android Adapter原理解析
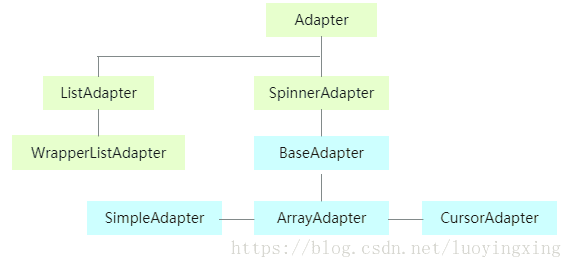
2、Adapter的实现原理其实就是一个观察者模式的应用。先上一幅简图:

3、首先看观察者抽象类:DataSetObserver,它有两个方法onChange()和onInvalidated(),源码:
public abstract class DataSetObserver {
/**
* This method is called when the entire data set has changed,
* most likely through a call to {@link Cursor#requery()} on a {@link Cursor}.
*/
public void onChanged() {
// Do nothing
}
/**
* This method is called when the entire data becomes invalid,
* most likely through a call to {@link Cursor#deactivate()} or {@link Cursor#close()} on a
* {@link Cursor}.
*/
public void onInvalidated() {
// Do nothing
}
}4、被观察者抽象类Observable,提供了注册观察者、注销观察者和清空观察者的方法。
public abstract class Observable<T> {
/**
* The list of observers. An observer can be in the list at most
* once and will never be null.
*/
protected final ArrayList mObservers = new ArrayList();
/**
* Adds an observer to the list. The observer cannot be null and it must not already
* be registered.
* @param observer the observer to register
* @throws IllegalArgumentException the observer is null
* @throws IllegalStateException the observer is already registered
*/
public void registerObserver(T observer) {
if (observer == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The observer is null.");
}
synchronized(mObservers) {
if (mObservers.contains(observer)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Observer " + observer + " is already registered.");
}
mObservers.add(observer);
}
}
/**
* Removes a previously registered observer. The observer must not be null and it
* must already have been registered.
* @param observer the observer to unregister
* @throws IllegalArgumentException the observer is null
* @throws IllegalStateException the observer is not yet registered
*/
public void unregisterObserver(T observer) {
if (observer == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The observer is null.");
}
synchronized(mObservers) {
int index = mObservers.indexOf(observer);
if (index == -1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Observer " + observer + " was not registered.");
}
mObservers.remove(index);
}
}
/**
* Remove all registered observers.
*/
public void unregisterAll() {
synchronized(mObservers) {
mObservers.clear();
}
}
} 该抽象类有一个继承类DataSetObservable,新增了两个方法,notifyChanged()和notifyInvalidated()用来提醒观察者更新操作。
public class DataSetObservable extends Observable<DataSetObserver> {
/**
* Invokes {@link DataSetObserver#onChanged} on each observer.
* Called when the contents of the data set have changed. The recipient
* will obtain the new contents the next time it queries the data set.
*/
public void notifyChanged() {
synchronized(mObservers) {
// since onChanged() is implemented by the app, it could do anything, including
// removing itself from {@link mObservers} - and that could cause problems if
// an iterator is used on the ArrayList {@link mObservers}.
// to avoid such problems, just march thru the list in the reverse order.
for (int i = mObservers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
mObservers.get(i).onChanged();
}
}
}
/**
* Invokes {@link DataSetObserver#onInvalidated} on each observer.
* Called when the data set is no longer valid and cannot be queried again,
* such as when the data set has been closed.
*/
public void notifyInvalidated() {
synchronized (mObservers) {
for (int i = mObservers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
mObservers.get(i).onInvalidated();
}
}
}
}5、Adapter基类的部分代码:
public interface Adapter {
/**
* Register an observer that is called when changes happen to the data used by this adapter.
*
* @param observer the object that gets notified when the data set changes.
*/
void registerDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver observer);
/**
* Unregister an observer that has previously been registered with this
* adapter via {@link #registerDataSetObserver}.
*
* @param observer the object to unregister.
*/
void unregisterDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver observer);
}可以看到有注册观察者和注销观察者的方法。
6、来看一下BaseAdapter的部分代码:
public abstract class BaseAdapter implements ListAdapter, SpinnerAdapter {
private final DataSetObservable mDataSetObservable = new DataSetObservable();
public void registerDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver observer) {
mDataSetObservable.registerObserver(observer);
}
public void unregisterDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver observer) {
mDataSetObservable.unregisterObserver(observer);
}
/**
* Notifies the attached observers that the underlying data has been changed
* and any View reflecting the data set should refresh itself.
*/
public void notifyDataSetChanged() {
mDataSetObservable.notifyChanged();
}
/**
* Notifies the attached observers that the underlying data is no longer valid
* or available. Once invoked this adapter is no longer valid and should
* not report further data set changes.
*/
public void notifyDataSetInvalidated() {
mDataSetObservable.notifyInvalidated();
}
}
可以看到,内部有个被观察者变量DataSetObservable,注册和注销观察者的方法,还有我们熟悉的notifyDataSetChanged()和notifyDataSetInvalidated()方法。我们通过ListView.setAdapter(Adapter adapter)来设置适配器,该适配器则通过notifyDataSetChanged()和notifyDataSetInvalidated()方法来通知被观察者调用相应的notifyChanged()和notifyInvalidated()去做更新操作。
7、附上ListView.setAdapter()的代码:
@Override
public void setAdapter(ListAdapter adapter) {
if (mAdapter != null && mDataSetObserver != null) {
mAdapter.unregisterDataSetObserver(mDataSetObserver);
}
resetList();
mRecycler.clear();
if (mHeaderViewInfos.size() > 0|| mFooterViewInfos.size() > 0) {
mAdapter = new HeaderViewListAdapter(mHeaderViewInfos, mFooterViewInfos, adapter);
} else {
mAdapter = adapter;
}
mOldSelectedPosition = INVALID_POSITION;
mOldSelectedRowId = INVALID_ROW_ID;
// AbsListView#setAdapter will update choice mode states.
super.setAdapter(adapter);
if (mAdapter != null) {
mAreAllItemsSelectable = mAdapter.areAllItemsEnabled();
mOldItemCount = mItemCount;
mItemCount = mAdapter.getCount();
checkFocus();
mDataSetObserver = new AdapterDataSetObserver();
mAdapter.registerDataSetObserver(mDataSetObserver);
mRecycler.setViewTypeCount(mAdapter.getViewTypeCount());
int position;
if (mStackFromBottom) {
position = lookForSelectablePosition(mItemCount - 1, false);
} else {
position = lookForSelectablePosition(0, true);
}
setSelectedPositionInt(position);
setNextSelectedPositionInt(position);
if (mItemCount == 0) {
// Nothing selected
checkSelectionChanged();
}
} else {
mAreAllItemsSelectable = true;
checkFocus();
// Nothing selected
checkSelectionChanged();
}
requestLayout();
}注意到下面两句:
mDataSetObserver = new AdapterDataSetObserver();
mAdapter.registerDataSetObserver(mDataSetObserver);
这个观察者是重新实例化了一个AdapterDataSetObserver类的对象,AdapterDataSetObserver类是AbsListView的一个内部类。
class AdapterDataSetObserver extends AdapterView<ListAdapter>.AdapterDataSetObserver {
@Override
public void onChanged() {
super.onChanged();
if (mFastScroll != null) {
mFastScroll.onSectionsChanged();
}
}
@Override
public void onInvalidated() {
super.onInvalidated();
if (mFastScroll != null) {
mFastScroll.onSectionsChanged();
}
}
}可以看到,更新时,又调用了父类的方法,来看看父类在更新时具体的操作。AdapterDataSetObserver类是AdapterView的一个内部类:
class AdapterDataSetObserver extends DataSetObserver {
private Parcelable mInstanceState = null;
@Override
public void onChanged() {
mDataChanged = true;
mOldItemCount = mItemCount;
mItemCount = getAdapter().getCount();
// Detect the case where a cursor that was previously invalidated has
// been repopulated with new data.
if (AdapterView.this.getAdapter().hasStableIds() && mInstanceState != null
&& mOldItemCount == 0 && mItemCount > 0) {
AdapterView.this.onRestoreInstanceState(mInstanceState);
mInstanceState = null;
} else {
rememberSyncState();
}
checkFocus();
requestLayout();
}
@Override
public void onInvalidated() {
mDataChanged = true;
if (AdapterView.this.getAdapter().hasStableIds()) {
// Remember the current state for the case where our hosting activity is being
// stopped and later restarted
mInstanceState = AdapterView.this.onSaveInstanceState();
}
// Data is invalid so we should reset our state
mOldItemCount = mItemCount;
mItemCount = 0;
mSelectedPosition = INVALID_POSITION;
mSelectedRowId = INVALID_ROW_ID;
mNextSelectedPosition = INVALID_POSITION;
mNextSelectedRowId = INVALID_ROW_ID;
mNeedSync = false;
checkFocus();
requestLayout();
}
public void clearSavedState() {
mInstanceState = null;
}
}可以看到,最后是调用了 requestLayout()来更新界面以达到更新数据的目的。
8、最后,Adapter和ListView是怎样实现数据更新的呢,平时我们是通过getView()来返回一个item的view给ListView,但是又在何时调用呢,首先来查看一下ListView的onMeasure()源码:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// Sets up mListPadding
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int childWidth = 0;
int childHeight = 0;
int childState = 0;
mItemCount = mAdapter == null ? 0 : mAdapter.getCount();
if (mItemCount > 0 && (widthMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED
|| heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)) {
final View child = obtainView(0, mIsScrap);
// Lay out child directly against the parent measure spec so that
// we can obtain exected minimum width and height.
measureScrapChild(child, 0, widthMeasureSpec, heightSize);
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (recycleOnMeasure() && mRecycler.shouldRecycleViewType(
((LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).viewType)) {
mRecycler.addScrapView(child, 0);
}
}
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
widthSize = mListPadding.left + mListPadding.right + childWidth +
getVerticalScrollbarWidth();
} else {
widthSize |= (childState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
heightSize = mListPadding.top + mListPadding.bottom + childHeight +
getVerticalFadingEdgeLength() * 2;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// TODO: after first layout we should maybe start at the first visible position, not 0
heightSize = measureHeightOfChildren(widthMeasureSpec, 0, NO_POSITION, heightSize, -1);
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
mWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
}可以注意到final View child = obtainView(0, mIsScrap);查看一下obtainView()这个方法的部分源码,这个方法在AbsListView类里面:
View obtainView(int position, boolean[] isScrap) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "obtainView");
isScrap[0] = false;
// Check whether we have a transient state view. Attempt to re-bind the
// data and discard the view if we fail.
final View transientView = mRecycler.getTransientStateView(position);
if (transientView != null) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) transientView.getLayoutParams();
// If the view type hasn't changed, attempt to re-bind the data.
if (params.viewType == mAdapter.getItemViewType(position)) {
final View updatedView = mAdapter.getView(position, transientView, this);
// If we failed to re-bind the data, scrap the obtained view.
if (updatedView != transientView) {
setItemViewLayoutParams(updatedView, position);
mRecycler.addScrapView(updatedView, position);
}
}
isScrap[0] = true;
// Finish the temporary detach started in addScrapView().
transientView.dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach();
return transientView;
}
}注意到final View updatedView = mAdapter.getView(position, transientView, this);这句话,我们的getView()就是在这里被调用的。
综上所述,Adapter的大概原理基本就是这样实现的。