博主最近看了一下公司刚刚开发的微服务,准备入手从基本的过滤器以及拦截器开始剖析,以及在帮同学们分析一下上次的jetty过滤器源码与本次Springboot中tomcat中过滤器的区别。正题开始,拦截器顾名思义是进行拦截请求的一系列操作。先给大家示例一下使用操作
1 @Configuration 2 public class WebConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer { 3 4 @Override 5 public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { 6 registry.addInterceptor(new TstCfg()); 7 } 8 }
1 /** 2 * @title: TstCfg 3 * @Author junyu 4 * 旧巷里有一个穿着白衬衫笑起来如太阳般温暖我的少年。 5 * 记忆里有一个穿着连衣裙哭起来如孩子般讨人喜的女孩。 6 * 他说,哪年树弯了腰,人见了老,桃花落了白发梢,他讲的笑话她还会笑,那便是好。 7 * 她说,哪年国改了号,坟长了草,地府过了奈何桥,她回头看时他还在瞧,就不算糟。 8 * @Date: 2020/7/29 11:53 9 * @Version 1.0 10 */ 11 public class TstCfg extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter { 12 13 @Override 14 public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { 15 System.out.println("前"); 16 return super.preHandle(request, response, handler); 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { 21 System.out.println("后"); 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { 26 System.out.println("一直会出现"); 27 System.out.println(1/0); 28 } 29 }
首先我们可能会想到,我们的拦截器是何时装配到拦截器数组中
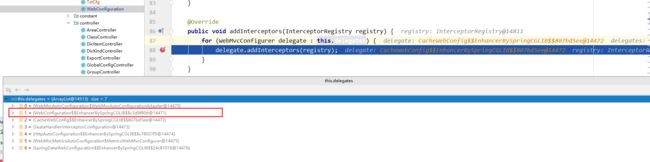
其实就是在springboot启动时执行doCreateBean时,进行调用创建的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$EnableWebMvcConfiguration会在这里放入进去所有实现了WebMvcConfigurer接口的类,一共有7个,其中就有我们自己实现了WebMvcConfigurer接口的WebConfiguration类,
我们的写的配置类WebConfiguration,继承了WebMvcConfigurer并重写了addInterceptors方法,所以我们的拦截器就在这时候装配进去了。这次知道为什么我们写的配置拦截器的配置示例需要继承------WebMvcConfigurer,我们当然也可以去继承已经实现了这个类的其他类,因为都可以去添加拦截器,博主亲试过,所以就不贴图了!
好了,拦截器已经添加完了,那什么时候调用我们拦截器呢?一步一步脚印来,当浏览器请求我们地址的 时候,分一下几步:
第一步:tomcat容器首先会接受到请求,这里将会走DispatcherServlet,看到这个大家都熟悉了。
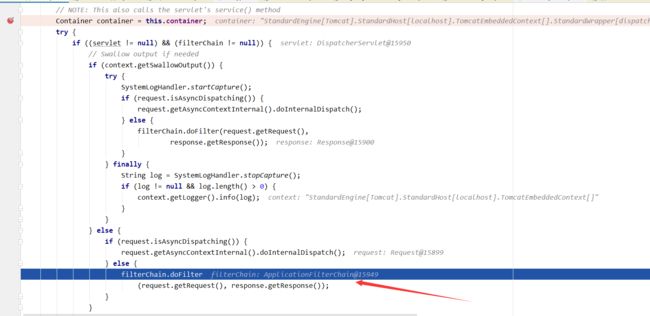
第二步:当然不会先走我们的拦截器了,我们的拦截器是在Springboot框架进行管理的,现在还在servlet,所以会先走到filter过滤器这一步,来贴图:官方代码太长,一屏截不下,前面有一个创建过滤器链的过程:等下次在给大家讲一下jetty的过滤器链与tomcat的过滤器链的区别
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
第三步:所以一旦连过滤器都没通过的话,会直接return回去,不会再进行拦截器的调用。来贴代码,过滤器通过后如何调用我们拦截器的
1 private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request, 2 ServletResponse response) 3 throws IOException, ServletException { 4 //这里将会调用所有过滤器链的过滤器,不做重点讲解了,看看下面拦截器的调用 5 // Call the next filter if there is one 6 if (pos < n) { 7 ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++]; 8 try { 9 Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter(); 10 11 if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase( 12 filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) { 13 request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE); 14 } 15 if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) { 16 final ServletRequest req = request; 17 final ServletResponse res = response; 18 Principal principal = 19 ((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal(); 20 21 Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res, this}; 22 SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege ("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal); 23 } else { 24 filter.doFilter(request, response, this); 25 } 26 } catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) { 27 throw e; 28 } catch (Throwable e) { 29 e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e); 30 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); 31 throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.filter"), e); 32 } 33 return; 34 } 35 36 // We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance 37 try { 38 if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) { 39 lastServicedRequest.set(request); 40 lastServicedResponse.set(response); 41 } 42 43 if (request.isAsyncSupported() && !servletSupportsAsync) { 44 request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, 45 Boolean.FALSE); 46 } 47 // Use potentially wrapped request from this point 48 if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) && 49 (response instanceof HttpServletResponse) && 50 Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) { 51 final ServletRequest req = request; 52 final ServletResponse res = response; 53 Principal principal = 54 ((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal(); 55 Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res}; 56 SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service", 57 servlet, 58 classTypeUsedInService, 59 args, 60 principal); 61 } else { 62 //过滤器终于完事了,现在终于开始正式调用我们的方法了,我们看看service方法做了什么吧! 63 servlet.service(request, response); 64 } 65 } catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) { 66 throw e; 67 } catch (Throwable e) { 68 e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e); 69 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); 70 throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.servlet"), e); 71 } finally { 72 if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) { 73 lastServicedRequest.set(null); 74 lastServicedResponse.set(null); 75 } 76 } 77 }
其实最终它会调用到DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法
1 protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; 3 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; 4 boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; 5 6 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); 7 8 try { 9 ModelAndView mv = null; 10 Exception dispatchException = null; 11 12 try { 13 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); 14 multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); 15 16 // Determine handler for the current request. 17 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); 18 if (mappedHandler == null) { 19 noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); 20 return; 21 } 22 23 // Determine handler adapter for the current request. 24 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); 25 26 // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. 27 String method = request.getMethod(); 28 boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); 29 if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { 30 long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 31 if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { 32 return; 33 } 34 } 35 //所有拦截器开始在调用方法前拦截,如果你拦截器中返回false,则直接return不会再调用该方法!下面有源代码 36 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { 37 return; 38 } 39 40 // Actually invoke the handler. 41 //底层进行invoke反射,调用当前请求的方法,不用再往里面看了 42 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 43 44 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 45 return; 46 } 47 48 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); 49 //调用拦截器的postHandle,下面有源代码 50 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); 51 } 52 catch (Exception ex) { 53 dispatchException = ex; 54 } 55 catch (Throwable err) { 56 // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, 57 // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. 58 dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); 59 } 60 //该方法中多做了一些逻辑,其实最后也调用了triggerAfterCompletion方法,最终调用拦截器方法的afterCompletion方法 61 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); 62 } 63 catch (Exception ex) { 64 //所以不管是否出现异常,拦截器方法的afterCompletion方法是一定会调用的! 65 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); 66 } 67 catch (Throwable err) { 68 //所以不管是否出现异常,拦截器方法的afterCompletion方法是一定会调用的! 69 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, 70 new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); 71 } 72 finally { 73 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 74 // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion 75 if (mappedHandler != null) { 76 mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); 77 } 78 } 79 else { 80 // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. 81 if (multipartRequestParsed) { 82 cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 }
现在终于开始了我们拦截器的方法了,一个一个来:
1 boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); 3 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { 4 for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) { 5 HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; 6 //调用所有拦截器的preHandle方法 7 if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) { 8 //就算preHandle方法没有通过,仍然会调用这个triggerAfterCompletion方法。 9 triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); 10 return false; 11 } 12 this.interceptorIndex = i; 13 } 14 } 15 return true; 16 }
1 void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv) 2 throws Exception { 3 4 HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); 5 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { 6 for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 7 HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; 8 //调用拦截器的postHandle方法, 9 interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv); 10 } 11 } 12 }
1 void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Exception ex) 2 throws Exception { 3 4 HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); 5 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { 6 for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) { 7 HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; 8 try { 9 //调用拦截器的afterCompletion方法,不管是否异常都会进行调用,但是如果该方法报异常,会被抓住。 10 //不会影响程序正常运行,只会打印出来 11 interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex); 12 } 13 catch (Throwable ex2) { 14 logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 }
下面这个就是打印了一下,但是不会影响我们的请求响应回去:
还是会正常响应回客户端:
好了,到此拦截器的实现以及源码分析流程到此结束,本来想给大家从Springboot的reflash方法开始解析拦截器,但是内容太多了,不仅跑题而且博主也一时半会给大家无法讲解明白。