Network POJ - 3694(边双连通分量, LCA)
A network administrator manages a large network. The network consists of N computers and M links between pairs of computers. Any pair of computers are connected directly or indirectly by successive links, so data can be transformed between any two computers. The administrator finds that some links are vital to the network, because failure of any one of them can cause that data can’t be transformed between some computers. He call such a link a bridge. He is planning to add some new links one by one to eliminate all bridges.
You are to help the administrator by reporting the number of bridges in the network after each new link is added.
Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. Each test case starts with a line containing two integers N(1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000) and M(N - 1 ≤ M ≤ 200,000).
Each of the following M lines contains two integers A and B ( 1≤ A ≠ B ≤ N), which indicates a link between computer A and B. Computers are numbered from 1 to N. It is guaranteed that any two computers are connected in the initial network.
The next line contains a single integer Q ( 1 ≤ Q ≤ 1,000), which is the number of new links the administrator plans to add to the network one by one.
The i-th line of the following Q lines contains two integer A and B (1 ≤ A ≠ B ≤ N), which is the i-th added new link connecting computer A and B.
The last test case is followed by a line containing two zeros.
Output
For each test case, print a line containing the test case number( beginning with 1) and Q lines, the i-th of which contains a integer indicating the number of bridges in the network after the first i new links are added. Print a blank line after the output for each test case.
Sample Input
3 2
1 2
2 3
2
1 2
1 3
4 4
1 2
2 1
2 3
1 4
2
1 2
3 4
0 0
Sample Output
Case 1:
1
0
Case 2:
2
0
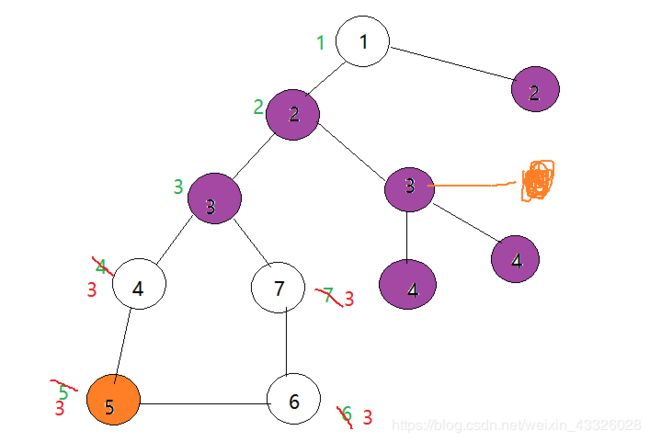
比如以下一副图,一开始各点的dfn值为圈中的值,low值为旁边绿色的值。
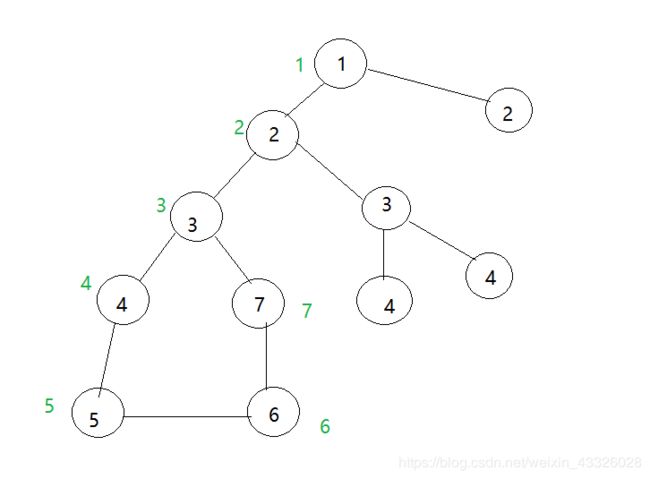
从7连到3时,开始回溯,更新low值

下图中紫色的点都被标记为1,记录了桥,如果查询图中橙色的两个点x, y,左边的点x的dfn值深,一步步找它的父节点,更新x=f[x], 当x, y的深度一样后,一起往上找父节点,由于下图中,a[x], a[y]都等于1,所以桥的数量减去了2,x=f[x],y=f[y],此时x=y,找到LCA
#include