自定义ViewGroup——自定义布局
自定义ViewGroup和自定义View的区别:
| 类型 | onMeasure | onLayout | onDraw |
|---|---|---|---|
| 自定义View | 测量控件本身的大小 | 一般不用重写此方法 | 在父布局指定的区域绘制图形 |
| 自定义ViewGroup | 一定要测量子控件及本身的大小 | 必须重写此方法,在布局中摆放子控件 | 一般不重写此方法 |
自定义ViewGroup的步骤:
- 继承ViewGroup;
- 重写onMeasure方法测量子控件和自身宽高;
- 实现onLayout方法完成子控件的摆放。
自定义属性
如果要像LinearLayout布局那样有自己的属性,如orientation属性,那么我们还要定义一些布局属性,步骤如下:
- 首先在app/src/main/res/values/attrs.xml里定义布局属性;
- 继承LayoutParams,也可以继承MarginLayoutParams,定义布局参数类,用于记录布局属性的;
- 重写generateLayoutParams(),如generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)在布局文件被填充为对象的时调用,会获得AttributeSet对象,里面有布局属性。可以在这里初始化LayoutParams或其子类;
- 在onMeasure和onLayout中使用布局参数。
示例
自定义ViewGroup:
package com.wong.layout;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/*第一步:继承ViewGroup*/
public class MyLayout extends ViewGroup {
public MyLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
/**
* 第二步: 重写onMeasure方法测量子控件和自身宽高;
* 在onMeasure方法里进行子控件测量及ViewGroup自身的测量
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
/*测量子控件的大小,计算出所有的childView的宽和高,如果不进行测量,那么子控件就会不显示*/
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
/**
* 第三步:实现onLayout方法完成子控件的摆放
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
/*用于记录子控件添加到同一行后的累计宽度,以此作为是否换行的依据*/
int cumulateLayoutWidth = 0;
/*累计每行最大的高度值,以此作为下一行与父容器的顶边距的值*/
int cumulateLayoutHeight = 0;
/*用于定位每个子控件的位置时用的临时变量*/
int left, top, right, bottom;
/*记录每行的最大高度的临时变量,在换行时使用*/
int maxLineHeight = 0;
/*ViewGroup容器里的子控件数*/
int count = getChildCount();
/*摆放ViewGroup容器里的子控件*/
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
/*子控件的测量宽度和高度,不要使用child.getWidth()和child.getHeight()*/
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
/*getWidth()是ViewGroup的宽度,如果累计的宽度再加一个子控件的宽度超过了父容器的宽度getWidth(),那么就要另起一行了*/
if (cumulateLayoutWidth + childWidth < getWidth()) {
left = cumulateLayoutWidth;
top = cumulateLayoutHeight;
right = left + childWidth;
bottom = top + childHeight;
} else {
cumulateLayoutWidth = 0;
cumulateLayoutHeight = cumulateLayoutHeight + maxLineHeight;
maxLineHeight = 0;
left = cumulateLayoutWidth;
top = cumulateLayoutHeight;
right = left + childWidth;
bottom = top + childHeight;
}
/*累加宽度*/
cumulateLayoutWidth = cumulateLayoutWidth + childWidth;
/*选出行高*/
maxLineHeight = Math.max(maxLineHeight, childHeight);
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
}
}
}
应用MyLayout.java:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.wong.layout.MyLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width= "200dp"
android:layout_height= "200dp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:text="按钮1" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮2" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮3" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮4" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮5" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮6" />
</com.wong.layout.MyLayout>
注意事项:
1、要在onMeasure调用measureChildren(int, int)测量子控件
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
/*测量子控件的大小,计算出所有的childView的宽和高,如果不进行测量,那么子控件就会不显示*/
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
在重写onMeasure方法时,一定要用measureChildren(int, int)测量子控件。如果不测量的话,子控件将不会显示,因为不知道其大小。ViewGroup或View的子类都应该重写这个方法,以提供更准确且有效的测量值。重写onMeasure方法,必须调用setMeasuredDimension(int, int)方法来保存测量的宽度和高度。
measureChildren(int, int)最后也会调用setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int,int)保存测量的宽度和高度,setMeasuredDimension(int,int)最终也是调这个方法来保存的。
2、在onLayout方法要用child.getMeasureWidth()和child.getMeasuredHeight()获取子控件的宽高:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
...
/*用于定位每个子控件的位置时用的临时变量*/
int left, top, right, bottom;
int count = getChildCount();
/*摆放ViewGroup容器里的子控件*/
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
/*子控件的测量宽度和高度,不要使用child.getWidth()和child.getHeight()*/
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
...
}
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
}
}
child.getMeasureWidth()和child.getMeasuredHeight()才能获得子控件的宽高,而通过child.getWidth()和child.getHeight()获得的值都是0。为什么呢?首先,我们先来搞清楚getMeasureWidth和getMeasureHeight为什么会有值。
自定义View/ViewGroup的初始过程所调用的方法的顺序:
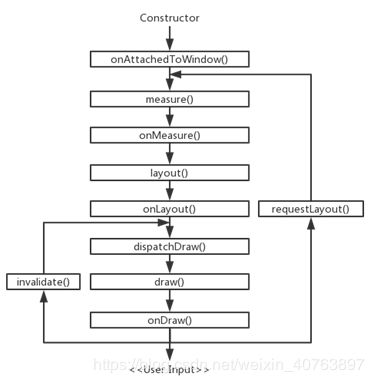 这些方法都主要在View类里,以getMeasuredWidth()为例:
这些方法都主要在View类里,以getMeasuredWidth()为例:
public final int getMeasuredWidth() {
return mMeasuredWidth & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
}
从上面的代码来看,只要mMeasuredWidth的初始化是在onLayout之前完成的,那么我们就能够在onLayout方法里通过getMeasuredWidth方法获得它的值,反之,则不能。
mMeasuredWidth变量是在setMeasuredDimensionRaw方法中完成初始化的:
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
...
}
setMeasuredDimension在onMeasure方法里被调用来保存测量的宽高,而它最终也会调setMeasuredDimensionRaw方法来做保存:
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
...
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
因此,mMeasuredWidth的初始化是在onLayout被执行之前完成的。getMeasuredHeight()同理的。
接下来我们看看在onLayout方法里child.getWidth()或child.getHeight()为什么都为0。以getWidth()为例:
/*视图左边离父视图左边的距离*/
protected int mLeft;
/*视图的右边离父视图左边的距离*/
protected int mRight;
public final int getWidth() {
return mRight - mLeft;
}
由上面的代码来看,如果mRight,mLeft在onLayout方法之前没有初始化的话,那么child.getWidth()就得到0。我们看看mRight,mLeft是在哪里被初始化的:
mRight,mLeft最终是在setFrame方法里被初始化的:
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
...
mLeft = left;
mTop = top;
mRight = right;
mBottom = bottom;
...
}
private boolean setOpticalFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
Insets parentInsets = mParent instanceof View ?
((View) mParent).getOpticalInsets() : Insets.NONE;
Insets childInsets = getOpticalInsets();
return setFrame(
left + parentInsets.left - childInsets.left,
top + parentInsets.top - childInsets.top,
right + parentInsets.left + childInsets.right,
bottom + parentInsets.top + childInsets.bottom);
}
上面的方法是在layout方法里被调用的:
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
...
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
...
}
而子控件的layout方法,在我们onLayout方法里刚要被执行:
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
所以,结合上面那张图可知我们通过child.getWidth()和child.getHeight()都在子控件自己的onLayout方法之前被调用了,那么获得的值当然是0了。
不完美之处
我们已成功实现了自定义ViewGroup,但是细心的你,可能已经发现了,在MyLayout布局里第一个Button的外边距没有效果:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.wong.layout.MyLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width= "200dp"
android:layout_height= "200dp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:text="按钮1" />
...
</com.wong.layout.MyLayout>
为什么呢?其实layout_margin不属于MyLayout的布局属性。那么我们就要进行自定义布局属性了。自定义布局的属性的四个步骤里,前两个不用做:
1. 首先在app/src/main/res/values/attrs.xml里定义布局属性;
2. 继承LayoutParams,也可以继承MarginLayoutParams,定义布局参数类,用于记录布局属性的;
3. 重写generateLayoutParams(),如generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)在布局文件被填充为对象的时调用,会获得AttributeSet对象,里面有布局属性。可以在这里初始化LayoutParams或其子类;
4. 在onMeasure和onLayout中使用布局参数。
因为布局参数类MarginLayoutParams是可以直接拿来用的,它可以用来记录外边距,而android系统的attrs.xml文件里已定义了layout_margin等外边距属性了。所以这两步我们都不用做,只需要实现后两步。
在ViewGroup里有两个类:LayoutParams、MarginLayoutParams,它们是专门用来告诉父布局它们想如何显示的,区别:
- LayoutParams:仅描述了宽高
- MarginLayoutParams:继承了LayoutParams,增加了记录外边距属性。
那么android系统是如何把布局属性初始化到MarginLayoutParams中的呢?**原来ViewGroup里有个方法generateLayoutParams (AttributeSet attrs),它是在布局文件被填充为对象的时候调用的。这样我们就可以在这个方法里初始化我们的布局参数类中去了。**如果不重写它,那么布局文件中设置的布局参数都不能拿到,除了宽高,因为这个方法在ViewGroup里的默认实现是返回LayoutParams对象的。还有几个方法,最好也能重写一下:
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return p;
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof MarginLayoutParams;
}
修改后的MyLayout.java:
package com.wong.layout;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class MyLayout extends ViewGroup {
public MyLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return p;
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof MarginLayoutParams;
}
/**
*
* 在onMeasure方法里进行子控件测量及ViewGroup自身的测量
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
/*测量子控件的大小,计算出所有的childView的宽和高,如果不进行测量,那么子控件就会不显示*/
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
/**
* 对子控件进行摆放
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
/*用于记录子控件添加到同一行后的累计宽度,以此作为是否换行的依据*/
int cumulateLayoutWidth = 0;
/*累计每行最大的高度值,以此作为下一行与父容器的顶边距的值*/
int cumulateLayoutHeight = 0;
/*用于定位每个子控件的位置时用的临时变量*/
int left, top, right, bottom;
/*记录每行的最大高度的临时变量,在换行时使用*/
int maxLineHeight = 0;
/*ViewGroup容器里的子控件数*/
int count = getChildCount();
/*摆放ViewGroup容器里的子控件*/
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
/*子控件的测量宽度和高度,不要使用child.getWidth()和child.getHeight()*/
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams lp = (ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams)child.getLayoutParams();
Log.i("YYY",lp.leftMargin+"#"+lp.topMargin+"#"+lp.rightMargin+"#"+lp.bottomMargin);
/*getWidth()是ViewGroup的宽度,如果累计的宽度再加一个子控件的宽度超过了父容器的宽度getWidth(),那么就要另起一行了*/
if (cumulateLayoutWidth + lp.leftMargin+childWidth+lp.rightMargin < getWidth()) {
left = cumulateLayoutWidth+lp.leftMargin;
top = cumulateLayoutHeight+lp.topMargin;
right = left + childWidth;
bottom = top + childHeight;
} else {
cumulateLayoutWidth = 0;
cumulateLayoutHeight = cumulateLayoutHeight + maxLineHeight;
maxLineHeight = 0;
left = cumulateLayoutWidth+lp.leftMargin;
top = cumulateLayoutHeight+lp.topMargin;
right = left + childWidth;
bottom = top + childHeight;
}
/*累加宽度*/
cumulateLayoutWidth = cumulateLayoutWidth + lp.leftMargin+childWidth+lp.rightMargin ;
/*选出行高*/
maxLineHeight = Math.max(maxLineHeight, lp.topMargin+childHeight+lp.bottomMargin);
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
}
}
}
MyLayout布局的使用:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.wong.layout.MyLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width= "200dp"
android:layout_height= "200dp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:text="按钮1" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮2" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮3" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮4" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮5" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:text="按钮6" />
</com.wong.layout.MyLayout>
接下来我们用一个完整的例子说明自定义布局属性
1、首先在app/src/main/res/values/attrs.xml里定义布局属性
2、继承LayoutParams,也可以继承MarginLayoutParams,定义布局参数类
3、重写generateLayoutParams()
4、在onMeasure和onLayout中使用布局参数
我们来一步一步实现:
第一步:在app/src/main/res/values/attrs.xml里定义布局属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="MySecondLayout">
<attr name="layout_position">
<enum name ="center" value="0" />
<enum name ="left" value="1" />
<enum name ="right" value="2" />
<enum name ="bottom" value="3" />
<enum name ="rightAndBottom" value="4" />
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
第二步:继承LayoutParams,也可以继承MarginLayoutParams(顺便可以获得外边距),定义布局参数类:
public static class MySecondLayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
public static final int POSITION_MIDDLE = 0; // 中间
public static final int POSITION_LEFT = 1; // 左上方
public static final int POSITION_RIGHT = 2; // 右上方
public static final int POSITION_BOTTOM = 3; // 左下角
public static final int POSITION_RIGHTANDBOTTOM = 4; // 右下角
public int position = POSITION_LEFT; // 默认我们的位置就是左上角
public MySecondLayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MySecondLayout_Layout);
//获取设置在子控件上的位置属性
position = a.getInt(R.styleable.MySecondLayout_Layout_layout_position, position);
a.recycle();
}
public MySecondLayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public MySecondLayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public MySecondLayoutParams(LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
第三步:重写generateLayoutParams():
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MySecondLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MySecondLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return p;
}
@Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return super.checkLayoutParams(p);
}
第四步:在onMeasure和onLayout中使用布局参数:
/**
* 在onMeasure方法里进行子控件测量及ViewGroup自身的测量
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//获得此ViewGroup上级容器为其推荐的宽和高,以及计算模式
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int layoutWidth = 0;
int layoutHeight = 0;
// 计算出所有的childView的宽和高
/*测量子控件的大小,计算出所有的childView的宽和高,如果不进行测量,那么子控件就会不显示*/
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int cWidth = 0;
int cHeight = 0;
int count = getChildCount();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
//如果布局容器的宽度模式是确定的(具体的size或者match_parent),直接使用父窗体建议的宽度
layoutWidth = sizeWidth;
} else {
//如果是未指定或者wrap_content,我们都按照包裹内容做,宽度方向上只需要拿到所有子控件中宽度做大的作为布局宽度
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
cWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
//获取子控件最大宽度
layoutWidth = cWidth > layoutWidth ? cWidth : layoutWidth;
}
}
//高度很宽度处理思想一样
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
layoutHeight = sizeHeight;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
cHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
layoutHeight = cHeight > layoutHeight ? cHeight : layoutHeight;
}
}
// 测量并保存layout的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(layoutWidth, layoutHeight);
}
/**
* 对子控件进行摆放
*
* @param changed
* @param l 距父容器的左边距
* @param t 距父容器的顶边距
* @param r 距父容器的右边距
* @param b 距父容器的底边距
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
/*用于定位每个子控件的位置时用的临时变量*/
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
/*ViewGroup容器里的子控件数*/
int count = getChildCount();
/*子控件的测量宽度和高度,不要使用child.getWidth()和child.getHeight()*/
int childMeasureWidth = 0;
int childMeasureHeight = 0;
MySecondLayoutParams params = null;
/*摆放ViewGroup容器里的子控件*/
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 注意此处不能使用getWidth和getHeight,这两个方法必须在onLayout执行完,才能正确获取宽高
childMeasureWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
childMeasureHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
params = (MySecondLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
switch (params.position) {
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_MIDDLE: // 中间
left = (getWidth() - childMeasureWidth) / 2;
top = (getHeight() - childMeasureHeight) / 2;
break;
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_LEFT: // 左上方
left = 0;
top = 0;
break;
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_RIGHT: // 右上方
left = getWidth() - childMeasureWidth;
top = 0;
break;
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_BOTTOM: // 左下角
left = 0;
top = getHeight() - childMeasureHeight;
break;
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_RIGHTANDBOTTOM:// 右下角
left = getWidth() - childMeasureWidth;
top = getHeight() - childMeasureHeight;
break;
default:
break;
}
// 确定子控件的位置,四个参数分别代表(左上右下)点的坐标值
child.layout(left, top, left + childMeasureWidth, top + childMeasureHeight);
}
}
MySecondLayout完整的代码:
package com.wong.layout;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class MySecondLayout extends ViewGroup {
public MySecondLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MySecondLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MySecondLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public MySecondLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MySecondLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MySecondLayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return p;
}
@Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return super.checkLayoutParams(p);
}
/**
* 在onMeasure方法里进行子控件测量及ViewGroup自身的测量
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//获得此ViewGroup上级容器为其推荐的宽和高,以及计算模式
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int layoutWidth = 0;
int layoutHeight = 0;
// 计算出所有的childView的宽和高
/*测量子控件的大小,计算出所有的childView的宽和高,如果不进行测量,那么子控件就会不显示*/
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int cWidth = 0;
int cHeight = 0;
int count = getChildCount();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
//如果布局容器的宽度模式是确定的(具体的size或者match_parent),直接使用父窗体建议的宽度
layoutWidth = sizeWidth;
} else {
//如果是未指定或者wrap_content,我们都按照包裹内容做,宽度方向上只需要拿到所有子控件中宽度做大的作为布局宽度
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
cWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
//获取子控件最大宽度
layoutWidth = cWidth > layoutWidth ? cWidth : layoutWidth;
}
}
//高度很宽度处理思想一样
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
layoutHeight = sizeHeight;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
cHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
layoutHeight = cHeight > layoutHeight ? cHeight : layoutHeight;
}
}
// 测量并保存layout的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(layoutWidth, layoutHeight);
}
/**
* 对子控件进行摆放
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
/*用于定位每个子控件的位置时用的临时变量*/
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
/*ViewGroup容器里的子控件数*/
int count = getChildCount();
/*子控件的测量宽度和高度,不要使用child.getWidth()和child.getHeight()*/
int childMeasureWidth = 0;
int childMeasureHeight = 0;
MySecondLayoutParams params = null;
/*摆放ViewGroup容器里的子控件*/
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 注意此处不能使用getWidth和getHeight,这两个方法必须在onLayout执行完,才能正确获取宽高
childMeasureWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
childMeasureHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
params = (MySecondLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
switch (params.position) {
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_MIDDLE: // 中间
left = (getWidth() - childMeasureWidth) / 2;
top = (getHeight() - childMeasureHeight) / 2;
break;
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_LEFT: // 左上方
left = 0;
top = 0;
break;
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_RIGHT: // 右上方
left = getWidth() - childMeasureWidth;
top = 0;
break;
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_BOTTOM: // 左下角
left = 0;
top = getHeight() - childMeasureHeight;
break;
case MySecondLayoutParams.POSITION_RIGHTANDBOTTOM:// 右下角
left = getWidth() - childMeasureWidth;
top = getHeight() - childMeasureHeight;
break;
default:
break;
}
// 确定子控件的位置,四个参数分别代表(左上右下)点的坐标值
child.layout(left, top, left + childMeasureWidth, top + childMeasureHeight);
}
}
public static class MySecondLayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
public static final int POSITION_MIDDLE = 0; // 中间
public static final int POSITION_LEFT = 1; // 左上方
public static final int POSITION_RIGHT = 2; // 右上方
public static final int POSITION_BOTTOM = 3; // 左下角
public static final int POSITION_RIGHTANDBOTTOM = 4; // 右下角
public int position = POSITION_LEFT; // 默认我们的位置就是左上角
public MySecondLayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MySecondLayout_Layout);
//获取设置在子控件上的位置属性
position = a.getInt(R.styleable.MySecondLayout_Layout_layout_position, position);
a.recycle();
}
public MySecondLayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public MySecondLayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public MySecondLayoutParams(LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
}
应用MySecondLayout:
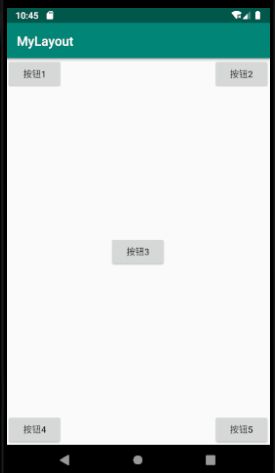
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.wong.layout.MySecondLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.wong.layout.MainMySecondLayoutActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
app:layout_position="left"
android:text="按钮1" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
app:layout_position="right"
android:text="按钮2" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
app:layout_position="center"
android:text="按钮3" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
app:layout_position="bottom"
android:text="按钮4" />
<Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
app:layout_position="rightAndBottom"
android:text="按钮5" />
</com.wong.layout.MySecondLayout>
谢谢阅读!