Android系统启动之Zygote
前段时间在看Android9.0的PackageManagerService的源码,看着看着就在想PackageManagerService是如何被启动的,发现它是被SystemServer启动的,然后就又想SystemServer又是怎么被创建的呢,就一步步跟代码,发现SystemServer是从zygote进程fork出来的,想把最近了解的内容总结下,于是就有了这篇文章(如果再跟下去你会发现zygote又是从init进程fork出来的)
zygote 是什么
简单地说,它是一个进程。如果稍微再详细点的话,它是孵化其他Android应用进程的进程。
zygote进程如何被创建的
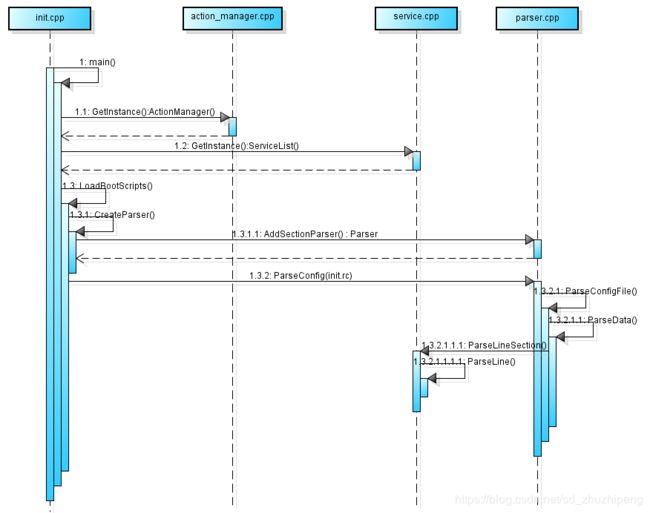
前面我们知道zygote进程能孵化其他Android进程,那么zygote进程又是由谁孵化的呢?我们知道Android是基于Linux内核,而Linux的第一个用户级进程为init进程(PID等于1),所以很容易联想到zygote进程很有可能就是init进程孵化出来的,实际上也确实如此。下面我们就看下zygote孵化的过程,过程主要包括:
- init 进程解析init.rc文件
- zygote孵化
init进程解析
system/core/init/init.cpp
system/core/init/init.h
system/core/init/action_manager.h
system/core/init/action_manager.cpp
system/core/init/service.h
system/core/init/service.cpp
system/core/init/parser.h
system/core/init/parser.cpp
下面就是init进程解析init.rc文件时与zygote相关的过程:
//system/core/init/init.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//省略部分无关代码......
const BuiltinFunctionMap function_map;
Action::set_function_map(&function_map);
subcontexts = InitializeSubcontexts();
ActionManager& am = ActionManager::GetInstance();
ServiceList& sm = ServiceList::GetInstance();
//开始解析初始化脚本文件
LoadBootScripts(am, sm);
// Turning this on and letting the INFO logging be discarded adds 0.2s to
// Nexus 9 boot time, so it's disabled by default.
if (false) DumpState();
//省略部分无关代码......
return 0;
}
static void LoadBootScripts(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
//创建不通的解析器,包括ActionParser、ImportParser和ServiceParser
Parser parser = CreateParser(action_manager, service_list);
//判断是否有配置ro.boot.init_rc属性
std::string bootscript = GetProperty("ro.boot.init_rc", "");
if (bootscript.empty()) {
//如果没有配置ro.boot.init_rc属性,则解析init.rc
parser.ParseConfig("/init.rc");
//后面的几个if语句判断对应的路径是否有配置文件,如果有则把路径加入容器
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/system/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/product/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/product/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/odm/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/odm/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/vendor/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/vendor/etc/init");
}
} else {
parser.ParseConfig(bootscript);
}
}
我们看下init.rc文件内容,由于篇幅原因,还是省略了部分内容;
#system/core/rootdir/init.rc
import /init.environ.rc
import /init.usb.rc
import /init.${ro.hardware}.rc
import /vendor/etc/init/hw/init.${ro.hardware}.rc
import /init.usb.configfs.rc
import /init.${ro.zygote}.rc
on early-init
# Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
write /proc/1/oom_score_adj -1000
# Disable sysrq from keyboard
write /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq 0
# Set the security context of /adb_keys if present.
restorecon /adb_keys
# Set the security context of /postinstall if present.
restorecon /postinstall
# Mount cgroup mount point for cpu accounting
mount cgroup none /acct nodev noexec nosuid cpuacct
mkdir /acct/uid
# root memory control cgroup, used by lmkd
mkdir /dev/memcg 0700 root system
mount cgroup none /dev/memcg nodev noexec nosuid memory
# app mem cgroups, used by activity manager, lmkd and zygote
mkdir /dev/memcg/apps/ 0755 system system
# cgroup for system_server and surfaceflinger
mkdir /dev/memcg/system 0550 system system
start ueventd
.......
文件开头import了其他的rc文件,init.${ro.zygote}.rc就是zygote的有关的初始化脚本,ro.zygote属性可以通过getprop ro.zygote 查看机型对应的属性,比如下面就是32位的机型初始化脚本文件。
#system/core/rootdir/init.zygote32.rc
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
service的格式如下:
service [ ]*
zygote进程的启动就是通过service命令“/system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server”。有关rc文件的更多内容可以参考system/core/init/README.md文件
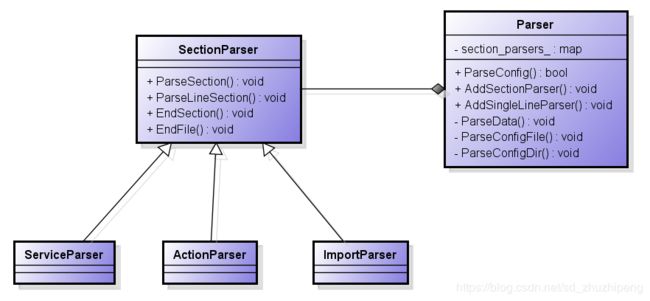
在前面的时序图中,我们了解到解析过程会调用Parser::ParseData函数,在这个过程中就是根据不同类型采用对应的parser来解析
//system/core/init/parse.cpp
void Parser::ParseData(const std::string& filename, const std::string& data, size_t* parse_errors) {
// TODO: Use a parser with const input and remove this copy
std::vector data_copy(data.begin(), data.end());
data_copy.push_back('\0');
parse_state state;
state.line = 0;
state.ptr = &data_copy[0];
state.nexttoken = 0;
SectionParser* section_parser = nullptr;
int section_start_line = -1;
std::vector args;
auto end_section = [&] {
if (section_parser == nullptr) return;
if (auto result = section_parser->EndSection(); !result) {
(*parse_errors)++;
LOG(ERROR) << filename << ": " << section_start_line << ": " << result.error();
}
section_parser = nullptr;
section_start_line = -1;
};
for (;;) {
switch (next_token(&state)) {
case T_EOF:
end_section();
return;
case T_NEWLINE:
state.line++;
if (args.empty()) break;
// If we have a line matching a prefix we recognize, call its callback and unset any
// current section parsers. This is meant for /sys/ and /dev/ line entries for
// uevent.
for (const auto& [prefix, callback] : line_callbacks_) {
if (android::base::StartsWith(args[0], prefix)) {
end_section();
if (auto result = callback(std::move(args)); !result) {
(*parse_errors)++;
LOG(ERROR) << filename << ": " << state.line << ": " << result.error();
}
break;
}
}
//section_parsers_是个map集合,数据初始化在init.cpp的CreateParser()函数中
if (section_parsers_.count(args[0])) {
end_section();
section_parser = section_parsers_[args[0]].get();
section_start_line = state.line;
if (auto result =
section_parser->ParseSection(std::move(args), filename, state.line);
!result) {
(*parse_errors)++;
LOG(ERROR) << filename << ": " << state.line << ": " << result.error();
section_parser = nullptr;
}
} else if (section_parser) {
if (auto result = section_parser->ParseLineSection(std::move(args), state.line);
!result) {
(*parse_errors)++;
LOG(ERROR) << filename << ": " << state.line << ": " << result.error();
}
}
args.clear();
break;
case T_TEXT:
args.emplace_back(state.text);
break;
}
}
}
//system/core/init/service.cpp
Result ServiceParser::ParseLineSection(std::vector&& args, int line) {
return service_ ? service_->ParseLine(std::move(args)) : Success();
}
Result Service::ParseLine(const std::vector& args) {
static const OptionParserMap parser_map;
auto parser = parser_map.FindFunction(args);
if (!parser) return parser.error();
//执行真正的命令,比如zygote.rc的“/system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server”
return std::invoke(*parser, this, args);
}
zygote启动
在了解init.rc解析后,我们再看下zygote进程对应的app_main.cpp文件的main函数执行过程
//app_main.cpp
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
if (!LOG_NDEBUG) {
String8 argv_String;
for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) {
argv_String.append("\"");
argv_String.append(argv[i]);
argv_String.append("\" ");
}
ALOGV("app_process main with argv: %s", argv_String.string());
}
//创建AppRuntime对象runtime(AppRuntime继承自AndroidRuntime)
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
//省略部分代码
//...........
if (zygote) {
//这里会调用ZygoteInit.java的main()方法
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
}
}
main()函数主要作用是创建java虚拟机并调用ZygoteInit.java类的main()方法,而又是怎么实现在C++中调用到Java层的ZygoteInit.main()方法的呢,这就要看下runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote)具体的实现,看下start()函数的具体实现
//AndroidRuntime.cpp
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector& options, bool zygote)
{
ALOGD(">>>>>> START %s uid %d <<<<<<\n",
className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)", getuid());
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
/*
* 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
* init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
*/
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
if (options[i] == startSystemServer) {
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START, ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
}
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL) {
rootDir = "/system";
if (!hasDir("/system")) {
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
return;
}
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
}
//const char* kernelHack = getenv("LD_ASSUME_KERNEL");
//ALOGD("Found LD_ASSUME_KERNEL='%s'\n", kernelHack);
/* start the virtual machine */
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
//创建虚拟机
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className != NULL ? className : "");
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
//JNI的方式得到startClass的main()方法的jmethodID
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
//这里就实现了调用startClass的main()方法
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}
zygote 作用
接下来,我们看下ZygoteInit.main()方法里面都做了些什么
//ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();
// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
// an error.
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// Zygote goes into its own process group.
try {
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
}
final Runnable caller;
try {
// Report Zygote start time to tron unless it is a runtime restart
if (!"1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_zygote_init",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
//创建socket
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false, 0);
// Zygote process unmounts root storage spaces.
Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();
// Set seccomp policy
Seccomp.setPolicy();
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
if (startSystemServer) {
//fork SystemServer进程
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}
在ZygoteInit.main()方法中主要做了两件事:
-
fork SystemServer进程;
-
在一个循环中等待命令fork 新的进程,该功能的实现是在ZygoteServer.runSelectLoop()方法中,该方法是一个无限循环,等待socket连接,然后根据连接中的参数fork新的进程,fork的过程与 fork SystemServer的过程类似
fork SystemServer
在ZygoteInit.forkSystemServer()方法中会设置SystemServer的参数,然后调用Zygote.forkSystemServer()方法
//ZygoteInit.java
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
OsConstants.CAP_IPC_LOCK,
OsConstants.CAP_KILL,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_PTRACE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG,
OsConstants.CAP_WAKE_ALARM
);
/* Containers run without this capability, so avoid setting it in that case */
if (!SystemProperties.getBoolean(PROPERTY_RUNNING_IN_CONTAINER, false)) {
capabilities |= posixCapabilitiesAsBits(OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND);
}
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
//fork systemserver,Zygote.forSystemServer()调用了Zygote.nativeForkSystemServer()方法,该JNI方法具体实现在com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp中
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
//pid =0 表示当前在子进程中
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return null;
}
Zygote.forkSystemServer()具体在com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp实现就不展开了,最终就是通过调用bionic(/bionic/libc/bionic/fork.cpp)库中的fork.cpp中的fork()函数。有点一点需要注意,当调用一次fork()函数会在父进程和子进程中各返回一次,在子进程的返回的是0,在父进程中返回的是子进程id。有关fork()函数请参考fork()函数,最后附上zygote main()函数的时序图。