强化学习系列11:从统计学习到深度学习
1. 用深度学习计算V
在传统的无模型强化学习中,v/q值的计算是用统计方法进行的,可以理解为一种贝叶斯方法。伴随着如今深度学习的火热,使用深度学习去刻画V值是一个不错的方向。
2. 基本概念
其次介绍一些基本概念:
感知机(perceptron):具有单一线性层的网络称为感知机,相当于一个全连接层+0/1函数。如果全连接层的个数多于一层,那么叫做多层感知机。
激活函数:sigmoid、ReLU、hyperbolic tangent函数等。在keras中可以使用Activation(‘softmax’)的方式来定义。
随机丢弃:dropout指的是数据传递的时候随机丢弃一些值的处理方法,减少每一个神经元对其他神经元的依赖。可以单独定义为一个dropout层。
one-hot编码:keras.utils.np_utils的方法to_categorical函数可以将数值转为one-hot编码。
损失函数:常用的损失函数有:均方差MSE、二分类交叉熵、多分类交叉熵,用于优化模型
评估目标:评估目标包括准确率/查准率/查全率。用于评估最后的模型。训练完之后可以用model.evaluate进行评估。
优化器:一般使用各种梯度下降法(比如SGD、RMSprop、Adam)的优化器。以上三者可以在model.compile中进行定义。
训练:使用fit函数进行训练,一般需要定义epochs(训练轮数)和batch_size(训练的批大小)和validation_split(用于验证的数据比例)。训练轮数一般是训练集和测试集的准确率相等时停止。如果训练集准确率还低于测试集,则模型需要继续训练。
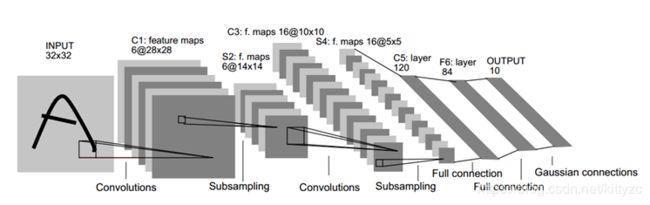
3. 卷积网络
在图像之类需要用到空间信息的地方,我们不能简单的把向量拉直,而是要用卷积网络CNN(convolutional neural network)做一下处理提取信息。
几个关键概念:
- 局部感受野:将相邻的输入神经元与下一层的单个隐藏神经元(称为局部感受野)连接,这样的操作叫做卷积
- 共享权重和偏差:学习与图像位置无关的特征。Conv2D(输出滤波器的维度、核、输入形状)
- 池化:对给定区域进行汇总,减小尺寸。比如keras.layers.pooling.MaxPooling2D(pool_size, strides)
生成图片的技巧:keras.preprocessing.image.ImageDataGenerator
获取中间特征:model.get_layer().output
下面看一下识别手写数字的简单例子:
# import the necessary packages
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.convolutional import Conv2D
from keras.layers.convolutional import MaxPooling2D
from keras.layers.core import Activation
from keras.layers.core import Flatten
from keras.layers.core import Dense
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.utils import np_utils
from keras.optimizers import SGD, RMSprop, Adam
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(1671) # for reproducibility
#define the convnet
class LeNet:
@staticmethod
def build(input_shape, classes):
model = Sequential()
# CONV => RELU => POOL
model.add(Conv2D(20, kernel_size=5, padding="same",
input_shape=input_shape))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)))
# CONV => RELU => POOL
model.add(Conv2D(50, kernel_size=5, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)))
# Flatten => RELU layers
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(500))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
# a softmax classifier
model.add(Dense(classes))
model.add(Activation("softmax"))
return model
# network and training
NB_EPOCH = 20
BATCH_SIZE = 128
VERBOSE = 1
OPTIMIZER = Adam()
VALIDATION_SPLIT=0.2
IMG_ROWS, IMG_COLS = 28, 28 # input image dimensions
NB_CLASSES = 10 # number of outputs = number of digits
INPUT_SHAPE = (1, IMG_ROWS, IMG_COLS)
# data: shuffled and split between train and test sets
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
K.set_image_dim_ordering("th")
# consider them as float and normalize
X_train = X_train.astype('float32')
X_test = X_test.astype('float32')
X_train /= 255
X_test /= 255
# we need a 60K x [1 x 28 x 28] shape as input to the CONVNET
X_train = X_train[:, np.newaxis, :, :]
X_test = X_test[:, np.newaxis, :, :]
print(X_train.shape[0], 'train samples')
print(X_test.shape[0], 'test samples')
# convert class vectors to binary class matrices
y_train = np_utils.to_categorical(y_train, NB_CLASSES)
y_test = np_utils.to_categorical(y_test, NB_CLASSES)
# initialize the optimizer and model
model = LeNet.build(input_shape=INPUT_SHAPE, classes=NB_CLASSES)
model.compile(loss="categorical_crossentropy", optimizer=OPTIMIZER,
metrics=["accuracy"])
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, epochs=NB_EPOCH,
verbose=VERBOSE, validation_split=VALIDATION_SPLIT)
score = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=VERBOSE)
print("\nTest score:", score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
# list all data in history
print(history.history.keys())
# summarize history for accuracy
plt.plot(history.history['acc'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_acc'])
plt.title('model accuracy')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['train', 'test'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
# summarize history for loss
plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])
plt.title('model loss')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['train', 'test'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
4. 生成对抗网络和WaveNet
生成对抗网络有两个神经网络,一个生成器G(generator),和一个判别器D(discriminator)。每次都先训练D使得判别损失最小,然后训练G使得生成损失最小。当固定生成网络 G 的时候,对于判别网络 D 的优化,可以这样理解:输入来自于真实数据,D 优化网络结构使自己输出 1,输入来自于生成数据,D 优化网络结构使自己输出 0;当固定判别网络 D 的时候,G 优化自己的网络使自己输出尽可能和真实数据一样的样本,并且使得生成的样本经过 D 的判别之后,D 输出高概率。
一般使用频率最高的都是DCGAN,对应的代码如下:
def generator_model():
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(input_dim=100, output_dim=1024))
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
model.add(Dense(128*7*7))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
model.add(Reshape((128, 7, 7), input_shape=(128*7*7,)))
model.add(UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Convolution2D(64, 5, 5, border_mode='same'))
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
model.add(UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Convolution2D(1, 5, 5, border_mode='same'))
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
return model
def discriminator_model():
model = Sequential()
model.add(Convolution2D(64, 5, 5,border_mode='same',input_shape=(1, 28, 28)))
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Convolution2D(128, 5, 5))
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1024))
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.add(Activation('sigmoid'))
return model