spark sql 2.3 源码解读 - Execute (7)
终于到了最后一步执行了:
/** Internal version of the RDD. Avoids copies and has no schema */
lazy val toRdd: RDD[InternalRow] = executedPlan.execute()
final def execute(): RDD[InternalRow] = executeQuery {
if (isCanonicalizedPlan) {
throw new IllegalStateException("A canonicalized plan is not supposed to be executed.")
}
doExecute()
}
protected final def executeQuery[T](query: => T): T = {
RDDOperationScope.withScope(sparkContext, nodeName, false, true) {
prepare()
waitForSubqueries()
query
}
}
final def prepare(): Unit = {
// doPrepare() may depend on it's children, we should call prepare() on all the children first.
children.foreach(_.prepare())
synchronized {
if (!prepared) {
prepareSubqueries()
doPrepare()
prepared = true
}
}
}
最关键的两个函数便是 doPrepare和 doExecute了。
还是以上一章的sql语句为例,其最终生成的sparkplan为:
*(2) Sort [B#6 ASC NULLS FIRST], true, 0
+- Exchange rangepartitioning(B#6 ASC NULLS FIRST, 200)
+- *(1) FileScan json [B#6] Batched: false, Format: JSON, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:/Users/neal/github/spark2.3/spark/examples/src/main/resources/test.json], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [], ReadSchema: struct
看一下SortExec的doPrepare 和 doExecute方法:
override protected def doPrepare(): Unit = {
coordinator match {
// 向exchangeCoordinator注册该exchange
case Some(exchangeCoordinator) => exchangeCoordinator.registerExchange(this)
case _ =>
}
// 注册就是添加到array中
def registerExchange(exchange: ShuffleExchangeExec): Unit = synchronized {
exchanges += exchange
}
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val peakMemory = longMetric("peakMemory")
val spillSize = longMetric("spillSize")
val sortTime = longMetric("sortTime")
// 逻辑很简单,调用child的execute方法,然后对每个partition进行排序
child.execute().mapPartitionsInternal { iter =>
val sorter = createSorter()
val metrics = TaskContext.get().taskMetrics()
// Remember spill data size of this task before execute this operator so that we can
// figure out how many bytes we spilled for this operator.
val spillSizeBefore = metrics.memoryBytesSpilled
// 排序
val sortedIterator = sorter.sort(iter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[UnsafeRow]])
sortTime += sorter.getSortTimeNanos / 1000000
peakMemory += sorter.getPeakMemoryUsage
spillSize += metrics.memoryBytesSpilled - spillSizeBefore
metrics.incPeakExecutionMemory(sorter.getPeakMemoryUsage)
sortedIterator
}
}
下面看child也就是ShuffleExchangeExec:
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = attachTree(this, "execute") {
// Returns the same ShuffleRowRDD if this plan is used by multiple plans.
// 有缓存则直接返回缓存
if (cachedShuffleRDD == null) {
cachedShuffleRDD = coordinator match {
// 有exchangeCoordinator
case Some(exchangeCoordinator) =>
val shuffleRDD = exchangeCoordinator.postShuffleRDD(this)
assert(shuffleRDD.partitions.length == newPartitioning.numPartitions)
shuffleRDD
// 没有exchangeCoordinator
case _ =>
val shuffleDependency = prepareShuffleDependency()
preparePostShuffleRDD(shuffleDependency)
}
}
cachedShuffleRDD
}
先看没有exchangeCoordinator的情况,
首先执行:
private[exchange] def prepareShuffleDependency()
: ShuffleDependency[Int, InternalRow, InternalRow] = {
ShuffleExchangeExec.prepareShuffleDependency(
child.execute(), child.output, newPartitioning, serializer)
}
上面的方法会返回一个ShuffleDependency,ShuffleDependency中最重要的是rddWithPartitionIds,它决定了每一条InternalRow shuffle后的partition id:
// Now, we manually create a ShuffleDependency. Because pairs in rddWithPartitionIds
// are in the form of (partitionId, row) and every partitionId is in the expected range
// [0, part.numPartitions - 1]. The partitioner of this is a PartitionIdPassthrough.
val dependency =
new ShuffleDependency[Int, InternalRow, InternalRow](
rddWithPartitionIds,
new PartitionIdPassthrough(part.numPartitions),
serializer)
接下来:
private[exchange] def preparePostShuffleRDD(
shuffleDependency: ShuffleDependency[Int, InternalRow, InternalRow],
specifiedPartitionStartIndices: Option[Array[Int]] = None): ShuffledRowRDD = {
// If an array of partition start indices is provided, we need to use this array
// to create the ShuffledRowRDD. Also, we need to update newPartitioning to
// update the number of post-shuffle partitions.
// 如果specifiedPartitionStartIndices存在,它将决定shuffle后的分区情况
// exchangeCoordinator 会用到specifiedPartitionStartIndices来实现功能
specifiedPartitionStartIndices.foreach { indices =>
assert(newPartitioning.isInstanceOf[HashPartitioning])
newPartitioning = UnknownPartitioning(indices.length)
}
new ShuffledRowRDD(shuffleDependency, specifiedPartitionStartIndices)
}
返回结果是ShuffledRowRDD:
class ShuffledRowRDD(
var dependency: ShuffleDependency[Int, InternalRow, InternalRow],
specifiedPartitionStartIndices: Option[Array[Int]] = None)
extends RDD[InternalRow](dependency.rdd.context, Nil) {
// 分区数目
private[this] val numPreShufflePartitions = dependency.partitioner.numPartitions
// 每个partition的startIndice
private[this] val partitionStartIndices: Array[Int] = specifiedPartitionStartIndices match {
case Some(indices) => indices
case None =>
// When specifiedPartitionStartIndices is not defined, every post-shuffle partition
// corresponds to a pre-shuffle partition.
(0 until numPreShufflePartitions).toArray
}
// rdd 的partitioner
private[this] val part: Partitioner =
new CoalescedPartitioner(dependency.partitioner, partitionStartIndices)
override def getDependencies: Seq[Dependency[_]] = List(dependency)
override val partitioner: Option[Partitioner] = Some(part)
// 获取所有的partition
override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {
assert(partitionStartIndices.length == part.numPartitions)
Array.tabulate[Partition](partitionStartIndices.length) { i =>
val startIndex = partitionStartIndices(i)
val endIndex =
if (i < partitionStartIndices.length - 1) {
partitionStartIndices(i + 1)
} else {
numPreShufflePartitions
}
new ShuffledRowRDDPartition(i, startIndex, endIndex)
}
}
}
CoalescedPartitioner的逻辑:
/**
* A Partitioner that might group together one or more partitions from the parent.
*
* @param parent a parent partitioner
// 这句注释将partitionStartIndices的作用讲的非常好
* @param partitionStartIndices indices of partitions in parent that should create new partitions
* in child (this should be an array of increasing partition IDs). For example, if we have a
* parent with 5 partitions, and partitionStartIndices is [0, 2, 4], we get three output
* partitions, corresponding to partition ranges [0, 1], [2, 3] and [4] of the parent partitioner.
*/
class CoalescedPartitioner(val parent: Partitioner, val partitionStartIndices: Array[Int])
extends Partitioner {
// 实现 partition 的转换
@transient private lazy val parentPartitionMapping: Array[Int] = {
val n = parent.numPartitions
val result = new Array[Int](n)
for (i <- 0 until partitionStartIndices.length) {
val start = partitionStartIndices(i)
val end = if (i < partitionStartIndices.length - 1) partitionStartIndices(i + 1) else n
for (j <- start until end) {
result(j) = i
}
}
result
}
override def numPartitions: Int = partitionStartIndices.length
override def getPartition(key: Any): Int = {
parentPartitionMapping(parent.getPartition(key))
}
}
再看有exchangeCoordinator的情况:
同样返回的是ShuffledRowRDD:
def postShuffleRDD(exchange: ShuffleExchangeExec): ShuffledRowRDD = {
doEstimationIfNecessary()
if (!postShuffleRDDs.containsKey(exchange)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
s"The given $exchange is not registered in this coordinator.")
}
postShuffleRDDs.get(exchange)
}
再看doEstimationIfNecessary:
private def doEstimationIfNecessary(): Unit = synchronized {
if (!estimated) {
// Make sure we have the expected number of registered Exchange operators.
assert(exchanges.length == numExchanges)
val newPostShuffleRDDs = new JHashMap[ShuffleExchangeExec, ShuffledRowRDD](numExchanges)
// Submit all map stages
val shuffleDependencies = ArrayBuffer[ShuffleDependency[Int, InternalRow, InternalRow]]()
val submittedStageFutures = ArrayBuffer[SimpleFutureAction[MapOutputStatistics]]()
var i = 0
// 依次执行每个注册的exchange的prepareShuffleDependency方法
while (i < numExchanges) {
val exchange = exchanges(i)
val shuffleDependency = exchange.prepareShuffleDependency()
shuffleDependencies += shuffleDependency
if (shuffleDependency.rdd.partitions.length != 0) {
// submitMapStage does not accept RDD with 0 partition.
// So, we will not submit this dependency.
submittedStageFutures +=
exchange.sqlContext.sparkContext.submitMapStage(shuffleDependency)
}
i += 1
}
// Wait for the finishes of those submitted map stages.
// 统计结果
val mapOutputStatistics = new Array[MapOutputStatistics](submittedStageFutures.length)
var j = 0
while (j < submittedStageFutures.length) {
// This call is a blocking call. If the stage has not finished, we will wait at here.
mapOutputStatistics(j) = submittedStageFutures(j).get()
j += 1
}
// Now, we estimate partitionStartIndices. partitionStartIndices.length will be the
// number of post-shuffle partitions.
// 得到partitionStartIndices
val partitionStartIndices =
if (mapOutputStatistics.length == 0) {
None
} else {
// 根据 mapOutputStatistics 获取 partitionStartIndices
Some(estimatePartitionStartIndices(mapOutputStatistics))
}
// 执行preparePostShuffleRDD,和没有exchangeCoordinator唯一的不同是有partitionStartIndices参数!
var k = 0
while (k < numExchanges) {
val exchange = exchanges(k)
val rdd =
exchange.preparePostShuffleRDD(shuffleDependencies(k), partitionStartIndices)
newPostShuffleRDDs.put(exchange, rdd)
k += 1
}
// Finally, we set postShuffleRDDs and estimated.
assert(postShuffleRDDs.isEmpty)
assert(newPostShuffleRDDs.size() == numExchanges)
// 结果放入缓存
postShuffleRDDs.putAll(newPostShuffleRDDs)
estimated = true
}
}
estimatePartitionStartIndices 函数得到了 partitionStartIndices:
/**
* Estimates partition start indices for post-shuffle partitions based on
* mapOutputStatistics provided by all pre-shuffle stages.
*/
def estimatePartitionStartIndices(
mapOutputStatistics: Array[MapOutputStatistics]): Array[Int] = {
// If we have mapOutputStatistics.length < numExchange, it is because we do not submit
// a stage when the number of partitions of this dependency is 0.
assert(mapOutputStatistics.length <= numExchanges)
// If minNumPostShufflePartitions is defined, it is possible that we need to use a
// value less than advisoryTargetPostShuffleInputSize as the target input size of
// a post shuffle task.
// 每个partition的目标inputsize,即每个分区数据量的大小
val targetPostShuffleInputSize = minNumPostShufflePartitions match {
case Some(numPartitions) =>
val totalPostShuffleInputSize = mapOutputStatistics.map(_.bytesByPartitionId.sum).sum
// The max at here is to make sure that when we have an empty table, we
// only have a single post-shuffle partition.
// There is no particular reason that we pick 16. We just need a number to
// prevent maxPostShuffleInputSize from being set to 0.
val maxPostShuffleInputSize =
math.max(math.ceil(totalPostShuffleInputSize / numPartitions.toDouble).toLong, 16)
math.min(maxPostShuffleInputSize, advisoryTargetPostShuffleInputSize)
case None => advisoryTargetPostShuffleInputSize
}
logInfo(
s"advisoryTargetPostShuffleInputSize: $advisoryTargetPostShuffleInputSize, " +
s"targetPostShuffleInputSize $targetPostShuffleInputSize.")
// Make sure we do get the same number of pre-shuffle partitions for those stages.
// 得到分区数,应该有且只有一个数值
val distinctNumPreShufflePartitions =
mapOutputStatistics.map(stats => stats.bytesByPartitionId.length).distinct
// The reason that we are expecting a single value of the number of pre-shuffle partitions
// is that when we add Exchanges, we set the number of pre-shuffle partitions
// (i.e. map output partitions) using a static setting, which is the value of
// spark.sql.shuffle.partitions. Even if two input RDDs are having different
// number of partitions, they will have the same number of pre-shuffle partitions
// (i.e. map output partitions).
assert(
distinctNumPreShufflePartitions.length == 1,
"There should be only one distinct value of the number pre-shuffle partitions " +
"among registered Exchange operator.")
val numPreShufflePartitions = distinctNumPreShufflePartitions.head
// 开始构建partitionStartIndices
val partitionStartIndices = ArrayBuffer[Int]()
// The first element of partitionStartIndices is always 0.
partitionStartIndices += 0
var postShuffleInputSize = 0L
// 根据targetPostShuffleInputSize,对分区进行调整,会做一些合并之类的操作。
var i = 0
while (i < numPreShufflePartitions) {
// We calculate the total size of ith pre-shuffle partitions from all pre-shuffle stages.
// Then, we add the total size to postShuffleInputSize.
var nextShuffleInputSize = 0L
var j = 0
while (j < mapOutputStatistics.length) {
nextShuffleInputSize += mapOutputStatistics(j).bytesByPartitionId(i)
j += 1
}
// If including the nextShuffleInputSize would exceed the target partition size, then start a
// new partition.
if (i > 0 && postShuffleInputSize + nextShuffleInputSize > targetPostShuffleInputSize) {
partitionStartIndices += i
// reset postShuffleInputSize.
postShuffleInputSize = nextShuffleInputSize
} else postShuffleInputSize += nextShuffleInputSize
i += 1
}
partitionStartIndices.toArray
}
有exchangeCoordinator的情况就生成了partitionStartIndices,从而对分区进行了调整。
最后来一个例子:
// 防止转化为BroadcastJoin
spark.conf.set("spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold", 1)
// 开启exchangeCoordinator
spark.conf.set("spark.sql.adaptive.enabled", "true")
val df = spark.read.json("examples/src/main/resources/test.json")
val df2 = spark.read.json("examples/src/main/resources/test2.json")
df.createOrReplaceTempView("A")
df2.createOrReplaceTempView("C")
spark.sql("SELECT A.B FROM A JOIN C ON A.B = C.B").explain()
未开启exchangeCoordinator的plan:
`*(5) Project [B#6]`
`+- *(5) SortMergeJoin [B#6], [B#14], Inner`
:- *(2) Sort [B#6 ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
: +- Exchange hashpartitioning(B#6, 200)
: +- *(1) Project [B#6]
: +- *(1) Filter isnotnull(B#6)
: +- *(1) FileScan json [B#6] Batched: false, Format: JSON, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:examples/src/main/resources/test.json], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [IsNotNull(B)], ReadSchema: struct
+- *(4) Sort [B#14 ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(B#14, 200)
+- *(3) Project [B#14]
+- *(3) Filter isnotnull(B#14)
`+- *(3) FileScan json [B#14] Batched: false, Format: JSON, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:examples/src/main/resources/test2.json], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [IsNotNull(B)], ReadSchema: struct
开启exchangeCoordinator的plan:
*(5) Project [B#6]
+- *(5) SortMergeJoin [B#6], [B#14], Inner
:- *(2) Sort [B#6 ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
: +- Exchange(coordinator id: 1121577170) hashpartitioning(B#6, 200), coordinator[target post-shuffle partition size: 67108864]
: +- *(1) Project [B#6]
: +- *(1) Filter isnotnull(B#6)
: +- *(1) FileScan json [B#6] Batched: false, Format: JSON, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:examples/src/main/resources/test.json], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [IsNotNull(B)], ReadSchema: struct
+- *(4) Sort [B#14 ASC NULLS FIRST], false, 0
+- Exchange(coordinator id: 1121577170) hashpartitioning(B#14, 200), coordinator[target post-shuffle partition size: 67108864]
+- *(3) Project [B#14]
+- *(3) Filter isnotnull(B#14)
+- *(3) FileScan json [B#14] Batched: false, Format: JSON, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:examples/src/main/resources/test2.json], PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [IsNotNull(B)], ReadSchema: struct
不同之处是 两个Exchange都带了coordinator,且都是同一个coordinator。
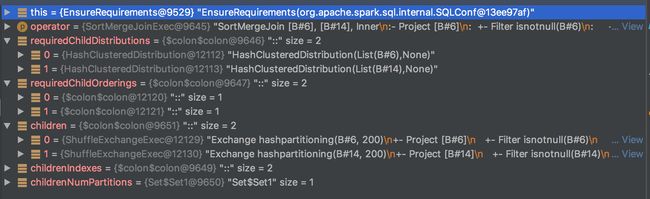
执行withExchangeCoordinator前:
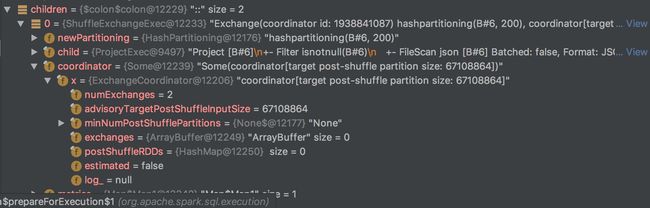
执行withExchangeCoordinator后:
生成了coordinator,且执行了 doPrepare后,可以看到两个exchange都向其注册了。
doExecute后:
原先的numPartitions是200,经过执行后,生成的partitionStartIndices为[1],也就是只有1个partition,显然在测试数据量很小的情况下,1个partition是更为合理的。这就是ExchangeCoordinator的功劳。
execute 最终的输出是rdd,剩下的结果便是spark对rdd的运算了。其实 spark sql 最终的目标便也是生成rdd,交给spark core来运算。
spark sql的介绍到这里就结束了。