linux 下 tcpdump 详解 前篇(libpcap库源码分析)
一 概述
用简单的话来定义tcpdump,就是:dump the traffic on a network,根据使用者的定义对网络上的数据包进行截获的包分析工具。 至于tcpdump参数如何使用,这不是本章讨论的重点。
liunx系统抓包工具,毫无疑问就是tcpdump。而windows的抓包工具,wireshark也是一款主流的抓包工具。wireshark 使用了winpcap库。tcpdump 基于 libpcap库。而winpcap库是类似于linux下的libpcap。 因此本文着重探讨libpcap库的原理。
二 libpcap库使用
在了解libpcap库原理前,先说下libpcap 库的几个接口。一般情况下我们要使用libpcap库抓包,会用到下面几个接口函数
1.打开一个用于捕获数据的网络接口
pcap_t *pcap_open_live(char *device, int snaplen, int promisc, int to_ms, char *ebuf)
/ * -------------------------------------
device:网络接口的名字,为第一步获取的网络接口字符串(pcap_lookupdev() 的返回值 ),也可人为指定,如“eth0”。
snaplen:捕获数据包的长度,长度不能大于 65535 个字节。
promise:“1” 代表混杂模式,其它非混杂模式。
to_ms:指定需要等待的毫秒数,超过这个数值后,获取数据包的函数就会立即返回(这个函数不会阻塞,后面的抓包函数才会阻塞)。0 表示一直等待直到有数据包到来。
ebuf:存储错误信息。
-------------------------------------------------------*/
2 获取指定网卡的 ip 地址,子网掩码
int pcap_lookupnet(const char *, bpf_u_int32 *, bpf_u_int32 *, char *);
/ *-------------------------------------
device:网络设备名,为第一步获取的网络接口字符串(pcap_lookupdev() 的返回值 ),也可人为指定,如“eth0”。
netp:存放 ip 地址的指针,bpf_u_int32 为 32 位无符号整型
maskp:存放子网掩码的指针,bpf_u_int32 为 32 位无符号整型
errbuf:存放出错信息
-------------------------------------------------------*/
3 编译 BPF 过滤规则
int pcap_compile(pcap_t *, struct bpf_program *, const char *, int, bpf_u_int32);
/ * -------------------------------------
p:pcap_open_live() 返回的 pcap_t 类型的指针
fp:存放编译后的 bpf,应用过滤规则时需要用到这个指针
buf:过滤条件
optimize:是否需要优化过滤表达式
mask:指定本地网络的网络掩码,不需要时可写 0
-------------------------------------------------------*/
4 应用 BPF 过滤规则,让bpf规则生效
int pcap_setfilter( pcap_t * p, struct bpf_program * fp );
/ * -------------------------------------
p:pcap_open_live() 返回的 pcap_t 类型的指针
fp:pcap_compile() 的第二个参数
-------------------------------------------------------*/
5 循环捕获网络数据包
int pcap_loop(pcap_t *, int, pcap_handler, u_char *);
/ * -------------------------------------
p:pcap_open_live()返回的 pcap_t 类型的指针。
cnt:指定捕获数据包的个数,一旦抓到了 cnt 个数据包,pcap_loop 立即返回。如果是 -1,就会永无休止的捕获,直到出现错误。
callback:回调函数,名字任意,根据需要自行起名。
user:向回调函数中传递的参数。
callback 回调函数的定义:void callback(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet)
userarg:pcap_loop() 的最后一个参数,当收到足够数量的包后 pcap_loop 会调用callback 回调函数,同时将pcap_loop()的user参数传递给它
pkthdr:是收到数据包的 pcap_pkthdr 类型的指针,和 pcap_next() 第二个参数是一样的。
packet :收到的数据包数据
-------------------------------------------------------*/
6 释放网络接口
void pcap_close(pcap_t *p);
libpcap 用到最多的6个接口,还有一个查找网络接口设备名
char *pcap_lookupdev(char *errbuf); 你要是自己知道要抓的那个网口,就可以直接指定即可。
libpcap主要有两个重要的功能 (抓包 ,过滤)
- 首先网络设备驱动程序会收集数据,会复制一份给内核BPF过滤器
- 但是应用层大多数只关心自己想要的数据。因此应用层每个抓包模块,都会有自己想过滤的数据包,最终符合过滤规则的就把数据传给应用层。
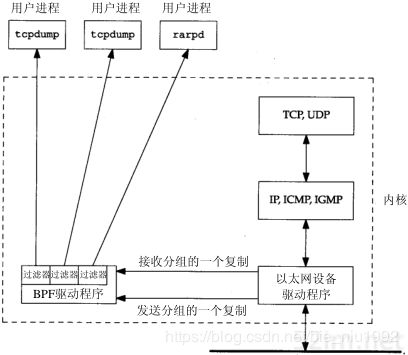
看图可以简单理解下,这里不深入内核底层的交互,中篇会再细说。回归正题,接下来看代码集成libpcap抓包使用。
static void ethernet_packet(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet) {
// 程序对抓到包的处理
return;
}
static void * sniffer_thread_callback(void *param) {
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
printf("sniffer_thread_callback enter\n");
int nDev =-(TYPE32)param;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
pcap_t *handle;
//bug modify flag jl
char *filter_exp = "not broadcast and not arp";
struct bpf_program fp;
bpf_u_int32 mask = 0;
bpf_u_int32 net = 0;
handle = pcap_open_live(option_struct.dev_interface[nDev], 65535, 1, 0, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "couldn't open device %s: %s\n", option_struct.dev_interface[nDev], errbuf);
pthread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
pcap_lookupnet(option_struct.dev_interface[nDev], &net, &mask, errbuf);
if (pcap_datalink(handle) != DLT_EN10MB) {
fprintf(stderr, "couldn't pcap_datalink %s\n", pcap_geterr(handle));
pcap_close(handle);
pthread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
if (pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0, net) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "couldn't parse filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
pcap_freecode(&fp);
pcap_close(handle);
pthread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
if (pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "couldn't install filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
pcap_freecode(&fp);
pcap_close(handle);
pthread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
if (pcap_loop(handle, -1, ethernet_packet, (u_char *)&nDev) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "couldn't pacp loop %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
}
pcap_freecode(&fp);
pcap_close(handle);
pthread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
这些接口上面基本都介绍过,大概就是打开捕获网络数据的接口,先获取网卡对应ip 子网掩码,用于创建规则bpf ,然后生效bpf规则,最后开始循环抓包数据。而怎么处理包的流程由ethernet_packet 回调函数内实现。
三 libpcap 源码理解
这里主要分析 pcap_open_live() , pcap_compile(),pcap_setfilter() ,pcap_loop四个接口函数
看函数前先介绍个重要的结构体 pcap_t
typedef struct pcap pcap_t;
struct pcap {
read_op_t read_op; //回调函数,用户获取数据包 Method to call to read packets on a live capture.
next_packet_op_t next_packet_op; /* * Method to call to read the next packet from a savefile. 从文件里读取报文的函数指针*/
int fd;
u_int bufsize; // Read buffer. 获取数据包大小
void *buffer; // Read buffer. 获取数据包缓存
u_char *bp;
int cc;
sig_atomic_t break_loop; /* flag set to force break from packet-reading loop */
void *priv; /* private data for methods 指针指向私有的方法结构体 */
int swapped;
FILE *rfile; /* null if live capture, non-null if savefile 当是是解析pcap文件的数据时,不为空*/
u_int fddipad;
struct pcap *next; /* list of open pcaps that need stuff cleared on close */
int snapshot; /* 抓取一个数据报的最大长度 */
int linktype; /* Network linktype */
int linktype_ext; /* Extended information stored in the linktype field of a file */
int offset; /* offset for proper alignment */
int activated; /* true if the capture is really started 表示抓包功能已经激活*/
int oldstyle; /* if we're opening with pcap_open_live() */
struct pcap_opt opt;
pcap_direction_t direction; /* We're accepting only packets in this direction/these directions. */
int bpf_codegen_flags; /* Flags to affect BPF code generation. */
struct bpf_program fcode;
struct pcap_pkthdr pcap_header; /* This is needed for the pcap_next_ex() to work */
/*
* More methods.
*/
activate_op_t activate_op; //激活函数,激活函数在得到调用后,会建立起与底层IPC的socket
. . .
}
1. pcap_open_live 接口函数源码
pcap_t *
pcap_open_live(const char *device, int snaplen, int promisc, int to_ms, char *errbuf)
{
pcap_t *p;
int status;
p = pcap_create(device, errbuf);
if (p == NULL)
return (NULL);
status = pcap_set_snaplen(p, snaplen); // 设置包的最大长度
if (status < 0)
goto fail;
status = pcap_set_promisc(p, promisc); //设置混杂模式
if (status < 0)
goto fail;
status = pcap_set_timeout(p, to_ms); // 设置超时时间
p->oldstyle = 1;
status = pcap_activate(p);
if (status < 0)
goto fail;
return (p);
}
pcap_create 里会调用 pcap_create_interface() 函数 ,而不同的操作系统环境会调用不同的pcap_create_interface函数。(可由编译宏来指定特定的pcap_create_interface来初始化read_op等函数指针。linux环境里默认是libpcap/pcap-linux.c中的 pcap_create_interface())
pcap_t *
pcap_create_interface(const char *device, char *ebuf)
{
pcap_t *handle;
handle = pcap_create_common(ebuf, sizeof (struct pcap_linux)); // 初始化一个pcap_t 结构体
if (handle == NULL)
return NULL;
//为pcap_t 的激活函数指针填充具体实现函数
handle->activate_op = pcap_activate_linux;
handle->can_set_rfmon_op = pcap_can_set_rfmon_linux;
return handle;
}
调用status = pcap_activate( p ),该函数执行status = p->activate_op( p ) ,
进而调用 pcap_activate_linux(), 完成read_op等重要函数指针的具体赋值。
static int
pcap_activate_linux(pcap_t *handle)
{
struct pcap_linux *handlep = handle->priv;
const char *device;
int is_any_device;
struct ifreq ifr;
int status = 0;
int ret;
device = handle->opt.device;
handle->inject_op = pcap_inject_linux;
handle->setfilter_op = pcap_setfilter_linux; // 设置过滤规则
handle->setdirection_op = pcap_setdirection_linux;
handle->set_datalink_op = pcap_set_datalink_linux;
handle->getnonblock_op = pcap_getnonblock_fd;
handle->setnonblock_op = pcap_setnonblock_fd;
handle->cleanup_op = pcap_cleanup_linux;
handle->read_op = pcap_read_linux; // 捕获包会调用这个接口
handle->stats_op = pcap_stats_linux;
...
ret = activate_new(handle, is_any_device);
if (ret < 0) {
if (ret != PCAP_ERROR_NO_PF_PACKET_SOCKETS) {
return ret;
}
ret = activate_old(handle, is_any_device);
if (ret != 0) {
status = ret;
goto fail;
}
}
...
handle->selectable_fd = handle->fd;
return status;
}
目前的liunx 系统用的协议簇 PF_PACKET 来获取所有到网口的包 ,而liunx 老的版本有一个特殊的套接字类型SOCK_PACKET 来实现这一特性的。所以为了兼容老版本,会看到activate_new 失败后 会调用一下activate_old 。正常情况下,我们分析activate_new的即可。
static int
activate_new(pcap_t *handle, int is_any_device)
{
struct pcap_linux *handlep = handle->priv;
const char *device = handle->opt.device;
int status = 0;
int sock_fd, arptype;
sock_fd = open_pf_packet_socket(handle, is_any_device);
if (sock_fd < 0) {
return sock_fd;
}
handlep->sock_packet = 0;
. . .
if (handlep->cooked) {
if (handle->snapshot < SLL_HDR_LEN + 1)
handle->snapshot = SLL_HDR_LEN + 1;
}
handle->bufsize = handle->snapshot;
//根据以太网链路层类型决定VLAN Tag在报文中的偏移值
switch (handle->linktype) {
case DLT_EN10MB:
handlep->vlan_offset = 2 * ETH_ALEN;
break;
case DLT_LINUX_SLL:
handlep->vlan_offset = 14;
break;
default:
handlep->vlan_offset = -1; /* unknown */
break;
}
...
其中 open_pf_packet_socket 函数是关键,里面创建了socket 和底层通讯,也是通过创建的socket来实现抓包。
static int
open_pf_packet_socket(pcap_t *handle, int cooked)
{
int protocol = pcap_protocol(handle);
int sock_fd, ret;
/*
* Open a socket with protocol family packet. If cooked is true,
* we open a SOCK_DGRAM socket for the cooked interface, otherwise
* we open a SOCK_RAW socket for the raw interface.
*/
sock_fd = cooked ?
socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_DGRAM, protocol) :
socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, protocol);
return sock_fd;
}
该函数根据cooked 的值,调用socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_DGRAM, protocol) :还是
socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, protocol);
这两个创建的socket 函数有啥区别呢?
- socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_DGRAM, htons(ETH_P_ALL))
当指定SOCK_DGRAM时,获取的数据包是去掉了数据链路层的头(link-layer header) - socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL))
当指定SOCK_RAW时,获取的数据包是一个完整的数据链路层数据包
发现libpcap 库是在抓any 网口的包时,cooked 值为true.
至此pcap_open_live 函数 完成了捕获数据的网络接口的准备 ,把pcap_t 结构体返回了出去。
2 pcap_compile 函数分析
若是想分析pcap_compile 你必须对bpf规则有一定的了解,该函数的主要工作就是创建一个bpf的结构体。后面pcap_setfilter 会把生产的规则设置到内核,让规则生效。该函数不打算深入分析。这里稍微提下bpf规则。你理解了这部分,你再去看代码应该会事半功倍。
tcpdump -d 会把匹配信息包(也就是规则)以人们能够理解的汇编格式给出
[root@wus ~]# tcpdump host 10.68.22.189 -d
(000) ldh [12]
(001) jeq #0x800 jt 2 jf 6
(002) ld [26]
(003) jeq #0xa4416bd jt 12 jf 4
(004) ld [30]
(005) jeq #0xa4416bd jt 12 jf 13
(006) jeq #0x806 jt 8 jf 7
(007) jeq #0x8035 jt 8 jf 13
(008) ld [28]
(009) jeq #0xa4416bd jt 12 jf 10
(010) ld [38]
(011) jeq #0xa4416bd jt 12 jf 13
(012) ret #65535
(013) ret #0
分析 上面汇编指令含义
- 第一行 (000) 表示你收到一个数据包,从第12个字节开始分析,而数据包要是从链路层开始,前12个字节表示mac,从12个字节后,刚好对应2字节的链路层协议类型
- 第二行(001) 表示链路层类型为 0x800 的 就执行jt 2 (跳到002指令执行)否则要是不等于0x800 就执行 jf 6(跳到006指令执行 ) (备注一般链路层协议都是0x800 Internet Protocol packet)
- 第三行(002) 表示从包的第26个字节开始
- 第四行(003) #0xa4416bd 其实就是 10.68.22.189 这个ip地址 表示源地址。而你对ip/tcp 协议比较清楚的话,链路层14个字节,ip层要是没有扩展字节的情况下20个字节,源地址ip就是在26个字节后四个字节。
。。。后面就按照上面的分析即可。
上面的规则对应代码结构体其实就是
struct sock_filter { /* Filter block */
__u16 code; /* Actual filter code */
__u8 jt; /* Jump true */
__u8 jf; /* Jump false */
__u32 k; /* Generic multiuse field */
};
其中code元素是一个16位宽的操作码,具有特定的指令编码。jt和jf是两个8位宽的跳转目标,一个用于条件“跳转如果真”,另一个“跳转如果假”。最后k元素包含一个可以用不同方式解析的杂项参数,依赖于code给定的指令。
3 pcap_setfilter 函数分析
pcap_setfilter 函数其实就是调用的 pcap_open_live 函数里激活函数设置的 pcap_setfilter_linux ,而pcap_setfilter_linux 函数 里面调用了pcap_setfilter_linux_common 函数
static int
pcap_setfilter_linux_common(pcap_t *handle, struct bpf_program *filter,
int is_mmapped)
{
struct pcap_linux *handlep;
#ifdef SO_ATTACH_FILTER
struct sock_fprog fcode;
int can_filter_in_kernel;
int err = 0;
#endif
if (!handle)
return -1;
if (!filter) {
pcap_strlcpy(handle->errbuf, "setfilter: No filter specified",
PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE);
return -1;
}
handlep = handle->priv;
if (install_bpf_program(handle, filter) < 0) // 该函数主要将libpcap bpf规则结构体,转换成符合liunx内核的 bpf规则,同时校验规则是否符合要求格式。
/* install_bpf_program() filled in errbuf */
return -1;
...
if (can_filter_in_kernel) {
if ((err = set_kernel_filter(handle, &fcode)) == 0) // 关键函数
{
handlep->filter_in_userland = 0;
}
}
...
return 0;
主要看set_kernel_filter 关键函数
static int
set_kernel_filter(pcap_t *handle, struct sock_fprog *fcode)
{
int total_filter_on = 0;
int save_mode;
int ret;
int save_errno;
...
ret = setsockopt(handle->fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ATTACH_FILTER,
fcode, sizeof(*fcode));
if (ret == -1 && total_filter_on) {
save_errno = errno;
if (reset_kernel_filter(handle) == -1) {
pcap_fmt_errmsg_for_errno(handle->errbuf,
PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE, errno,
"can't remove kernel total filter");
return -2; /* fatal error */
}
errno = save_errno;
}
return ret;
}
最终其实是调用了 setsockopt(handle->fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ATTACH_FILTER,fcode, sizeof(*fcode));函数将规则 通过SO_ATTACH_FILTER 下发给内核底层,从而让规则生效。
4 pcap_loop 函数分析
规则设置好了,socket 其实也已经创建了,最后一部其实就是抓包了。而怎么抓包了,其实就是recvfrom 设置好的socket
int
pcap_loop(pcap_t *p, int cnt, pcap_handler callback, u_char *user)
{
register int n;
for (;;) {
if (p->rfile != NULL) {
n = pcap_offline_read(p, cnt, callback, user);
} else {
do {
n = p->read_op(p, cnt, callback, user);
} while (n == 0);
}
if (n <= 0)
return (n);
if (!PACKET_COUNT_IS_UNLIMITED(cnt)) {
cnt -= n;
if (cnt <= 0)
return (0);
}
}
}
可以看到调用了回调函数 p->read_op(p, cnt, callback, user); 而回调函数就是在pcap_open_live 设置的 pcap_read_linux 函数,该函数里面调用了pcap_read_packet 函数。
static int
pcap_read_packet(pcap_t *handle, pcap_handler callback, u_char *userdata)
{
struct pcap_linux *handlep = handle->priv;
u_char *bp;
int offset;
#ifdef HAVE_PF_PACKET_SOCKETS
struct sockaddr_ll from;
#else
struct sockaddr from;
#endif
ssize_t packet_len;
int caplen;
struct pcap_pkthdr pcap_header;
if (handlep->cooked) {
if (handle->linktype == DLT_LINUX_SLL2)
offset = SLL2_HDR_LEN;
else
offset = SLL_HDR_LEN;
} else
offset = 0;
bp = (u_char *)handle->buffer + handle->offset;
do {
if (handle->break_loop) { // 当 pcap_breakloop() 调用时会跳出循环
handle->break_loop = 0;
return PCAP_ERROR_BREAK;
}
fromlen = sizeof(from);
packet_len = recvfrom(handle->fd, bp + offset,
handle->bufsize - offset, MSG_TRUNC,
(struct sockaddr *) &from, &fromlen); // 就是通过该抓包
} while (packet_len == -1 && errno == EINTR);
...
if (!handlep->sock_packet) {
if (handlep->ifindex != -1 && from.sll_ifindex != handlep->ifindex)
return 0;
if (!linux_check_direction(handle, &from)) // 根据方向会过滤数据
return 0;
}
pcap_header.caplen = caplen;
pcap_header.len = (bpf_u_int32)packet_len;
handlep->packets_read++;
/* Call the user supplied callback function */
callback(userdata, &pcap_header, bp); // 调用回到函数
return 1;
每次抓到一个完整包都会调用一次回调函数,同时linux_check_direction 函数 会根据方向丢弃不需要的包,而这里面还有个重要的性质,就是抓的lo口,你要是抓包能抓到两条相同的数据包,因此linux_check_direction 对于lo口的包还做了相关处理。
static inline int
linux_check_direction(const pcap_t *handle, const struct sockaddr_ll *sll)
{
struct pcap_linux *handlep = handle->priv;
/*Outgoing packet. If this is from the loopback device, reject it;we'll see the packet as an incoming packet as well,*/
if (sll->sll_pkttype == PACKET_OUTGOING) {
if (sll->sll_ifindex == handlep->lo_ifindex)
return 0;
if ((sll->sll_protocol == LINUX_SLL_P_CAN ||
sll->sll_protocol == LINUX_SLL_P_CANFD) &&handle->direction != PCAP_D_OUT)
return 0;
if (handle->direction == PCAP_D_IN)
return 0;
} else {
if (handle->direction == PCAP_D_OUT)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
四 总结
对libpcap库关键函数分析下来,它是如何实现最终抓包的呢?其实是它函数内部调用几个真正跟内核交互的几个函数。
- pcap_open_live 函数调用了 sock_fd = cooked ?socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_DGRAM, protocol) :socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, protocol); 来创建一个socket套接字
- pcap_setfilter 函数调用了 setsockopt(handle->fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ATTACH_FILTER, fcode, sizeof(*fcode)); 将规则设置到内核,从而内核可以根据该应用层设置的规则,过来数据
- pcap_loop 函数本质就是根据创建的socket循环接收数据包 packet_len = recvfrom(handle->fd, bp + offset,handle->bufsize - offset, MSG_TRUNC,(struct sockaddr *) &from, &fromlen);
注意点:
- 创建socket 是SOCK_DGRAM 还是SOCK_RAW,你会发现libpcap处理方式是不一样的,还会根据不同协议,偏移量来处理包。这个后续要是处理到对应协议,可以再参考libpcap 。
- lo口的包是能抓到两次的,libpcap库是做了处理的,当是PACKET_OUTGOING 的数据包直接就丢弃了。
最后本篇其实只分析了用户层做了哪些处理,通过哪些函数跟内核层交互的。其实真正的原理还是在内核,内核层收到用户层如何处理的才是关键,中篇会继续深入分析。。。。。。未完待续