python 画图 例子
Python画图主要用到matplotlib这个库。具体来说是pylab和pyplot这两个子库。这两个库可以满足基本的画图需求,而条形图,散点图等特殊图,下面再单独具体介绍。
首先给出pylab神器镇文:pylab.rcParams.update(params)。这个函数几乎可以调节图的一切属性,包括但不限于:坐标范围,axes标签字号大小,xtick,ytick标签字号,图线宽,legend字号等。
具体参数参看官方文档:http://matplotlib.org/users/customizing.html
首先给出一个Python3画图的例子。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
import
matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import
matplotlib.pylab as pylab
import
scipy.io
import
numpy as np
params
=
{
'axes.labelsize'
:
'35'
,
'xtick.labelsize'
:
'27'
,
'ytick.labelsize'
:
'27'
,
'lines.linewidth'
:
2
,
'legend.fontsize'
:
'27'
,
'figure.figsize'
:
'12, 9'
# set figure size
}
pylab.rcParams.update(params)
#set figure parameter
#line_styles=['ro-','b^-','gs-','ro--','b^--','gs--'] #set line style
#We give the coordinate date directly to give an example.
x1
=
[
-
20
,
-
15
,
-
10
,
-
5
,
0
,
0
,
5
,
10
,
15
,
20
]
y1
=
[
0
,
0.04
,
0.1
,
0.21
,
0.39
,
0.74
,
0.78
,
0.80
,
0.82
,
0.85
]
y2
=
[
0
,
0.014
,
0.03
,
0.16
,
0.37
,
0.78
,
0.81
,
0.83
,
0.86
,
0.92
]
y3
=
[
0
,
0.001
,
0.02
,
0.14
,
0.34
,
0.77
,
0.82
,
0.85
,
0.90
,
0.96
]
y4
=
[
0
,
0
,
0.02
,
0.12
,
0.32
,
0.77
,
0.83
,
0.87
,
0.93
,
0.98
]
y5
=
[
0
,
0
,
0.02
,
0.11
,
0.32
,
0.77
,
0.82
,
0.90
,
0.95
,
1
]
plt.plot(x1,y1,
'bo-'
,label
=
'm=2, p=10%'
,markersize
=
20
)
# in 'bo-', b is blue, o is O marker, - is solid line and so on
plt.plot(x1,y2,
'gv-'
,label
=
'm=4, p=10%'
,markersize
=
20
)
plt.plot(x1,y3,
'ys-'
,label
=
'm=6, p=10%'
,markersize
=
20
)
plt.plot(x1,y4,
'ch-'
,label
=
'm=8, p=10%'
,markersize
=
20
)
plt.plot(x1,y5,
'mD-'
,label
=
'm=10, p=10%'
,markersize
=
20
)
fig1
=
plt.figure(
1
)
axes
=
plt.subplot(
111
)
#axes = plt.gca()
axes.set_yticks([
0.1
,
0.2
,
0.3
,
0.4
,
0.5
,
0.6
,
0.7
,
0.8
,
0.9
,
1.0
])
axes.grid(
True
)
# add grid
plt.legend(loc
=
"lower right"
)
#set legend location
plt.ylabel(
'Percentage'
)
# set ystick label
plt.xlabel(
'Difference'
)
# set xstck label
plt.savefig(
'D:\\commonNeighbors_CDF_snapshots.eps'
,dpi
=
1000
,bbox_inches
=
'tight'
)
plt.show()
|
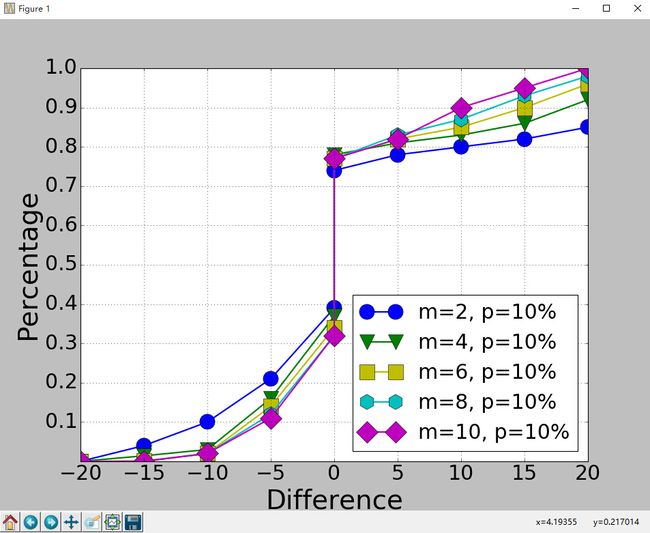
显示效果如下:
代码没什么好说的,这里只说一下plt.subplot(111)这个函数。
plt.subplot(111)和plt.subplot(1,1,1)是等价的。意思是将区域分成1行1列,当前画的是第一个图(排序由行至列)。
plt.subplot(211)意思就是将区域分成2行1列,当前画的是第一个图(第一行,第一列)。以此类推,只要不超过10,逗号就可省去。
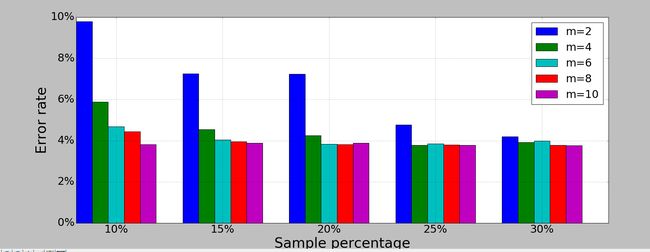
python画条形图。代码如下。
import scipy.io import numpy as np import matplotlib.pylab as pylab import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.ticker as mtick params={ 'axes.labelsize': '35', 'xtick.labelsize':'27', 'ytick.labelsize':'27', 'lines.linewidth':2 , 'legend.fontsize': '27', 'figure.figsize' : '24, 9' } pylab.rcParams.update(params) y1 = [9.79,7.25,7.24,4.78,4.20] y2 = [5.88,4.55,4.25,3.78,3.92] y3 = [4.69,4.04,3.84,3.85,4.0] y4 = [4.45,3.96,3.82,3.80,3.79] y5 = [3.82,3.89,3.89,3.78,3.77] ind = np.arange(5) # the x locations for the groups width = 0.15 plt.bar(ind,y1,width,color = 'blue',label = 'm=2') plt.bar(ind+width,y2,width,color = 'g',label = 'm=4') # ind+width adjusts the left start location of the bar. plt.bar(ind+2*width,y3,width,color = 'c',label = 'm=6') plt.bar(ind+3*width,y4,width,color = 'r',label = 'm=8') plt.bar(ind+4*width,y5,width,color = 'm',label = 'm=10') plt.xticks(np.arange(5) + 2.5*width, ('10%','15%','20%','25%','30%')) plt.xlabel('Sample percentage') plt.ylabel('Error rate') fmt = '%.0f%%' # Format you want the ticks, e.g. '40%' xticks = mtick.FormatStrFormatter(fmt) # Set the formatter axes = plt.gca() # get current axes axes.yaxis.set_major_formatter(xticks) # set % format to ystick. axes.grid(True) plt.legend(loc="upper right") plt.savefig('D:\\errorRate.eps', format='eps',dpi = 1000,bbox_inches='tight') plt.show()
结果如下:
画散点图,主要是scatter这个函数,其他类似。
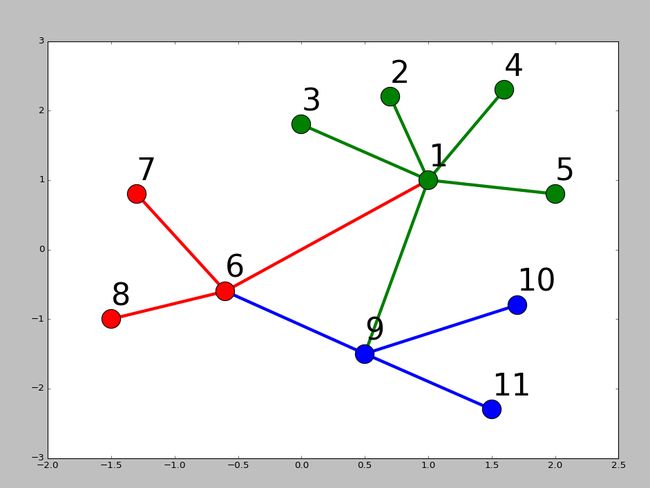
画网络图,要用到networkx这个库,下面给出一个实例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
import
networkx as nx
import
pylab as plt
g
=
nx.Graph()
g.add_edge(
1
,
2
,weight
=
4
)
g.add_edge(
1
,
3
,weight
=
7
)
g.add_edge(
1
,
4
,weight
=
8
)
g.add_edge(
1
,
5
,weight
=
3
)
g.add_edge(
1
,
9
,weight
=
3
)
g.add_edge(
1
,
6
,weight
=
6
)
g.add_edge(
6
,
7
,weight
=
7
)
g.add_edge(
6
,
8
,weight
=
7
)
g.add_edge(
6
,
9
,weight
=
6
)
g.add_edge(
9
,
10
,weight
=
7
)
g.add_edge(
9
,
11
,weight
=
6
)
fixed_pos
=
{
1
:(
1
,
1
),
2
:(
0.7
,
2.2
),
3
:(
0
,
1.8
),
4
:(
1.6
,
2.3
),
5
:(
2
,
0.8
),
6
:(
-
0.6
,
-
0.6
),
7
:(
-
1.3
,
0.8
),
8
:(
-
1.5
,
-
1
),
9
:(
0.5
,
-
1.5
),
10
:(
1.7
,
-
0.8
),
11
:(
1.5
,
-
2.3
)}
#set fixed layout location
#pos=nx.spring_layout(g) # or you can use other layout set in the module
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(g,pos
=
fixed_pos,nodelist
=
[
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
],
node_color
=
'g'
,node_size
=
600
)
nx.draw_networkx_edges(g,pos
=
fixed_pos,edgelist
=
[(
1
,
2
),(
1
,
3
),(
1
,
4
),(
1
,
5
),(
1
,
9
)],edge_color
=
'g'
,width
=
[
4.0
,
4.0
,
4.0
,
4.0
,
4.0
],label
=
[
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
],node_size
=
600
)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(g,pos
=
fixed_pos,nodelist
=
[
6
,
7
,
8
],
node_color
=
'r'
,node_size
=
600
)
nx.draw_networkx_edges(g,pos
=
fixed_pos,edgelist
=
[(
6
,
7
),(
6
,
8
),(
1
,
6
)],width
=
[
4.0
,
4.0
,
4.0
],edge_color
=
'r'
,node_size
=
600
)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(g,pos
=
fixed_pos,nodelist
=
[
9
,
10
,
11
],
node_color
=
'b'
,node_size
=
600
)
nx.draw_networkx_edges(g,pos
=
fixed_pos,edgelist
=
[(
6
,
9
),(
9
,
10
),(
9
,
11
)],width
=
[
4.0
,
4.0
,
4.0
],edge_color
=
'b'
,node_size
=
600
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
1
][
0
],fixed_pos[
1
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'1'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
2
][
0
],fixed_pos[
2
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'2'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
3
][
0
],fixed_pos[
3
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'3'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
4
][
0
],fixed_pos[
4
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'4'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
5
][
0
],fixed_pos[
5
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'5'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
6
][
0
],fixed_pos[
6
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'6'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
7
][
0
],fixed_pos[
7
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'7'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
8
][
0
],fixed_pos[
8
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'8'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
9
][
0
],fixed_pos[
9
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'9'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
10
][
0
],fixed_pos[
10
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'10'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.text(fixed_pos[
11
][
0
],fixed_pos[
11
][
1
]
+
0.2
, s
=
'11'
,fontsize
=
40
)
plt.show()
|
结果如下: