openCV学习笔记(十一)-- 模板匹配,轮廓操作
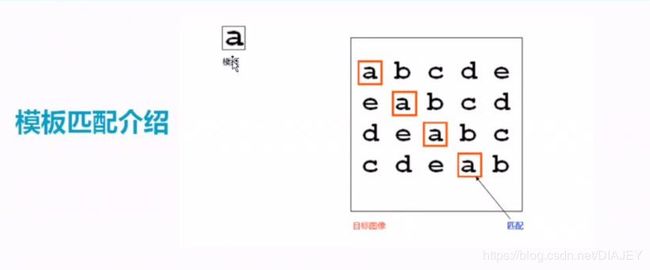
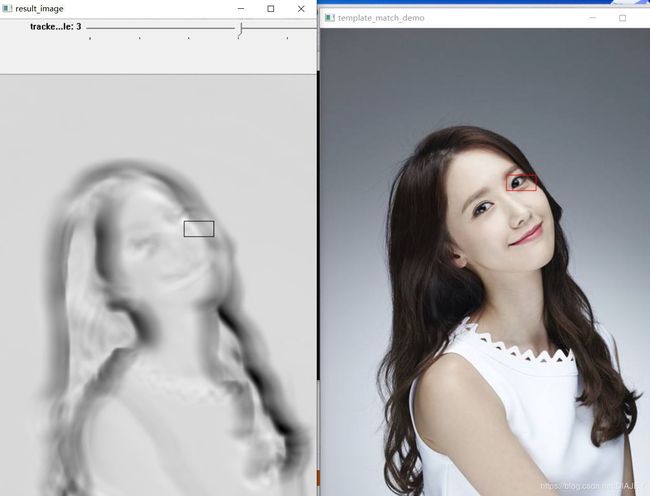
- 模板匹配
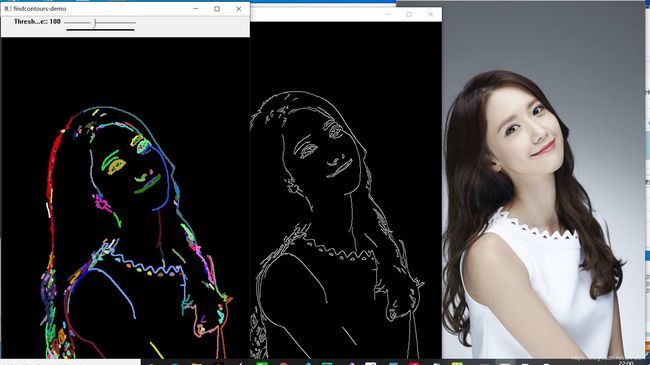
- 轮廓发现及绘制轮廓
- 凸包
- 轮廓周围绘制矩形或圆形
具体实现:
//模板匹配
#include#include效果:
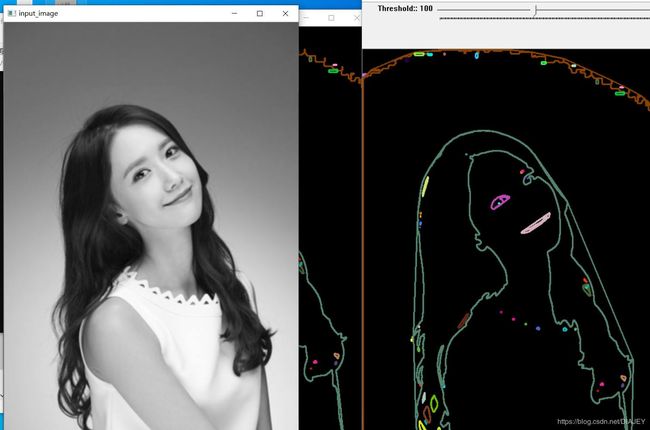
可以看见,凸包会将所有轮廓包围在内,大小轮廓都有对应的凸包
代码实现:
//凸包
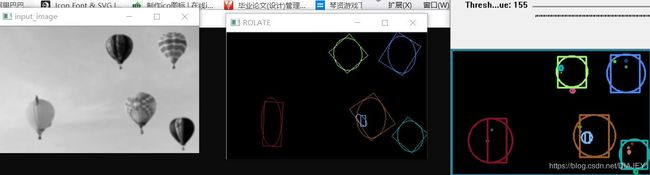
#include4. 轮廓周围绘制矩形或圆形
绘制矩形

什么是RDP算法?

对应就是设定最短距离,两点间最短距离小于最短距离的就要舍去中间点
openCV代码:
//绘制边缘矩形和圆形
#include