一些面条式的代码, 并没有使用面向对象的方式去开发,我们来重构下,我们需要编写控制器类,然后让路由指向到对应的控制器的方法,这样在我们以后的工作流中就会方便很多。
我们在controllers文件夹下建立 PagesController.php 的文件, 编写以下的代码,将之前控制器中的文件中的代码都以方法的形式写在这个类中
class PagesController
{
public function home()
{
$tasks = App::get('database')->selectAll('tasks', 'Task');
require 'views/index.view.php';
}
public function about()
{
require 'views/about.view.php';
}
public function contact()
{
require 'views/contact.view.php';
}
}现在可以将controllers文件夹下的index.php, about.php, contact.php都删除了,将路由文件中的代码改成下面这样:
2.更改路由文件
$router->get('', 'PagesController@home');
$router->get('about', 'PagesController@about');
$router->get('contact', 'PagesController@contact');3.初次修改 direct() 方法
现在我的意图是这样的,以about路由举例,当我们访问about, 就会调用PagesController类的about方法, 在about方法中直接运行逻辑代码。所以我们需要修改Router.php中的direct()方法。
目前direct()是根据相对路径返回对应控制器类的路径,然后在入口页面将其引入进来执行,现在我们只需要通过实例化控制器类,然后调用对应的方法即可。 那direct()的核心代码应该是类式这样的:(new PagesController)->about(); 我们暂且把这个功能命名为 callAction() 方法,先将定已经有了这个方法, 我们先去 direct()方法中调用它, 如下:
public function direct($uri, $requestType)
{
if (array_key_exists($uri, $this->routes[$requestType])) {
return $this->callAction('这里应该有参数');
}
throw new Exception('No route defined for this URI');
}4.实现私有方法 callAction()
下面考虑下 Router 类中的 callAction() 方法该怎么实现,刚才说了这个方法的核心是 (new Controller)->action(); 不多考虑,我们给这个方法两个参数,$controller 和 $action, 代码如下:
private function callAction($controller, $action)
{
$controllerObj = new $controller;
if (! method_exists($controllerObj, $action)) {
throw new Exception(
"{$controller} does not respond to the {$action} action."
);
}
return $controllerObj->$action();
}5. ... 运算符和 explode() 函数用法
上面的 method_exists($obj, $action) 方法是判断一个对象中是否某个方法,那在 direct() 中调用callAction()的参数我们该如何获取呢? 我们现在的 $this->routes$requestType的值是类式于 PagesController@about 这样的字符串,我们只需将该值拆分为 ['PagesController', 'about'] 这样的数组,然后使用 php5.6 之后出现的 ...运算符,将其作为参数传递,关于拆分字符串为数组,php 也给我们提供了一个这样的函数,叫做 explode(), 我们先看下这个函数的用法,
打开终端,输入 php --interactive 进入命令行交互模式
好了,现在就可以修改下direct() 这个方法了,如下:
public function direct($uri, $requestType)
{
if (array_key_exists($uri, $this->routes[$requestType])) {
return $this->callAction(
...explode('@', $this->routes[$requestType][$uri])
);
}
throw new Exception('No route defined for this URI');
}关于...explode('@', $this->routes$requestType) 这里的 ... 操作符, 它会把一维数组中的第一个元素作为参数1, 第二个元素作为参数2,以此类推,这是 php5.6 后新出的语法,可以自己查阅文档。
6.修改入口页面的代码
ok, 现在将入口页面的这句代码require Router::load('routes.php')->direct(Request::uri(), Request::method());的 require 去掉吧。再测试之前不要忘记了在命令行运行 composer dump-autoload 来重新加载文件。
七、全局函数 view()
下面更改下 PagesController 的 require 'views/about.view.php'; 这句代码,我们改成 return view('about'); 这样,可读性会好很多。同时在 psr标准中 也有这样的规定,在声明一个类的文件中是不能存在 require 代码的。
我们在core下创建一个functions.php的文件,把所有的全局函数都放在这里,准确来说帮助函数的文件不应该放在这里,它并不属于核心文件,但是为了我们这里写的帮助函数基本都是给我们的框架使用的,不设计业务开发,所以暂时还是先放这里。view()函数很简单,如下:
function view($name)
{
$name = trim($name, '/');
return require "views/{$name}.view.php";
}在PagesController的home 方法当中有$tasks对象集合, 我们怎么传递它到view()函数中呢? 我们需要给view()设置第二个数组形式的参数,调用view()的时候,将数据以数组的形式传递给view()即可,如下:
return view('index', ['tasks' => $tasks]);现在在view()函数中会出现问题了,我们传入的数据是一个数组,而在index.view.php中使用的是$tasks这样的变量,怎么转化?使用PHP提供的extract()函数可以做到这点,它可以将数组中的元素以变量的形式导入到当前的符号表,这句话不好懂,我们来演示下就明白了,还是进入 php 的命令行交互模式, 如下:
使用了extract()函数就会自动帮我们定义好与数组 key 同名的变量,并将 key 对应的 value 赋值给了该变量,好了,下面我们把view()方法完善下,如下:
function view($name, $data =[])
{
extract($data);
return require "views/{$name}.view.php";
}八、通过 composer 加载不是类的文件
下面自己把控制器中与view()相关的代码都更改过来,然后运行composer dump-autoload,它还是会提示找不到view()函数,原因在于我们的composer.json中的配置,我们需要将配置改成下面这样:
{
"autoload": {
"classmap": [
"./"
],
"files": [
"core/functions.php"
]
}
}上面的classmap只会加载类文件,要加载普通的文件需要使用 "files": [],好了,最后别忘记了composer dump-autoload.
九、控制器和路由的一些命名规范及命名空间
控制器和路由我们可以按照Laravel的风格:
// tasks 的列表页
$router->get('tasks', 'TasksController@index');
// TasksController.php
class TasksController
{
public function index()
{
$tasks = App::get('database')->selectAll('tasks', 'Task');
return view('index', compact('tasks'));
}
public function store()
{
App::get('database')->create('tasks', [
'description' => $_POST['description'],
'completed' => 0
]);
return redirect('/');
}
}从 PHP5.3 开始就支持命名空间了,关于命名空间的介绍看官方文档: http://php.net/manual/zh/lang... 。其实也很简单,你把命名空间想象层文件夹就行
本项目Github地址:php-framework
参考文章:论PHP框架是如何诞生的?