MVVM 架构,ViewModel和LiveData(二)
MVVM 架构,ViewModel和LiveData(二)
标签(空格分隔): 翻译计划 Android开发
原文链接
- MVVM architecture, ViewModel and LiveData — Part 2 (DI)
在Google I / O期间(去年),Google推出了包含LiveData和ViewModel的Architecture Components,这有助于使用MVVM模式开发Android应用程序。
在本系列的第一篇文章中,我们讨论了这些组件如何服务遵循MVVM的android应用程序。
在第二篇文章中,我们将回答的一个问题,那就是第一篇文章中提到的依赖注入(Dependency injection)。
在阅读本文的时候,假设读者已经对Dagger有了简单的了解,我们将会在我们的MVVM程序使用最新的Dagger(V2.11)来实现我们的依赖注入(Dependency injection)
如果你想要了解Dagger(V2.11)的相关信息,请查看user guide
Configuring Dagger 2.11(配置Dagger)
首先要在我们的MVVM例子中配置Dagger的相关依赖
指定Dagger版本(project的build.gradle)
project.ext {
// …
dagger_version = "2.11"
}引入Dagger核心库(project的build.gradle中)
annotationProcessor "com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:$dagger_version"
compile "com.google.dagger:dagger:$project.dagger_version"引入Dagger的安卓相关(module的build.gradle)
compile "com.google.dagger:dagger-android:$project.dagger_version"
compile "com.google.dagger:dagger-android-support:$project.dagger_version"
annotationProcessor "com.google.dagger:dagger-android-processor:$dagger_version"Dagger(2.11) 项目设置
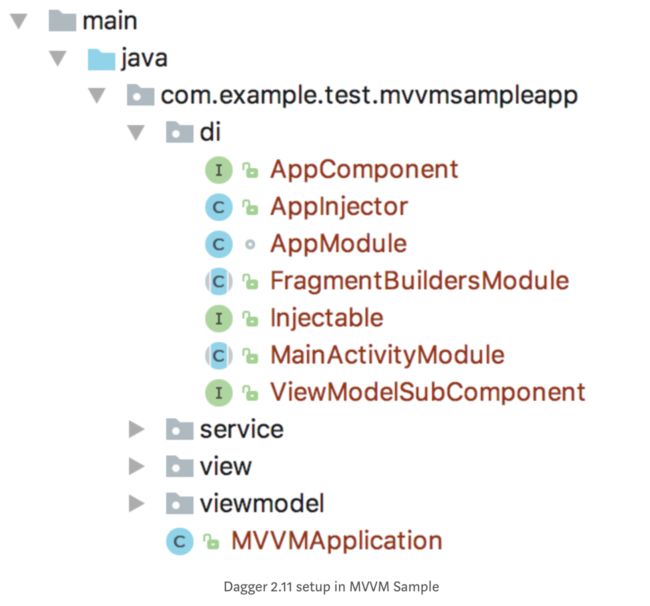
下图展示了在这个示例中有关Dagger(2.11)的设置。
我们主要针对以下的几个类或者接口:
* 1、AppModule是Dagger模块负责提供单服务,类似于项目中的GitHubService 和 ProjectViewModelFactory
* 2、AppComponent 负责注入 AppModule
* 3、ViewModelSubComponent是创建View Model实例的子组件
* 4、MainActivityModule和FragmentBuildersModule是activity和fragment的instances的提供者
* 5、Injectable是为那些可进行注入的fragments的一个接口
* 6、AppInjector是一个助手类,自动注入fragments如果他们实现注射接口.
现在让我们进入每一个Dagger设置的具体情况
Creating View Model SubComponent(创建 View Model子组件)
下面的代码片段显示了ViewModelSubComponent接口,负责创建ViewModel实例
@Subcomponent
public interface ViewModelSubComponent {
@Subcomponent.Builder
interface Builder {
ViewModelSubComponent build();
}
ProjectListViewModel projectListViewModel();
ProjectViewModel projectViewModel();
}注意,ViewModelSubComponent将通过调用 ProjectViewModelFactory获得ViewModel实例
但是什么是ProjectViewModelFactory?
下一节就会回答这个问题。
Creating custom View Model Factory(创建自定义的View Model 工厂)
ProjectViewModelFactory是继承自ViewModelProvider的一个工厂类。ProjectViewModelFactory是为fragments(消费者)提供ViewModel实例
下面的代码片段显示了ProjectViewModelFactory通过实现ViewModelProvider.Factory工厂实现的
public class ProjectViewModelFactory implements ViewModelProvider.Factory {
private final ArrayMap> creators;
@Inject
public ProjectViewModelFactory(ViewModelSubComponent viewModelSubComponent) {
creators = new ArrayMap<>();
// View models cannot be injected directly because they won't be bound to the owner's
// view model scope.
creators.put(ProjectViewModel.class, () -> viewModelSubComponent.projectViewModel());
creators.put(ProjectListViewModel.class, () -> viewModelSubComponent.projectListViewModel());
}
@Override
public T create(Class modelClass) {
Callable creator = creators.get(modelClass);
if (creator == null) {
for (Map.Entry> entry : creators.entrySet()) {
if (modelClass.isAssignableFrom(entry.getKey())) {
creator = entry.getValue();
break;
}
}
}
if (creator == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown model class " + modelClass);
}
try {
return (T) creator.call();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
现在,让我们看下一节的main app module
Creating App Module(创建App Module)
AppModul是Dagger注入模块中是一个Applicaption级别的一个负责提供单(并非单利)服务,比如供GitHubService和 ProjectViewModelFactory服务,下面的代码片段显示了AppModule类
@Module(subcomponents = ViewModelSubComponent.class)
class AppModule {
@Singleton @Provides
GitHubService provideGithubService() {
return new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(GitHubService.HTTPS_API_GITHUB_URL)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build()
.create(GitHubService.class);
}
@Singleton
@Provides
ViewModelProvider.Factory provideViewModelFactory(
ViewModelSubComponent.Builder viewModelSubComponent) {
return new ProjectViewModelFactory(viewModelSubComponent.build());
}
}重要的东西要注意,不要忘记写subcomponents = ViewModelSubComponent.class,AppModule通过指定它的子组件参数@Module达成和子类的通信。
Creating Injectable and AppInjector(创建Injectable和AppInjector)
Injectable接口就是一个简单的接口,代码如下
public interface Injectable {
}Injectable将会被fragments实现以方便fragments进行注入
为了方便fragments实现自动注入如果他们实现Injectable接口,创建以下AppInjector助手类注入fragments实例onFragmentCreated()方法,如下所示
public class AppInjector {
private AppInjector() {}
public static void init(MVVMApplication mvvmApplication) {
DaggerAppComponent.builder().application(mvvmApplication)
.build().inject(mvvmApplication);
mvvmApplication
.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(new Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks() {
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Activity activity, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
handleActivity(activity);
}
// Other methods are omitted for simplification …
});
}
private static void handleActivity(Activity activity) {
if (activity instanceof HasSupportFragmentInjector) {
AndroidInjection.inject(activity);
}
if (activity instanceof FragmentActivity) {
((FragmentActivity) activity).getSupportFragmentManager()
.registerFragmentLifecycleCallbacks(
new FragmentManager.FragmentLifecycleCallbacks() {
@Override
public void onFragmentCreated(FragmentManager fm, Fragment fragment,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (fragment instanceof Injectable) {
AndroidSupportInjection.inject(fragment);
}
}
}, true);
}
}
}需要注意的一点是,AppInjector.init()将在应用程序启动时(正如我们在自定义应用程序将显示类部分)。
Creating Activity and Fragment Modules(创建Activity和Fragment单元)
下面的代码片段显示了Fragment的Dagger模块。
@Module
public abstract class FragmentBuildersModule {
@ContributesAndroidInjector
abstract ProjectFragment contributeProjectFragment();
@ContributesAndroidInjector
abstract ProjectListFragment contributeProjectListFragment();
}自从Dagger2.10开始,@ContributesAndroidInjector可以很方便的依附activitys和fragments,下面的代码片段显示了MainActivityModule。
@Module
public abstract class MainActivityModule {
@ContributesAndroidInjector(modules = FragmentBuildersModule.class)
abstract MainActivity contributeMainActivity();
}现在,让我们看看在我们的最后一项Dagger2.11的设置,那就是,AppComponent。
Creating AppComponent(创建AppComponent)
在下一个代码片段显示了AppComponent接口。
@Singleton
@Component(modules = {
AndroidInjectionModule.class,
AppModule.class,
MainActivityModule.class
})
public interface AppComponent {
@Component.Builder
interface Builder {
@BindsInstance Builder application(Application application);
AppComponent build();
}
void inject(MVVMApplication mvvmApplication);
}这里要注意一件重要的事情,我们为AppComponent增加了A**ppModule,AndroidInjectionModule,MainActivityModule**.
按照官方文档,它是必要的,以确保所有必要的绑定是可用的。
在dagger-android AndroidSupportInjectionModule是一个内置的模块:
https://github.com/google/dagger/blob/master/java/dagger/android/support/AndroidSupportInjectionModule.java
Updating Repository Layer Implementation(更新存储库实现)
现在,我们已经完成了Dagger的相关配置,让我们来改变程序的代码结构吧.
ProjectRepository将不再需要手动创建GitHubService服务实例,他所有需要做的就是在它的构造函数使用@Inject GitHubService实例如下所示:
@Singleton
public class ProjectRepository {
private GitHubService gitHubService;
@Inject
public ProjectRepository(GitHubService gitHubService) {
this.gitHubService = gitHubService;
}
// Other methods here are omitted for simplicity …
}Updating ViewModel Layer Implementation(更新ViewModel层实现)
更新ViewModel层也需要避免在这一层从ProjectRepository手动创建一个实例。
下面的代码片段显示了一个示例从ProjectViewModel使用@ Inject注释注入Application和ProjectRepository的代码示例。
public class ProjectViewModel extends AndroidViewModel {
private static final String TAG = ProjectViewModel.class.getName();
private static final MutableLiveData ABSENT = new MutableLiveData();
{
//noinspection unchecked
ABSENT.setValue(null);
}
private final LiveData projectObservable;
private final MutableLiveData projectID;
public ObservableField project = new ObservableField<>();
@Inject
public ProjectViewModel(@NonNull ProjectRepository projectRepository, @NonNull Application application) {
super(application);
this.projectID = new MutableLiveData<>();
projectObservable = Transformations.switchMap(projectID, input -> {
if (input.isEmpty()) {
return ABSENT;
}
return projectRepository.getProjectDetails("Google", projectID.getValue());
});
}
// Code is omitted for simplicity …
} Updating View Implementation (Fragments and Main Activity)(更新视图实现(fragments和activity))
更新视图层也需要避免创建实例从ViewModel类手动在这一层
查看下面的代码片段(ProjectFragment)
public class ProjectFragment extends LifecycleFragment implements Injectable {
@Inject
ViewModelProvider.Factory viewModelFactory;
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
final ProjectViewModel viewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this, viewModelFactory)
.get(ProjectViewModel.class);
// …
}
// …
}这里要注意一些重要的点
- 1、现在每个fragment/activity都必须实现Injectable接口
- 2、每个fragment/activity都应该通过@Inject依赖于ViewModelProvider工厂为了得到ViewModel实例
Creating Custom Application class(创建Application)
最后,我们的自定义Application class的代码如下所示
public class MVVMApplication extends Application implements HasActivityInjector {
@Inject
DispatchingAndroidInjector dispatchingAndroidInjector;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
AppInjector.init(this);
}
@Override
public DispatchingAndroidInjector activityInjector() {
return dispatchingAndroidInjector;
}
} 两个主要的注意事项
- 1、Application必须实现 HasActivityInjector这个接口,并且通过@Inject依赖DispatchingAndroidInjector以便于通过activityInjector()方法返回DispatchingAndroidInjector实例。
- 2、在onCreate()方法中调用AppInjector.init(this)实现自动依赖。
Source Code(源代码)
- https://github.com/hazems/mvvm-sample-app/tree/part2