队列(Queue):与栈相对的一种数据结构, 集合(Collection)的一个子类。队列允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表,栈的特点是后进先出,而队列的特点是先进先出。队列的用处很大,比如实现消息队列。Queue 类关系图,如下图所示: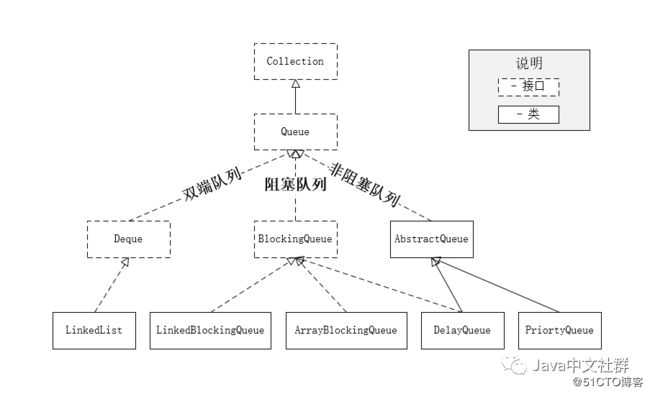
注:为了让读者更直观地理解,上图为精简版的 Queue 类关系图。本文如无特殊说明,内容都是基于 Java 1.8 版本。
队列(Queue)
1)Queue 分类
从上图可以看出 Queue 大体可分为以下三类。
- 双端队列:双端队列(Deque)是 Queue 的子类也是 Queue 的补充类,头部和尾部都支持元素插入和获取。
- 阻塞队列:阻塞队列指的是在元素操作时(添加或删除),如果没有成功,会阻塞等待执行。例如,当添加元素时,如果队列元素已满,队列会阻塞等待直到有空位时再插入。
- 非阻塞队列:非阻塞队列和阻塞队列相反,会直接返回操作的结果,而非阻塞等待。双端队列也属于非阻塞队列。
2)Queue 方法说明
Queue 常用方法,如下图所示: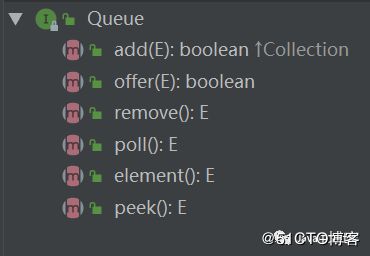
方法说明:
- add(E):添加元素到队列尾部,成功返回 true,队列超出时抛出异常;
- offer(E):添加元素到队列尾部,成功返回 true,队列超出时返回 false;
- remove():删除元素,成功返回 true,失败返回 false;
- poll():获取并移除此队列的第一个元素,若队列为空,则返回 null;
- peek():获取但不移除此队列的第一个元素,若队列为空,则返回 null;
- element():获取但不移除此队列的第一个元素,若队列为空,则抛异常。
3)Queue 使用实例Queue < String > linkedList =
new
LinkedList
<>();
linkedList
.
add
(
"Dog"
);
linkedList
.
add
(
"Camel"
);
linkedList
.
add
(
"Cat"
);
while
(!
linkedList
.
isEmpty
())
{
System
.
out
.
println
(
linkedList
.
poll
());
}
程序执行结果:
`Dog Camel Cat`
# 阻塞队列
**1)BlockingQueue**
BlockingQueue 在 java.util.concurrent 包下,其他阻塞类都实现自 BlockingQueue 接口,BlockingQueue 提供了线程安全的队列访问方式,当向队列中插入数据时,如果队列已满,线程则会阻塞等待队列中元素被取出后再插入;当从队列中取数据时,如果队列为空,则线程会阻塞等待队列中有新元素再获取。
**BlockingQueue 核心方法插入方法:**
* add(E):添加元素到队列尾部,成功返回 true,队列超出时抛出异常;
* offer(E):添加元素到队列尾部,成功返回 true,队列超出时返回 false ;
* put(E):将元素插入到队列的尾部,如果该队列已满,则一直阻塞。
**删除方法:**
* remove(Object):移除指定元素,成功返回 true,失败返回 false;
* poll(): 获取并移除队列的第一个元素,如果队列为空,则返回 null;
* take():获取并移除队列第一个元素,如果没有元素则一直阻塞。
**检查方法:**
* peek():获取但不移除队列的第一个元素,若队列为空,则返回 null。
**2)LinkedBlockingQueue**
LinkedBlockingQueue 是一个由链表实现的有界阻塞队列,容量默认值为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,也可以自定义容量,建议指定容量大小,默认大小在添加速度大于删除速度情况下有造成内存溢出的风险,LinkedBlockingQueue 是先进先出的方式存储元素。
**3)ArrayBlockingQueue**
ArrayBlockingQueue 是一个有边界的阻塞队列,它的内部实现是一个数组。它的容量是有限的,我们必须在其初始化的时候指定它的容量大小,容量大小一旦指定就不可改变。ArrayBlockingQueue 也是先进先出的方式存储数据,ArrayBlockingQueue 内部的阻塞队列是通过重入锁 ReenterLock 和 Condition 条件队列实现的,因此 ArrayBlockingQueue 中的元素存在公平访问与非公平访问的区别,对于公平访问队列,被阻塞的线程可以按照阻塞的先后顺序访问队列,即先阻塞的线程先访问队列。而非公平队列,当队列可用时,阻塞的线程将进入争夺访问资源的竞争中,也就是说谁先抢到谁就执行,没有固定的先后顺序。示例代码如下:
// 默认非公平阻塞队列
ArrayBlockingQueue
queue
new
ArrayBlockingQueue
(
6
);
// 公平阻塞队列
ArrayBlockingQueue
queue2
new
ArrayBlockingQueue
(
6
,
true
);
// ArrayBlockingQueue 源码展示
public
ArrayBlockingQueue
(
int
capacity
)
{
this
(
capacity
,
false
);
}
public
ArrayBlockingQueue
(
int
capacity
,
boolean
fair
)
{
if
(
capacity
<=
0)
throw
new
IllegalArgumentException
();
this
.
items
new
Object
[
capacity
];
lock
new
ReentrantLock
(
fair
);
notEmpty
lock
.
newCondition
();
notFull
lock
.
newCondition
();
}
**4)DelayQueue**
DelayQueue 是一个支持延时获取元素的***阻塞队列,队列中的元素必须实现 Delayed 接口,在创建元素时可以指定延迟时间,只有到达了延迟的时间之后,才能获取到该元素。实现了 Delayed 接口必须重写两个方法 ,getDelay(TimeUnit) 和 compareTo(Delayed),如下代码所示:
class
DelayElement
implements
Delayed
{
@Override
// 获取剩余时间
public
long
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
unit
)
{
// do something
}
@Override
// 队列里元素的排序依据
public
int
compareTo
(
Delayed
o
)
{
// do something
}
}
DelayQueue 使用的完整示例,请参考以下代码:
public
class
DelayTest
{
public
static
void
main
(
String
[]
args
)
throws
InterruptedException
{
DelayQueue
delayQueue
new
DelayQueue
();
delayQueue
.
put
(
new
DelayElement
(
1000
));
delayQueue
.
put
(
new
DelayElement
(
3000
));
delayQueue
.
put
(
new
DelayElement
(
5000
));
System
.
out
.
println
(
"开始时间:"
+
DateFormat
.
getDateTimeInstance
().
format
(
new
Date
()));
while
(!
delayQueue
.
isEmpty
()){
System
.
out
.
println
(
delayQueue
.
take
());
}
System
.
out
.
println
(
"结束时间:"
+
DateFormat
.
getDateTimeInstance
().
format
(
new
Date
()));
}
static
class
DelayElement
implements
Delayed
{
// 延迟截止时间(单面:毫秒)
long
delayTime
System
.
currentTimeMillis
();
public
DelayElement
(
long
delayTime
)
{
this
.
delayTime
(
this
.
delayTime
+
delayTime
);
}
@Override
// 获取剩余时间
public
long
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
unit
)
{
return
unit
.
convert
(
delayTime
System
.
currentTimeMillis
(),
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
);
}
@Override
// 队列里元素的排序依据
public
int
compareTo
(
Delayed
o
)
{
if
(
this
.
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
)
o
.
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
))
{
return
1
;
}
else
if
(
this
.
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
)
<
o
.
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
))
{
return
-
1
;
}
else
{
return
0;
}
}
@Override
public
String
toString
()
{
return
DateFormat
.
getDateTimeInstance
().
format
(
new
Date
(
delayTime
));
}
}
}
程序执行结果:
`开始时间:2019-6-13 20:40:38 2019-6-13 20:40:39 2019-6-13 20:40:41 2019-6-13 20:40:43 结束时间:2019-6-13 20:40:43`
# 非阻塞队列
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是一个基于链接节点的***线程安全队列,它采用先进先出的规则对节点进行排序,当我们添加一个元素的时候,它会添加到队列的尾部;当我们获取一个元素时,它会返回队列头部的元素。它的入队和出队操作均利用 CAS(Compare And Set)更新,这样允许多个线程并发执行,并且不会因为加锁而阻塞线程,使得并发性能更好。ConcurrentLinkedQueue 使用示例:
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
concurrentLinkedQueue
new
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
();
concurrentLinkedQueue
.
add
(
"Dog"
);
concurrentLinkedQueue
.
add
(
"Cat"
);
while
(!
concurrentLinkedQueue
.
isEmpty
())
{
System
.
out
.
println
(
concurrentLinkedQueue
.
poll
());
}
执行结果:
`Dog Cat`
可以看出不管是阻塞队列还是非阻塞队列,使用方法都是类似的,区别是底层的实现方式。
# 优先级队列
PriorityQueue 一个基于优先级堆的***优先级队列。优先级队列的元素按照其自然顺序进行排序,或者根据构造队列时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于所使用的构造方法。优先级队列不允许使用 null 元素。PriorityQueue 代码使用示例:
Queue
<
Integer
priorityQueue
new
PriorityQueue
(
new
Comparator
<
Integer
()
{
@Override
public
int
compare
(
Integer
o1
,
Integer
o2
)
{
// 非自然排序,数字倒序
return
o2
o1
;
}
});
priorityQueue
.
add
(
3
);
priorityQueue
.
add
(
1
);
priorityQueue
.
add
(
2
);
while
(!
priorityQueue
.
isEmpty
())
{
Integer
i
priorityQueue
.
poll
();
System
.
out
.
println
(
i
);
}
程序执行的结果是:
`3 2 1`
PriorityQueue 注意的点:
1. PriorityQueue 是非线程安全的,在多线程情况下可使用 PriorityBlockingQueue 类替代;
1. PriorityQueue 不允许插入 null 元素。
# 相关面试题
**1.ArrayBlockingQueue 和 LinkedBlockingQueue 的区别是什么?**
答:ArrayBlockingQueue 和 LinkedBlockingQueue 都实现自阻塞队列 BlockingQueue,它们的区别主要体现在以下几个方面:
* ArrayBlockingQueue 使用时必须指定容量值,LinkedBlockingQueue 可以不用指定;
* ArrayBlockingQueue 的最大容量值是使用时指定的,并且指定之后就不允许修改;而 LinkedBlockingQueue 最大的容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE;
* ArrayBlockingQueue 数据存储容器是采用数组存储的;而 LinkedBlockingQueue 采用的是 Node 节点存储的。
**2.LinkedList 中 add() 和 offer() 有什么关系?**
答:add() 和 offer() 都是添加元素到队列尾部。offer 方法是基于 add 方法实现的,Offer 的源码如下:
public
boolean
offer
(
E e
)
{
return
add
(
e
);
}
3.Queue 和 Deque 有什么区别?
答:Queue 属于一般队列,Deque 属于双端队列。一般队列是先进先出,也就是只有先进的才能先出;而双端队列则是两端都能插入和删除元素。
4.LinkedList 属于一般队列还是双端队列?
答:LinkedList 实现了 Deque 属于双端队列,因此拥有 addFirst(E)、addLast(E)、getFirst()、getLast() 等方法。
5.以下说法错误的是?
A:DelayQueue 内部是基于 PriorityQueue 实现的 B:PriorityBlockingQueue 不是先进先出的数据存储方式 C:LinkedBlockingQueue 容量是无限大的 D:ArrayBlockingQueue 内部的存储单元是数组,初始化时必须指定队列容量 答:C 题目解析:LinkedBlockingQueue 默认容量是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,并不是无限大的,源码如下图所示:

6.关于 ArrayBlockingQueue 说法不正确的是?
A:ArrayBlockingQueue 是线程安全的 B:ArrayBlockingQueue 元素允许为 null C:ArrayBlockingQueue 主要应用场景是“生产者-消费者”模型 D:ArrayBlockingQueue 必须显示地设置容量 答:B 题目解析:ArrayBlockingQueue 不允许元素为 null,如果添加一个 null 元素,会抛 NullPointerException 异常。
7.以下程序执行的结果是什么?PriorityQueue
priorityQueue
new
PriorityQueue
();
priorityQueue
.
add
(
null
);
System
.
out
.
println
(
priorityQueue
.
size
());
答:程序执行报错,PriorityQueue 不能插入 null。
8.Java 中常见的阻塞队列有哪些?
答:Java 中常见的阻塞队列如下:
* ArrayBlockingQueue,由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列;
* PriorityBlockingQueue,支持优先级排序的***阻塞队列;
* SynchronousQueue,是一个不存储元素的阻塞队列,会直接将任务交给消费者,必须等队列中的添加元素被消费后才能继续添加新的元素;
* LinkedBlockingQueue,由链表结构组成的阻塞队列;
* DelayQueue,支持延时获取元素的***阻塞队列。
9.有界队列和***队列有哪些区别?
答:有界队列和***队列的区别如下:
* 有界队列:有固定大小的队列叫做有界队列,比如:new ArrayBlockingQueue(6),6 就是队列的大小。
* ***队列:指的是没有设置固定大小的队列,这些队列的特点是可以直接入列,直到溢出。它们并不是真的***,它们最大值通常为 Integer.MAXVALUE,只是平常很少能用到这么大的容量(超过 Integer.MAXVALUE),因此从使用者的体验上,就相当于 “***”。
10.如何手动实现一个延迟消息队列?
答:说到延迟消息队列,我们应该可以第一时间想到要使用 DelayQueue 延迟队列来解决这个问题。实现思路,消息队列分为生产者和消费者,生产者用于增加消息,消费者用于获取并消费消息,我们只需要生产者把消息放入到 DelayQueue 队列并设置延迟时间,消费者循环使用 take() 阻塞获取消息即可。完整的实现代码如下:
public
class
CustomDelayQueue
{
// 消息编号
static
AtomicInteger
MESSAGENO
new
AtomicInteger
(
1
);
public
static
void
main
(
String
[]
args
)
throws
InterruptedException
{
DelayQueue
<
DelayedElement
delayQueue
new
DelayQueue
<>();
// 生产者1
producer
(
delayQueue
,
"生产者1"
);
// 生产者2
producer
(
delayQueue
,
"生产者2"
);
// 消费者
consumer
(
delayQueue
);
}
//生产者
private
static
void
producer
(
DelayQueue
<
DelayedElement
delayQueue
,
String
name
)
{
new
Thread
(
new
Runnable
()
{
@Override
public
void
run
()
{
while
(
true
)
{
// 产生 1~5 秒的随机数
long
time
1000L
*
(
new
Random
().
nextInt
(
5
)
+
1
);
try
{
Thread
.
sleep
(
time
);
}
catch
(
InterruptedException
e
)
{
e
.
printStackTrace
();
}
// 组合消息体
String
message
String
.
format
(
"%s,消息编号:%s 发送时间:%s 延迟:%s 秒"
,
name
,
MESSAGENO
.
getAndIncrement
(),
DateFormat
.
getDateTimeInstance
().
format
(
new
Date
()),
time
/
1000
);
// 生产消息
delayQueue
.
put
(
new
DelayedElement
(
message
,
time
));
}
}
}).
start
();
}
//消费者
private
static
void
consumer
(
DelayQueue
<
DelayedElement
delayQueue
)
{
new
Thread
(
new
Runnable
()
{
@Override
public
void
run
()
{
while
(
true
)
{
DelayedElement
element
null
;
try
{
// 消费消息
element
delayQueue
.
take
();
System
.
out
.
println
(
element
);
}
catch
(
InterruptedException
e
)
{
e
.
printStackTrace
();
}
}
}
}).
start
();
}
// 延迟队列对象
static
class
DelayedElement
implements
Delayed
{
// 过期时间(单位:毫秒)
long
time
System
.
currentTimeMillis
();
// 消息体
String
message
;
// 参数:delayTime 延迟时间(单位毫秒)
public
DelayedElement
(
String
message
,
long
delayTime
)
{
this
.
time
+=
delayTime
;
this
.
message
message
;
}
@Override
// 获取过期时间
public
long
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
unit
)
{
return
unit
.
convert
(
time
System
.
currentTimeMillis
(),
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
);
}
@Override
// 队列元素排序
public
int
compareTo
(
Delayed
o
)
{
if
(
this
.
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
)
o
.
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
))
return
1
;
else
if
(
this
.
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
)
<
o
.
getDelay
(
TimeUnit
.
MILLISECONDS
))
return
-
1
;
else
return
0;
}
@Override
public
String
toString
()
{
// 打印消息
return
message
+
" |执行时间:"
+
DateFormat
.
getDateTimeInstance
().
format
(
new
Date
());
}
}
}
以上程序支持多生产者,执行的结果如下:
`生产者1,消息编号:1 发送时间:2019-6-12 20:38:37 延迟:2 秒 |执行时间:2019-6-12 20:38:39 生产者2,消息编号:2 发送时间:2019-6-12 20:38:37 延迟:2 秒 |执行时间:2019-6-12 20:38:39 生产者1,消息编号:3 发送时间:2019-6-12 20:38:41 延迟:4 秒 |执行时间:2019-6-12 20:38:45 生产者1,消息编号:5 发送时间:2019-6-12 20:38:43 延迟:2 秒 |执行时间:2019-6-12 20:38:45 ......`
总结
队列(Queue)按照是否阻塞可分为:阻塞队列 BlockingQueue 和 非阻塞队列。其中,双端队列 Deque 也属于非阻塞队列,双端队列除了拥有队列的先进先出的方法之外,还拥有自己独有的方法,如 addFirst()、addLast()、getFirst()、getLast() 等,支持首未插入和删除元素。队列中比较常用的两个队列还有 PriorityQueue(优先级队列)和 DelayQueue(延迟队列),可使用延迟队列来实现延迟消息队列,这也是面试中比较常考的问题之一。需要面试朋友对延迟队列一定要做到心中有数,动手写一个消息队列也是非常有必要的。
本文来自:《Java面试全解析》

【END】
关注下方二维码,订阅更多精彩内容

老王著
转发更佳
喜欢作者