Android studio中TextView改变字体的两种方式(如仿宋、隶书)
在Android中系统默认的字体有三种,通过在TextView中加上android:typeface=”sans”来改变,而sans就是三种当中的其中的一种,还有两种分别是“monospace”和“serif”;当我们不想用着三种方式的话还可以使用外在的字体—–导入字体文件
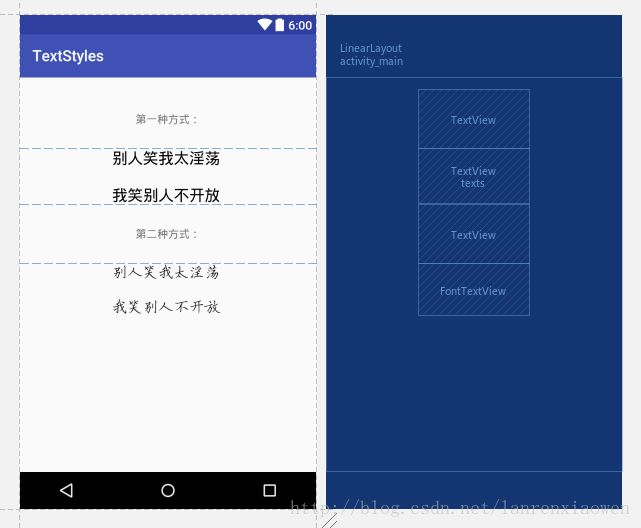
使用外在字体的方式有很多,下面简单分享一下使用外在字体其中的两种方式,效果图:

第一种方式:在代码中定义TextView的字体
步骤:
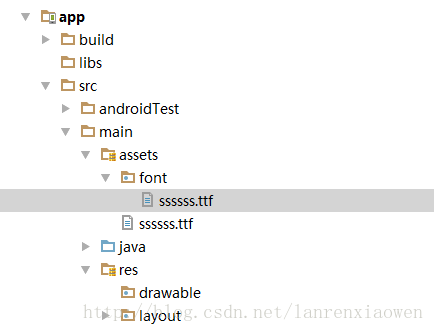
1、我们首先在src/main文件下创建assets文件夹,为了规范起见,我们再在assets文件夹下创建font文件夹,然后将我们的字体文件(*.ttf)放进fonts文件夹下,如图所示:
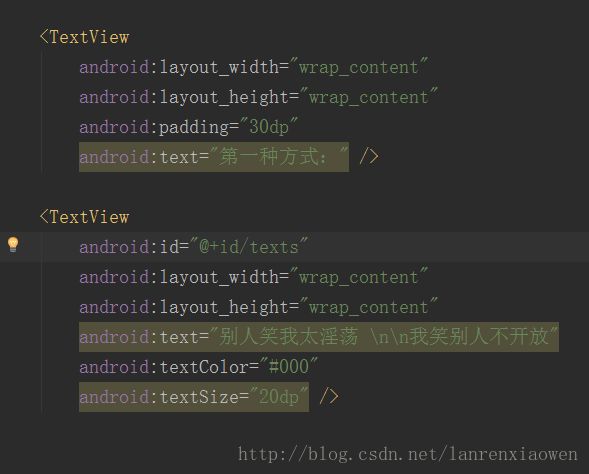
2、在我们的布局文件中做准备工作,拖入一个TextView控件
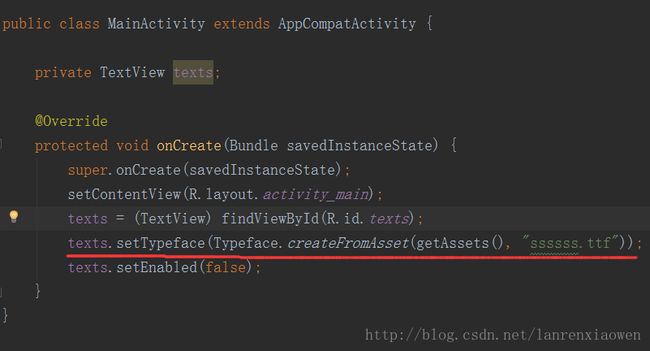
3、在代码中找到我们导进来的字体并在TextView上使用
第二种方式:写一个类继承TextView,所有的东西都放入到这个类里面,在要用到换字体的地方就使用这个类
步骤:
1,新建一个类,让这个类继承TextView
/**
* 1.version:
* 2.date:2017/1/13 15:26
* 3.update:2017/1/13.
* 4.autour:张玉杰
*/
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.TextView;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2015/10/27.
*/
public class FontTextView extends TextView {
/** The file name of the font data in the assets directory*/
private String mFontPath = null;
public FontTextView(Context context) {
super(context);
init(context, null, 0);
}
public FontTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context, attrs, 0);
}
public FontTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public String getFontPath() {
return mFontPath;
}
/**
* Set font file fontPath
* @param fontPath The file name of the font data in the assets directory
*/
public void setFontPath(String fontPath) {
mFontPath = fontPath;
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(mFontPath)) {
FontUtils.getInstance().replaceFontFromAsset(this, mFontPath);
}
}
private void init(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.FontTextView, defStyleAttr, 0);
mFontPath = typedArray.getString(R.styleable.FontTextView_font_path);
typedArray.recycle();
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(mFontPath)) {
FontUtils.getInstance().replaceFontFromAsset(this, mFontPath);
}
}
}2、在写一个类用来选择字体
/**
* 1.version:
* 2.date:2017/1/13 15:27
* 3.update:2017/1/13.
* 4.autour:张玉杰
*/
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Typeface;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.lang.ref.SoftReference;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class FontUtils {
private static final String TAG = FontUtils.class.getSimpleName();
private Map> mCache = new HashMap<>();
private static FontUtils sSingleton = null;
public static Typeface DEFAULT = Typeface.DEFAULT;
// disable instantiate
private FontUtils() {
}
public static FontUtils getInstance() {
// double check
if (sSingleton == null) {
synchronized (FontUtils.class) {
if (sSingleton == null) {
sSingleton = new FontUtils();
}
}
}
return sSingleton;
}
public void replaceFontFromAsset(@NonNull View root, @NonNull String fontPath) {
replaceFont(root, createTypefaceFromAsset(root.getContext(), fontPath));
}
public void replaceFontFromAsset(@NonNull View root, @NonNull String fontPath, int style) {
replaceFont(root, createTypefaceFromAsset(root.getContext(), fontPath), style);
}
public void replaceFontFromFile(@NonNull View root, @NonNull String fontPath) {
replaceFont(root, createTypefaceFromFile(fontPath));
}
public void replaceFontFromFile(@NonNull View root, @NonNull String fontPath, int style) {
replaceFont(root, createTypefaceFromFile(fontPath), style);
}
private void replaceFont(@NonNull View root, @NonNull Typeface typeface) {
if (root == null || typeface == null) {
return;
}
if (root instanceof TextView) { // If view is TextView or it's subclass, replace it's font
TextView textView = (TextView) root;
// Extract previous style of TextView
int style = Typeface.NORMAL;
if (textView.getTypeface() != null) {
style = textView.getTypeface().getStyle();
}
textView.setTypeface(typeface, style);
} else if (root instanceof ViewGroup) { // If view is ViewGroup, apply this method on it's child views
ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) root;
for (int i = 0; i < viewGroup.getChildCount(); ++i) {
replaceFont(viewGroup.getChildAt(i), typeface);
}
} // else return
}
private void replaceFont(@NonNull View root, @NonNull Typeface typeface, int style) {
if (root == null || typeface == null) {
return;
}
if (style < 0 || style > 3) {
style = Typeface.NORMAL;
}
if (root instanceof TextView) { // If view is TextView or it's subclass, replace it's font
TextView textView = (TextView) root;
textView.setTypeface(typeface, style);
} else if (root instanceof ViewGroup) { // If view is ViewGroup, apply this method on it's child views
ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) root;
for (int i = 0; i < viewGroup.getChildCount(); ++i) {
replaceFont(viewGroup.getChildAt(i), typeface, style);
}
} // else return
}
private Typeface createTypefaceFromAsset(Context context, String fontPath) {
SoftReference typefaceRef = mCache.get(fontPath);
Typeface typeface = null;
if (typefaceRef == null || (typeface = typefaceRef.get()) == null) {
typeface = Typeface.createFromAsset(context.getAssets(), fontPath);
typefaceRef = new SoftReference<>(typeface);
mCache.put(fontPath, typefaceRef);
}
return typeface;
}
private Typeface createTypefaceFromFile(String fontPath) {
SoftReference typefaceRef = mCache.get(fontPath);
Typeface typeface = null;
if (typefaceRef == null || (typeface = typefaceRef.get()) == null) {
typeface = Typeface.createFromFile(fontPath);
typefaceRef = new SoftReference<>(typeface);
mCache.put(fontPath, typefaceRef);
}
return typeface;
}
public void replaceSystemDefaultFontFromAsset(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull String fontPath) {
replaceSystemDefaultFont(createTypefaceFromAsset(context, fontPath));
}
public void replaceSystemDefaultFontFromFile(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull String fontPath) {
replaceSystemDefaultFont(createTypefaceFromFile(fontPath));
}
private void replaceSystemDefaultFont(@NonNull Typeface typeface) {
modifyObjectField(null, "MONOSPACE", typeface);
}
private void modifyObjectField(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) {
try {
Field defaultField = Typeface.class.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
defaultField.setAccessible(true);
defaultField.set(obj, value);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3、在布局文件里面直接用上类的全类名,这样在实时视图里面就能看到效果

项目地址:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/lanrenxiaowen/9737027