概述
在面试或者浏览技术网站时,经常会遇到这样一个问题:ES6 和 ES5 的继承机制有哪些不同 ? 本文章带你深入了解 ES6 和 ES5 继承的原理。
原型链
聊 js 的继承,肯定是绕不开原型链,我们先来复习一下 js 的原型链:
('').__proto__ === String.prototype // true
({}).__proto__ === Object.prototype // true
Object.prototype.__prototype === null // true
function Person () {}
Person.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true
(new Person).__proto__ === Person.prototype // true
(class {}).__proto__ === Function.prototype // true
Function instanceof Function // true
Object instanceof Function // true从这里我们可以看出,字符串、对象、函数等内置一些方法是因为原型链 __proto__ 指向了相应的构造函数的原型 prototype ,从而继承了原型上的方法。 在 Javascript 中也是通过原型链来实现继承,先说 es6的 class
ES 6 class
class Person {
constructor (name) {
this.name = name
}
walk () {}
// 静态属性
static staticFun = function () {
console.log('staticFun')
}
}
class Student extends Person {
constructor (name) {
super(name)
this.school = 'NO.3 middle school'
}
learn () {}
}
const ming = new Student()
ming.learn()
ming.walk()
Student.staticFun()例子中,ming 有 learn 方法是因为,ming 的 __proto__ 指向 Student 类的原型
ming.__proto__ === Student.prototype // trueming 有 walk 方法是因为 Student 的原型能通过 __proto__ 连接到父类的原型,能找到父类的 walk 方法
Student.prototype.__proto__ === Person.prototype
ming.__proto__.__proto__ === Person.prototype但是,为什么 Student 为什么继承了 staticFun 方法 ? Student 通过自己原型的 __proto__ 去寻找肯定找不到,因为父类的原型上根本就没有这个方法,这个是一个静态的方法。
其实不仅 Student.prototype 有 __proto__ Student 有自己的 __proto__ ,而他的原型链指向父类的构造函数:
Student.__proto__ === Person // true这就解释了,Student 类上没有静态函数 staticFun,进而通过原型链向上寻找,发现 Person 类有静态方法 staticFun。
ES5 的继承
JavaScript 高级程序设计(第三版)提到寄生组合式继承:
function SuperType (name) {
this.name = name
}
SuperType.staticFun = function () { console.log('staticFun') }
SuperType.prototype.sayName = function () { return this.name }
function SubType (name, age) {
SuperType.call(this, name)
this.age = age
}
SubType.prototype = Object.create(SuperType.prototype)
SubType.prototype.constructor = SubType
SubType.prototype.sayAge = function () { return this.age }
const demo = new SubType('ming', 22)
demo.sayAge() // ming
demo.sayName() // 22
SubType.staticFun() // throw TypeErrordemo 的 sayAge 、sayName 方法正常调用可以预期到:
demo.__proto__ === SubType.prototype // true
SubType.prototype.__proto__ === SuperType.prototype // true那么,为什么 SubType 没有 staticFun 方法呢 ?肯定是 SubType.__proto__ 没有指向 SuperType ,那指向哪里了呢?
SubType.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true
SuperType.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true还记得文章开始,原型链部分的复习吗?
function Person () {}
Person.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true这里就可以发现,传统的寄生组合式继承方式与 ES6 class 的一个区别,无法自动继承父级的静态方法。
要想实现静态方法的继承也很简单,只需要修改 SubType 的原型链,指向到 SuperType 即可:
SubType.__proto__ = Super // 或者 Object.setPrototypeOf(SubType, SuperType)
SubType.staticFun() // staticFun总结
两者继承机制不同
ES5 中,子类对于父类构造函数的继承时,子类的 this 已经存在,通过 SuperType.call(this, ...args) 的方式来修改子类的 this
而 ES6 的子类必须要调用 super(...args) 来生成 this
两者构造函数的原型链指向不同
ES5 的子类和父类的构造函数函数的原型链都指向 Function.prototype
而 ES6 的子类的构造函数的原型链指向父类的构造函数
附录
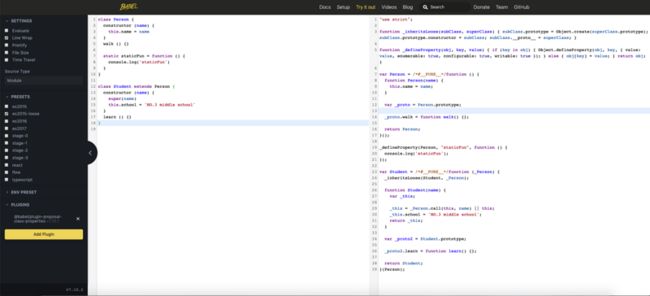
贴一张 babel 编译 ES6 class 为 ES5 的图片: