Qualcomm messaging Interface(QMI)消息定义概述
QMI概述
QMI是高通提供的一种多处理器进程间通信的功能接口,用于AP和BP侧的交互,通俗说法就是让终端设备TE(可以是手机,PDA,计算机)对高通BP侧的AMSS系统进行操作,如调用函数,读取数据,设置其中的NV项等。
其具有的特点如下:
- 具有同步和异步接口;
- 支持在在多个处理器之间进行通信;
- 良好的可扩展性;
- 支持多客户端并发运行;
- 支持多个服务端并发运行,且每个服务端还对应多个客户端;
- 每个服务端还支持版本信息;
QMI的消息路由通过IPC Router来完成,IPC路由器是一个面向消息(message-oriented)的路由器,用于支持Qualcomm commo client interface(QCCI)以及Qualcomm common service interface(QCSI)。
QCCI是一套用于客户端从服务器接收信息或者发送消息到服务器的API集合。
QCSI则是与QMI IDL(interface definition language)自动编译生成的代码一起使用,用于接收客户端的请求及对其作出响应。另外,它也用来发送指示消息(indication message)以及对消息进行编解码(encode/decode),这个消息由server端主动发出。
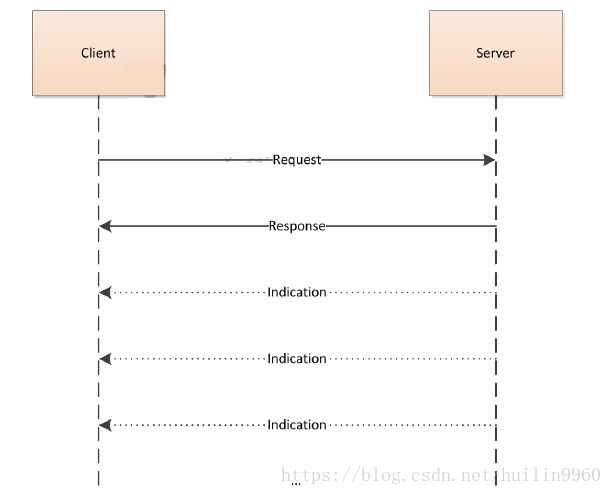
每一个服务都对应于一个service.idl的文件定义。.idl文件定义了每一个massage相关的常量,枚举类型以及和消息相关的数据结构。消息的类型有如下三种:
Request message ——一条request消息由客户端发往服务端,并由服务端进行处理。
Reponse message——每一个request的消息都会有一个reponse消息与之对应,类似于一个函数的返回值。如果请求消息等效于调用函数,则响应消息等效于返回给调用方的结果。
Indiction message——这类消息是由服务端发给客户端的异步消息。sensor1 API的规范要求:在任何indication message发送之前,客户端首先需要通过request message与服务端建立连接。indication消息可以在任何时候发送。
客户端与服务端的消息发送形式如下:
请求QMI消息
每一个server都应该支持如下的消息请求,每一条消息都有固定的消息ID,当每一个服务定义了以后,都需要在第一条定义一个cancel的消息类型,第二条为version 的消息。
service {
//! @ID _CANCEL
sns_common_cancel_req_msg _CANCEL_REQ,
sns_common_cancel_resp_msg _CANCEL_RESP
= 0x00; // msg ID 0
//! @ID _VERSION
sns_common_version_req_msg _VERSION_REQ,
sns_common_version_resp_msg _VERSION_RESP
= 0x01; // msg ID 1
… …
} = _SERVICE_ID; 取消所有的请求cancel msg(message id = 0)
该条消息类型用于取消该客户端与指定服务端的所有消息请求。当该消息请求发送到服务端,服务端将会deregister所有未完成的请求,并且停止向客户端发送indication message。
该消息体可以为null,且reponse消息会携带成功码。
获取版本get version(message id = 1)
该条消息类型用于获取服务端的版本。
QMI消息编码标准
1. 不使用浮点型数据,而是使用Q16类型的固定点数,即提供16位2位补码整数部分和16位小数部分的定点实现。
2. 命名约定
- 为了使所有消息实现保持一致,service端需要固定的独有的前缀
- 结构体以_type结尾
- 枚举以_enum结尾
- 请求消息以_req_msg结尾,类型以_REQ结尾
- 消息回应以_resp_msg结尾,类型以_RESP结尾
- 指示消息以_ind_msg结尾,类型以_IND结尾
QMI IDL Service实现样例
这里将以rotation vector service为例,讲解怎样通过.idl文件来定义service端的QMI消息。
IDL服务定义
上面提到,所有的消息类型都要以cancel开头,接着是version的定义开始,且要有其相应的类型结尾,如
*_req_msg
*_resp_msg
*_ind_msg//======================================================================
// Service definition
//======================================================================
service SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_SVC {
//! @ID SNS_COMMON_CANCEL
sns_common_cancel_req_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_CANCEL_REQ,
sns_common_cancel_resp_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_CANCEL_RESP
= 0x00;
//! @ID SNS_COMMON_VERSION
sns_common_version_req_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_VERSION_REQ,
sns_common_version_resp_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_VERSION_RESP
= 0x01;
//! @ID SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_ENABLE
sns_sam_rotation_vector_enable_req_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_ENABLE_REQ,
sns_sam_rotation_vector_enable_resp_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_ENABLE_RESPs
= 0x02;
//! @ID SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_DISABLE
sns_sam_rotation_vector_disable_req_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_DISABLE_REQ,
sns_sam_rotation_vector_disable_resp_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_DISABLE_RESP
= 0x03;
//! @ID SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_REPORT
sns_sam_rotation_vector_report_ind_msg SNS_SAM_ROTATION_VECTOR_REPORT_IND
= 0x05;
} = SNS_QMI_SVC_ID_18;消息定义
消息类型也在.idl中进行定义
message {
mandatory uint32 report_period;
optional uint32 sample_rate;
optional uint8 coordinate_sys;
optional sns_suspend_notification_s notify_suspend;
} sns_sam_rotation_vector_enable_req_msg;由上可知,消息类型定义了四种元素,每一种都有其强制或者可选的来标识。将IDL文件进行编译可以生成如下的C类型的结构:
typedef struct {
/* Mandatory */
uint32_t report_period;
/* Optional */
uint8_t sample_rate_valid; /**< Must be set to true if sample_rate is being passed */
uint32_t sample_rate;
/* Optional */
uint8_t coordinate_sys_valid; /**< Must be set to true if coordinate_sys is being passed */
uint8_t coordinate_sys;
/* Optional */
uint8_t notify_suspend_valid; /**< Must be set to true if notify_suspend is being passed */
sns_suspend_notification_s_v01 notify_suspend;
}sns_sam_rotation_vector_enable_req_msg_v01; /* Message */在IDL消息结构中定义为可选的元素将在相应的C结构中产生两个字段,第一个字段指示后续字段的值是否有效。
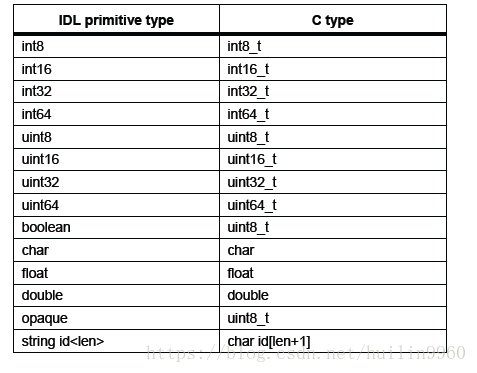
IDL原始类型每个映射到一个C类型,它将用于IDL编译生成的.c和.h文件中的对应字段。
客户端使用SMGR的实例,这在之前的文章中我们已经见过具体的使用方法了。
// Include the sensor framework APIs
#include "sensor1.h"
// Include the Sensor Manager service
#include "sensor_smgr_01.h"
sensor_handle_type *my_handle;
// Callback function to handle incoming data
// NOTE: This function is called in the context of a sensor
// framework thread.
void my_data_callback(int32 cb_data,
void* msg_ptr,
int32 msg_id,
sensor1_type_of_message_type msg_type,
int8 txn_id,
int32 svc_number)
{
int i;
if(msg_type == SENSOR1_COMMAND) {
// handle an error!
}
// Copy the data somewhere:
if(svc_number == SENSOR_MGR_SVC_ID)
{
if(msg_type == SENSOR1_INDICATION)
{
switch(msg_id)
{
SENSOR_REPORT_IND:
{
for( i=0; i < ((sensor_report_ind_msg_V01*)msg_ptr)->report_len;i++)
{
// For each data element in the report, put a message in our
// client message queue
sensor_report_data_type_V01 *report =
((sensor_report_ind_msg_V01*)msg_ptr)->report[i];
my_queue_put(report->data, report->data_len);
}
}
break;
}
}
}
// Signal the client thread to process the queue
os_signal( client_thread );
sensor1_free_msg_buf( msg_ptr );
}
// Callback function to let the client know data can now
// be written
// NOTE: This function is called in a sensor framework thread,
// and should return quickly.
void my_writable_cb(uint32 cb_data)
{
// Signal the client thread that writing is now possible
os_signal(client_thread);
}
// Setup a sensor report
void my_accel_report_request(void)
{
sensor_report_req_msg_V01 *req_ptr;
report_req_ptr = sensor1_alloc_msg_buf(sizeof(sensor_report_req_msg_V01));
if(req_ptr == NULL)
{
// handle an error!
}
req_ptr->report_id = 1; // Use any client-defined report ID here.
req_ptr->report_type = SENSOR_REPORT_TYPE_PERIODIC;
req_ptr->report_interval = -30; // 30 Hz
// Configure just one report for accel data
req_ptr->config_len = 1;
req_ptr->config[0].sensor_type = SENSOR_TYPE_ACCEL;
req_ptr->config[0].report_unit = SENSOR_REPORT_UNIT_ENGINEERING;
req_ptr->config[0].scale_factor = 0; // No scalling.
req_ptr->config[0].oversample_rate = 0; // No oversampling
req_ptr->config[0].sensor_sensitivity = 0; // Default sensitivity
req_ptr->config[0].decimation = 1; // Average multilpe samples if the sensor
// is running at a higher sampling rate.
if(sensor1_write(my_handle,req_ptr,SENSOR_REPORT_REQ,
sizeof(sensor_report_req_msg_V01),1,SENSOR_MGR_SVC_ID)
== SENSOR1_WOULDBLOCK)
{
// Can't send the message now.
sensor1_writable( my_handle, my_writable_cb,0 /* Data to be passed to the callback function */);
}
}
void my_init(void)
{
// Register this client with the sensor framework
sensor1_open( my_handle, my_data_callback, 0 /* Data to be passed to the callback function */);
}QMI之QCCI接口
下面主要列出QCCI的主要接口。
1 建立连接:
qmi_client_notifier_init
qmi_client_get_service_list
qmi_client_init2 断开连接:
qmi_client_release3 发送消息
qmi_client_send_msg_sync
qmi_client_send_msg_async
qmi_client_send_raw_msg_sync
qmi_client_send_raw_msg_async4 回调函数类型
qmi_client_ind_cb
qmi_client_recv_msg_async_cb
qmi_client_recv_raw_msg_async_cb5 编解码API
qmi_client_message_encode
qmi_client_message_decodeQCCI发送同步消息流程
// Sends a synchronous QMI service message on the specified connection.
extern qmi_client_error_type
qmi_client_send_msg_sync
(
qmi_client_type user_handle,
int msg_id,
void *req_c_struct,
int req_c_struct_len,
void *resp_c_struct,
int resp_c_struct_len,
int timeout_msecs
)QCCI发送异步消息流程
// Sends a asynchronous QMI service message on the specified connection.
qmi_client_error_type
qmi_client_send_msg_async
(
qmi_client_type user_handle,
unsigned long msg_id,
void *req_c_struct,
int req_c_struct_len,
void *resp_c_struct,
int resp_c_struct_len,
qmi_client_recv_msg_async_cb resp_cb,
void *resp_cb_data,
qmi_txn_handle *txn_handle
)TLV数据格式如下(Type-Length-Value)
使用encode方法进行编码,decode方法进行解码
// Encodes a message
qmi_client_error_type
qmi_client_message_encode
(
qmi_client_type user_handle,
qmi_idl_type_of_message_type req_resp_ind,
int message_id,
const void *p_src,
int src_len,
void *p_dst,
int dst_len,
int *dst_encoded_len
)
// Decodes a message
qmi_client_error_type
qmi_client_message_decode
(
qmi_client_type user_handle,
qmi_idl_type_of_message_type req_resp_ind,
int msg_id,
const void *p_src,
int src_len,
void *p_dst,
int dst_len
)由于很多文档及代码涉及高通私密许可和权限问题,不能再这里贴出,还请见谅..........