机器学习:SVC实战+源码解读(支持向量机用于分类)
这部分只是对支持向量机sklearn库函数调用,参数解释,以及各个参数对测试结果的影响分析。个人认为入门机器学习实战的最快实例。
一.线性分类SVM
调用sklearn包中的LinearSVC
下面是调用的初始值:
def __init__(self, penalty='l2', loss='squared_hinge', dual=True, tol=1e-4,
C=1.0, multi_class='ovr', fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, class_weight=None, verbose=0,
random_state=None, max_iter=1000)其中参数如下:
C:一个浮点数,惩罚参数
Loss:字符串,表示损失函数,
‘hinge’:合页损失,标准SVM的损失函数;
‘squared_hinge’:合页损失的平方。
penalty:指定‘l1’或者'l2',惩罚项的范数,默认为‘l2’
dual: 布尔值,如果为true,则解决对偶问题;如果是false,则解决原始问题。当样本数大于特征数,倾向于false;
tol:指定终止迭代的阈值。
multi_class:指定多分类策略,
‘ovr’:采用one-vs-rest分类策略;默认
'crammer_singer':多类联合分类,很少用
fit_intercept:布尔值,如果为true,则计算截距,即决策函数中的常数项,否则,忽略截距。
class_weight:可以是一个字典,指定各个类的权重,若未提供,则认为类的权重为1;
其属性如下:
coef_:返回各个特征的权重。
intercept_:一个数组,决策函数的常数项
方法:
fit(x,y):训练模型
predict(x):用模型进行预测,返回预测值;
score(x,y):返回预测准确率
1.简单的线性可分支持向量机
from sklearn import svm, datasets,cross_validation
#加载鸢尾花数据集
def load_data_classfication():
iris=datasets.load_iris()
X_train=iris.data
y_train=iris.target
return cross_validation.train_test_split(X_train,y_train,test_size=0.25,random_state=0,stratify=y_train)
#使用svc分类器对其分类
def test_LinearSVC(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
cls=svm.LinearSVC()
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('Score:%.2f'% cls.score(X_test,y_test))
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept:%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)将鸢尾花数据分类三类,其中每一个样本都有四个特征,花萼的长宽,花瓣的长宽
Score:0.97
Coefficients:[[ 0.20959539 0.3992385 -0.81739225 -0.44231995]
[-0.12568317 -0.78049158 0.51754286 -1.0251776 ]
[-0.80282255 -0.87632578 1.21360546 1.80985929]],intercept:[ 0.1197369 2.02403826 -1.4441551 ]上面是检测结果,以及每个特征对于分类的影响
2.考察损失函数对于分类结果的影响
def test_LinearSVC_loss(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
losses=['hinge','squared_hinge']
for loss in losses:
cls=svm.LinearSVC(loss=loss)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print("loss:%s"%loss)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept %s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f' % cls.score(X_test, y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)结果:
loss:hinge
Coefficients:[[ 0.36636819 0.32163591 -1.07533939 -0.57004684]
[ 0.46789769 -1.55869702 0.39897097 -1.34402625]
[-1.21507089 -1.15278116 1.84779924 1.98442388]],intercept [ 0.18050217 1.36129524 -1.42624543]
Score:0.97
loss:squared_hinge
Coefficients:[[ 0.20959889 0.39924259 -0.8173887 -0.44231943]
[-0.12966115 -0.78597293 0.52178887 -1.02424942]
[-0.80322699 -0.87607737 1.21376071 1.81009443]],intercept [ 0.11973969 2.04293055 -1.44409524]
Score:0.97
3.惩罚项的系数对结果的影响,C衡量了误分类点的重要性,C越大则错误分类点越重要
def test_LinearSVC_C(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
Cs=np.logspace(-2,1)
train_score=[]
test_score=[]
for C in Cs:
cls=svm.LinearSVC(C=C)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_score.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_score.append(cls.score(X_test,y_test))
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.plot(Cs,train_score,label="Traing score")
ax.plot(Cs,test_score,label="test score")
ax.set_xlabel(r"C")
ax.set_ylabel(r"score")
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_title("LinearSVC")
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC_C(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
可以看出,C越小,错误分类点重要性低,误分类点较多,分类器性能较差。
二、非线性分类器
from sklearn import svm
svm.SVC()
#下面是初始化参数
def __init__(self, C=1.0, kernel='rbf', degree=3, gamma='auto',
coef0=0.0, shrinking=True, probability=False,
tol=1e-3, cache_size=200, class_weight=None,
verbose=False, max_iter=-1, decision_function_shape='ovr',
random_state=None):非线性分类器就是引入了核函数,将在原始空间中的特征映射到更高维度,用于分类
参数解释:
keral:指定核函数
'linear':线性核函数
'poly':多项式核函数
'rbf':高斯核函数
'sigmoid':S核函数
属性解释:
support_:一个数组,支持向量下标
support_vectors_:一个数组,支持向量
方法:
predict_log_proba(x):返回一个数组,数组元素依次是预测为各个类别的概率的对数值。
predict_proba(x):返回一个数组,数组的元素依次是预测为各个类别的概率值
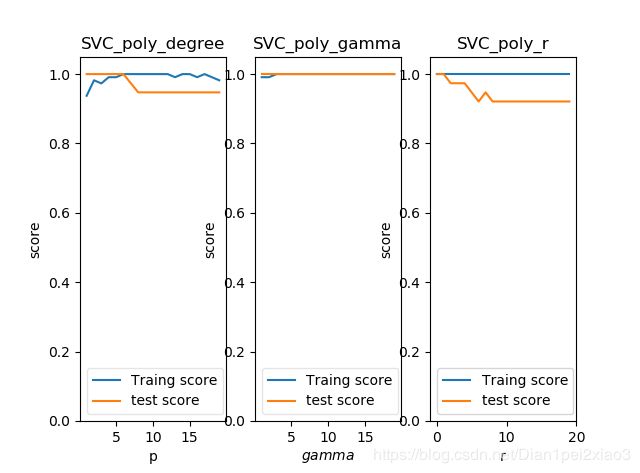
1.查看多项式中的参数如何影响测试结果
def test_SVC_poly(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig=plt.figure()
degrees=range(1,20)
train_score = []
test_score = []
for degree in degrees:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='poly',degree=degree)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_score.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_score.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 1)
ax.plot(degrees, train_score, label="Traing score")
ax.plot(degrees, test_score, label="test score")
ax.set_xlabel("p")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.set_title("SVC_poly_degree")
ax.legend(loc='best',framealpha=0.5)
##测试gamma
gammas=range(1,20)
train_score = []
test_score = []
for gamma in gammas:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='poly', gamma=gamma,degree=3)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_score.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_score.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 2)
ax.plot(degrees, train_score, label="Traing score")
ax.plot(degrees, test_score, label="test score")
ax.set_xlabel(r"$gamma$")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title("SVC_poly_gamma")
ax.legend(loc='best', framealpha=0.5)
###测试R
rs=range(0,20)
train_score = []
test_score = []
for r in rs:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='poly',gamma=10,degree=3,coef0=r)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_score.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_score.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 3)
ax.plot(rs, train_score, label="Traing score")
ax.plot(rs, test_score, label="test score")
ax.set_xlabel(r"r")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title("SVC_poly_r")
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classfication()
test_SVC_poly(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)2.高斯核函数的影响
def test_SVC_rbf(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
gammas = range(1, 20)
train_score = []
test_score = []
for gamma in gammas:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf', gamma=gamma)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_score.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_score.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
fig=plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.plot(gammas, train_score, label="Traing score")
ax.plot(gammas, test_score, label="test score")
ax.set_xlabel(r"$gammas$")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title("SVC_rbf")
ax.legend(loc='best', framealpha=0.5)
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classfication()
test_SVC_rbf(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
预测性能随gammas变化比较平稳。
参考书籍:
《Python大战机器学习》