FPGA面试笔试专题——一些基础电路设计
1、全加器设计
全加器考虑进位输入与进位输出,以4位全加器为例:
module full_add(
input rst_n,
input clk,
input [3:0]a,
input [3:0]b,
input cin,
output reg [3:0]sum,
output reg cout
);
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
{cout,sum} <= 5'b0;
end
else
begin
{cout,sum} <= a+b+cin;
end
end
endmodule2、4选1数据选择器
按照组合逻辑实现,可以使用case语句(应注意case的语法):
module choose41(
input a1,
input a2,
input a3,
input a4,
input [1:0]sel,
output reg c
);
always@(*)
begin
case(sel)
2'b00:begin
c = a1;
end
2'b01:begin
c = a2;
end
2'b10:begin
c = a3;
end
2'b11:begin
c = a4;
end
default:begin
c = a1;
end
end3 、译码器
译码器将输入编码转换为对应输出,以3_8译码器为例:
module decode3_8(
input en,
input [2:0]code,
output reg[7:0]state,
);
always@(*)
begin
if(!en)
begin
state <= 8'd0;
end
else
begin
case(code)
3'b000:begin
state = 8'b0000_0001;
end
3'b001:begin
state = 8'b0000_0010;
end
3'b010:begin
state = 8'b0000_0100;
end
3'b011:begin
state = 8'b0000_1000;
end
3'b100:begin
state = 8'b0001_0000;
end
3'b101:begin
state = 8'b0010_0000;
end
3'b110:begin
state = 8'b0100_0000;
end
3'b111:begin
state = 8'b1000_0000;
end
default:begin
state = 8'b0000_0000;
end
endcase
end
end
endmodule4、计数器
计数器比较简单,此处重点在于回顾parameter的使用;设计一个模值任意的计数器;
module cnt
#(parameter W = 4,C = 2<<(W-1))
(
input clk,
input rst_n,
output reg[C-1:0]cnt
);
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
cnt <= W'd0;
end
else
begin
if(cnt==C-1)
begin
cnt <= W'd0;
end
else
begin
cnt <= cnt+1'b1;
end
end
end
endmodule5、模为60的BCD码计数器
BCD码计数器与普通2进制计数器不同,
module cntBCD_60(
input clk,
input rst_n,
output reg [7:0]cnt
);
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin
cnt <= 8'd0;
end
else
begin
if(cnt[3:0]==4'd9)
begin
cnt[3:0] <= 4'd0;
if(cnt[7:4]==4'd5)
begin
cnt[7:4] <= 4'd0;
end
else
begin
cnt[7:4] <= cnt[7:4]+1'b1;
end
end
else
begin
cnt[3:0] <= cnt[3:0]+1'b1;
end
end
end
endmodule6、两数乘法
乘法的本质就是移位,因此可以通过循环移位与求和实现,以8位数相乘为例:
module multy(
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
output [15:0]c
);
integer i;
always@(*)
begin
c = 16'd0;
for(i=0;i<8;i=i+1)
begin
if(a[i]) c = c + (a<应注意:
- 输出的位宽为输入之和
- for循环必须在always块中
- for()中为;而不是,
用repeat应该也能实现相同功能:
module multy(
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
output [15:0]c
);
integer i;
always@(*)
begin
c = 16'd0;
i = 0;
repeat(8)
begin
if(a[i]) c = c + (a<7、调用门元件实现4选1 MUX
调用门原件实现电路,实际上就是结构化描述电路(数据流、行为级抽象层次更高,不关心具体电路实现)
module Mux4_1(
input a,
input b,
input c,
input d,
input sel1,
input sel0,
output out
);
wire a1,b1,c1,d1;
wire sel1_n,sel0_n;
NOT (sel1_n,sel1);
NOT (sel0_n,sel0);
AND (a1,sel1_n,sel0_n,a);
AND (b1,sel1_n,sel0,b);
AND (c1,sel1,sel0_n,c);
AND (d1,sel1,sel0,d);
OR (out,a1,b1,c1,d1);
endmodule其行为级描述为:
assign out = (a & ~cont1 & ~cont2)| (b & ~cont1 & cont2)| (c & cont1 & ~cont2)| (d & cont1 & cont2);
8、环形计数器
环形计数器实际就是循环右移寄存器,因此N位环形计数器有N个状态(N位计数);
以8位环形计数器为例:
module hcnt(
input rst_n,
input clk,
output reg [7:0]out
);
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
out <= 8'd0;
else
out <= {out[0],out[7:1]};
end
endmodule9、扭环形计数器
环形计数器也是由循环右移寄存器构成,与环形计数器不同的是最低位取反后移到最高位,因此N位环形计数器有2N个状态(2N位计数);
以8位扭环形计数器为例:
module ncnt(
input rst_n,
input clk,
output reg [7:0]out
);
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
out <= 8'd0;
else
out <= {~out[0],out[7:1]};
end
endmodule10、使用一个二选一MUX和一个INV实现异或
由异或逻辑可以知道,out = ~a&b + a&~b;
即:a=0时,out = b;
a=1时,out = ~b;
因此电路可以设计为:
assign out = a?~b:b;其中,a作为MUX的选择信号,b与~b(INV实现)作为MUX输入。
11、利用4选1实现F(x,y,z)=xz+yz'
从真值表入手:
| xy=00 | xy=01 | xy=10 | xy=11 | |
| z=0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| z=1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
进一步化简:
| xy=00 | xy=01 | xy=10 | xy=11 | |
| out | 0 | ~z | z | 1 |
可以看出4选1实现逻辑:
always@(*)
begin
case({x,y})
2'b00:begin
out = 1'b0;
end
2'b01:begin
out = ~z;
end
2'b10:begin
out = z;
end
2'b11:begin
out = 1'b1;
end
default:begin
out = 1'b0;
end
endcase
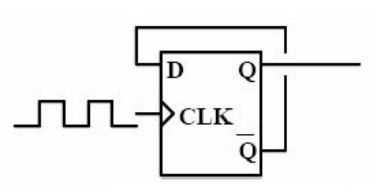
end12、利用D触发器实现2分频