underscore源码学习笔记(五):Array相关的方法
获取数组的后n个元素
_.initial = function(array, n, guard) {
return slice.call(array, 0, Math.max(0, array.length - (n == null || guard ? 1 : n)));
};
获取数组前n个元素,调用了initial方法,当然,直接调用slice是更高效的
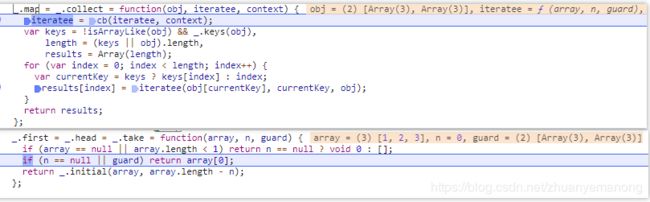
_.first = _.head = _.take = function(array, n, guard) {
if (array == null || array.length < 1) return n == null ? void 0 : [];
if (n == null || guard) return array[0];
return _.initial(array, array.length - n); //slice.call(array, 0 , n)
};
获取数组的非前n个元素
_.rest = _.tail = _.drop = function(array, n, guard) {
return slice.call(array, n == null || guard ? 1 : n);
};
获取数组的后n个元素
_.last = function(array, n, guard) {
if (array == null || array.length < 1) return n == null ? void 0 : [];
if (n == null || guard) return array[array.length - 1];
return _.rest(array, Math.max(0, array.length - n));
};
这里你可能会说,我直接用slice就好了啊,为什么还要搞4个api出来,其实,这种统一的形式有利于函数的组合
还有一点需要注意的是guard参数,好像多此一举,我们来看一个例子:获取二维数组中的第一个元素,返回新的数组
var array = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6] ]; //期待[1,4]
用for循环当然是可以的,但是函数式编程是极排斥for循环这种命令式的写法的.那么申明式的函数式写法是怎样的呢?
_.map(array, _.first)
但是如果没有guard,返回的结果是
[ [], [4] ]
我们试着在浏览器中打断点就会发现:此时的n为0,如果没有guard这个条件的话,会执行return语句,也就是_.initial([1,2,3], 3),最终调用的是slice.call([1,2,3], 0,0), 返回[], 进入第二次循环,此时n=1, 返回的是[4]
_.compact(list) : 剔除数组中的false值,包括false, null, 0, “”, undefined和NaN,
例子:
_.compact([0, 1, false, 2, '', 3]); //[1,2,3]
源码:
_.compact = function(array) {
return _.filter(array, Boolean);
};
这里内部使用了filter实现,Boolean作为过滤的条件,因此要注意的一点是0也会被过滤掉,返回的结果为[1,2,3],Boolean()可以将一个参数转化为布尔值
for (var value of [0, 1, -1, "0", "1", "cat", true, false, undefined, null]) {
console.log(`Boolean(${typeof value} ${value}) is ${Boolean(value)}`);
}
Boolean(number 0) is false
Boolean(number 1) is true
Boolean(number -1) is true
Boolean(string 0) is true
Boolean(string 1) is true
Boolean(string cat) is true
Boolean(boolean true) is true
Boolean(boolean false) is false
Boolean(undefined undefined) is false
Boolean(object null) is false
_.uniq(array, [isSorted], [iteratee]) : 数组去重
例子:
_.uniq([1, 2, 1, 4, 1, 3]);
=> [1, 2, 4, 3]
源码:
_.uniq = _.unique = function(array, isSorted, iteratee, context) {
if (!_.isBoolean(isSorted)) { //对不定参数进行处理,从后往前
context = iteratee;
iteratee = isSorted;
isSorted = false;
}
if (iteratee != null) iteratee = cb(iteratee, context); //生成回调
var result = [];
var seen = [];
for (var i = 0, length = getLength(array); i < length; i++) {
var value = array[i],
computed = iteratee ? iteratee(value, i, array) : value;
if (isSorted && !iteratee) {
if (!i || seen !== computed) result.push(value);
seen = computed;
} else if (iteratee) {
if (!_.contains(seen, computed)) {
seen.push(computed);
result.push(value);
}
} else if (!_.contains(result, value)) {
result.push(value);
}
}
return result;
};
_.union(*arrays) :对传入的多个数组去并集
例子:
_.union([1, 2, 3], [101, 2, 1, 10], [2, 1]);
=> [1, 2, 3, 101, 10]
源码:
_.union = restArguments(function(arrays) {
return _.uniq(flatten(arrays, true, true));
});
intersection: 对传入的多个数组取交集
_.intersection([1, 2, 3], [101, 2, 1, 10], [2, 1]);
=> [1, 2]
_.difference(array, *others): 和without类似,但是接受的是一个数组,剔除第一个数组中含有第二个数组的值
_.difference([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [5, 2, 10]);
=> [1, 3, 4]
zip_.zip(*arrays):在制作表格的时候有用
例子:
_.zip(['moe', 'larry', 'curly'], [30, 40, 50], [true, false, false]);
=> [["moe", 30, true], ["larry", 40, false], ["curly", 50, false]]
源码:
_.object(list, [values]) :将键数组和值数组提取组合
_.object(['moe', 'larry', 'curly'], [30, 40, 50]);
=> {moe: 30, larry: 40, curly: 50}
_.chunk(array, length) :将一纬数组拆分成二维数组,每个数组的长度等于或者小于length参数
例子:
var arr = ["Tyrone", "Elie", "Aidan", "Sam", "Katrina", "Billie", "Little Timmy"]
var chunkArr = _.chunk(arr, 2)
[["Tyrone", "Elie"], ["Aidan", "Sam"], ["Katrina", "Billie"], ["Little Timmy"]]
源码:
flatten_.flatten(array, [shallow]) :将多维数组拍平,估计用了递归
_.flatten = function(array, shallow) {
return flatten(array, shallow, false);
};
var flatten = function(input, shallow, strict, output) {
output = output || [];
var idx = output.length;
for (var i = 0, length = getLength(input); i < length; i++) {
var value = input[i];
if (isArrayLike(value) && (_.isArray(value) || _.isArguments(value))) {
// Flatten current level of array or arguments object.
if (shallow) { //
var j = 0, len = value.length;
while (j < len) output[idx++] = value[j++];
} else {
flatten(value, shallow, strict, output);
idx = output.length;
}
} else if (!strict) {
output[idx++] = value;
}
}
return output;
};
_.without(array, *values) :剔除数组中的值
_.without([1, 2, 1, 0, 3, 1, 4], 0, 1);
=> [2, 3, 4]
_.without = restArguments(function(array, otherArrays) {
return _.difference(array, otherArrays);
});
_.difference = restArguments(function(array, rest) {
rest = flatten(rest, true, true);
return _.filter(array, function(value){
return !_.contains(rest, value);
});
});
_.contains = _.includes = _.include = function(obj, item, fromIndex, guard) {
if (!isArrayLike(obj)) obj = _.values(obj);
if (typeof fromIndex != 'number' || guard) fromIndex = 0;
return _.indexOf(obj, item, fromIndex) >= 0;
};
_.indexOf = createIndexFinder(1, _.findIndex, _.sortedIndex);
var createIndexFinder = function(dir, predicateFind, sortedIndex) {
return function(array, item, idx) {
var i = 0, length = getLength(array);
if (typeof idx == 'number') {
if (dir > 0) {
i = idx >= 0 ? idx : Math.max(idx + length, i);
} else {
length = idx >= 0 ? Math.min(idx + 1, length) : idx + length + 1;
}
} else if (sortedIndex && idx && length) {
idx = sortedIndex(array, item);
return array[idx] === item ? idx : -1;
}
if (item !== item) {
idx = predicateFind(slice.call(array, i, length), _.isNaN);
return idx >= 0 ? idx + i : -1;
}
for (idx = dir > 0 ? i : length - 1; idx >= 0 && idx < length; idx += dir) {
if (array[idx] === item) return idx;
}
return -1;
};
};
_.findIndex(array, predicate, [context]) 和 _.findLastIndex(array, predicate, [context])
例子:
var isOdd = function(num) {return num % 2 == 1}
_.findIndex([4, 6, 8, 12], isOdd); // -1, not found
_.findIndex([4, 6, 7, 12], isOdd); // 2
_.findLastIndex([1, 4, 6, 8, 9], isOdd) ; //4
源码:
_.findIndex = createPredicateIndexFinder(1);
_.findLastIndex = createPredicateIndexFinder(-1);
var createPredicateIndexFinder = function(dir) {
return function(array, predicate, context) {
predicate = cb(predicate, context);
var length = getLength(array);
var index = dir > 0 ? 0 : length - 1;
for (; index >= 0 && index < length; index += dir) {
if (predicate(array[index], index, array)) return index;
}
return -1;
};
};
这里没有太多特别的地方,当涉及到数组中的顺序处理的时候使用一个dir作为参数,我们已经多次见到了
.indexOf(array, value, [isSorted]) 和.lastIndexOf(array, value, [fromIndex])
例子:
_.indexOf([1, 2, 3], 2); // 1
_.lastIndexOf([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3], 2); // 4
源码:
_.indexOf = createIndexFinder(1, _.findIndex, _.sortedIndex);
_.lastIndexOf = createIndexFinder(-1, _.findLastIndex);
var createIndexFinder = function(dir, predicateFind, sortedIndex) {
return function(array, item, idx) { //被查找的数组,被查找的对象,开始位置
var i = 0, length = getLength(array);
if (typeof idx == 'number') {
if (dir > 0) {
i = idx >= 0 ? idx : Math.max(idx + length, i);
} else {
length = idx >= 0 ? Math.min(idx + 1, length) : idx + length + 1;
}
} else if (sortedIndex && idx && length) {
idx = sortedIndex(array, item);
return array[idx] === item ? idx : -1;
}
if (item !== item) {
idx = predicateFind(slice.call(array, i, length), _.isNaN);
return idx >= 0 ? idx + i : -1;
}
for (idx = dir > 0 ? i : length - 1; idx >= 0 && idx < length; idx += dir) {
if (array[idx] === item) return idx;
}
return -1;
};
};
range:
_.range = function(start, stop, step) {
if (stop == null) {
stop = start || 0;
start = 0;
}
if (!step) {
step = stop < start ? -1 : 1;
}
var length = Math.max(Math.ceil((stop - start) / step), 0);
var range = Array(length);
for (var idx = 0; idx < length; idx++, start += step) {
range[idx] = start;
}
return range;
};
这里,range方法允许接受任意个参数,注意只传一个参数的时候,我们认为该参数是stop而不是start,因此我们要进行参数换位,这种技巧在其他的库比如vue中也可以看到;
例子: TODO
该方法支持step为正负的情况,作者在在range数组添加元素的时候,是先指定了一个Array(length)这样一个长度为length的数组,根据网上的说法,知道数组的长度,用下标赋值比push要快;但是数组的长度更改耗时比较大。