(小游戏)详解前端俄罗斯方块代码:HTML+JS+CANVAS实现原理
喜欢就给我点个星吧:https://github.com/Chenyating/easyGame
想写个俄罗斯方块的小游戏,发现网上的各位大佬的代码,我看不明白。
好吧,其实我一直都看不懂别人的代码。
可是,flag已经立了,写肯定是要写的啦。
嗯……还是自力更生,自给自足。撸起袖子,说写就写。现在就说说我自己的经验;
查看效果,请点击这个地址哦~,你们可以玩一把,告诉我需要改进的地方:http://www.yating.online/game/tetris.html
不介意的话,贪吃蛇也可以哦:http://www.yating.online/game/retroSnaker.html
最终效果图为:手指滑动屏幕即可。
俄罗斯方块显然比贪吃蛇难度大点。
但是
经过我的一步一步分析,我似乎看到了一条明朗的道路,现在我将我是如何一步一步的写出这俄罗斯方块的过程告诉你们吧。
第一步:俄罗斯单方块——shap【】 和 游戏界面——all【】;
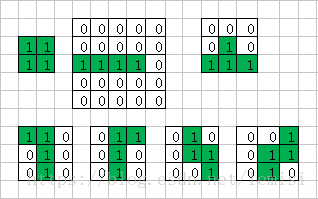
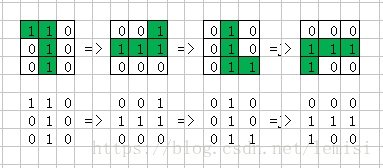
1.1:我们来分析一下,俄罗斯单个方块有7种不同的样子,以下我用Excel表格,画出这7个类型。
1.2:其中,上色状态为:0表示没有颜色,1表示有颜色。这7个类型的俄罗斯单方块,我暂且用shap数组来表示他们
以下开始以shap来表示单方块。例如:
所以,shap就有7种不同的值;
为什么要是一个正方形呢?这样就方便我们去旋转改变shap的方向;
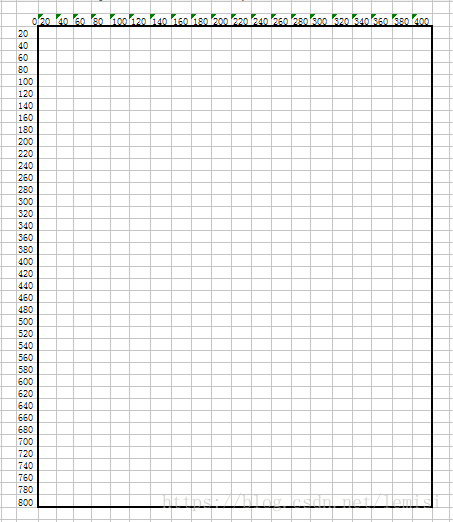
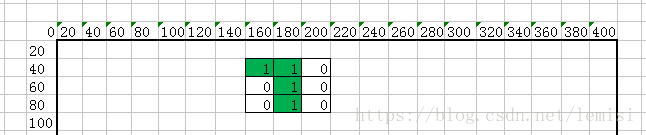
1.3:接着设置一下游戏的界面,是这一个宽400 * 高800 的canvas 画布,其中小小方格![]() 的尺寸为20*20;
的尺寸为20*20;
这个画布是一张二维数组的表,shap们会在这个表堆积起来。我将这个表叫all[ ]。
所以我们已经得出了,横的有20个小方格,竖的有40个小方格;
默认每个小方格都是不上色的,例如all【1,1】=0表示 小小方格位置在【1,1】是没有上色的;
//初始化堆积方块
for (let i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
this.all[i] = new Array(0);
for (let j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
this.all[i][j] = 0;
}
}根据上色的小方格,我们就可以知道all对应的值:
1.4:现在我们开始初始化,shap的各个形状。
shap的【】每个值,也就是每个小方块:![]() 都存3个数值,它们分别表示x坐标,y坐标,上色状态(0或1);
都存3个数值,它们分别表示x坐标,y坐标,上色状态(0或1);
- shap【i】【j】【0】---->x;
- shap【i】【j】【1】---->y;
- shap【i】【j】【2】---->上色状态;
我们主要改变的是shap【i】【j】【2】的值,即上色状态;
通过x和y我们就能得到小小方格在all的位置:(x/20,y/20 )
radomID:表示随机的初始化第radomID种shap;因为shap肯定是要在整个all看不到的上面中间,所以200是默认的中间位置,y 必须设置成小于0;以下就是,shap【】的7种初始状态:都在all画布之上。
switch (this.radomID) {
case 0:
//长条
let defaultX = 200;
let defaultY = -60;
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
defaultX = 200;
if (i == 2) {
this.$set(this.shap, i, [
[defaultX, defaultY, 1],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 1],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 1],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 1],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0]
]);
} else {
this.$set(this.shap, i, [
[defaultX, defaultY, 0],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0]
]);
}
defaultY += 20;
}
console.log(this.shap)
break;
case 1:
//正方形
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -40, 1],
[220, -40, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -20, 1],
[220, -20, 1]
]);
break;
case 2:
//正7
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 1],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 0],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 1],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
case 3:
//反7
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 0],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 0],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 1],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
case 4:
//正2
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 1],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 0],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 0],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
case 5:
//反2
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 0],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 1],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 0],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
case 6:
//土
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 0],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 1],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 0],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
default:
break;
}
1.5:现在我们来写一个每次出现随机的shap的方法吧:radomShap()。
radomShap() {
this.scope += 1;
this.pain();
this.radomID = parseInt(Math.random() * 7);
// this.deleteShap();
this.shap.splice(0, this.shap.length); //清空存放单方块的数组
//shap数组开始存储不同单方块
【这里是随机的shap初始状态,上面已经展示过代码了,这里就不在复制了】
this.rotate();
this.painShap();
},每次随机出现一个shap,就要执行这些操作;
- 分值就要加1分;
- 然后开始准备画笔:pain()
- 随机生成一个shap编号。
- 然后清空之前存储过的shap【】数据,
- 开始存储新的随机shap形状。
- 因为初始的shap形状都是固定住的,这里我们还要在出一个随机的旋转状态的shap。这里就使用rotate()方法来旋转shap【】,这个时候shap【】的值也发生了变化;
- 变化后的shap【】,我们就可以开始绘制shap【】。这里就使用painShap()方法;
pain():设置一下要画的颜色黑色;
//绘制
pain() {
var c = document.getElementById("stage");
this.context = c.getContext("2d");
this.context.fillStyle = "#000000";
},
rotate():随机0-3次shap;这里我们可以先不看这个代码,下面我再解释这个旋转的问题;
painShap():绘制shap【】。当shap【i】【j】【2】==1的时候,我们就给它上色;为0我们就不管它;
painShap() {
for (var i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.fillRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
}
}
},第二步:旋转rotate();
现在我们就来讲旋转的这个问题;
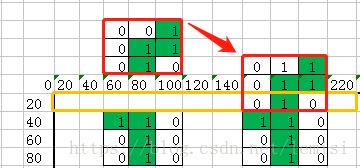
2.1:如果要把一个shap,旋转90度,有什么变化呢?
没错,我们已经看出来,旋转90度,就是把行变列,列变行。我们只要把上色状态改变一下就可以了。
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = this.shap[i].length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
shap1[i][j][2] = this.shap[this.shap[i].length - 1 - j][i][2];
}
}
那现在我们就可以开始写rotate()随机旋转的方法了:
//旋转90度的方法
rotate() {
var changge = parseInt(Math.random() * 4);
console.log("变" + changge + "次")
for (i = 0; i <= changge; i++) {
let shap1 = [];
// 深拷贝
shap1 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.shap));
//行变列。列变行,把结果先存在shap1里;
【行变列。列变行,把结果先存在shap1里。这里上面已经展示过代码了,就不复制了。】
}
this.deleteShap();
//那么就把shap1的值赋给shap
this.shap = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(shap1));
this.painShap();
}
},deleteShap()方法:将最初shap【】的上色小方块给清理掉。
因为每次变化shap【】我们就要清除原来最初的shap【】。
清理完之后,才用painShap方法绘制新的shap【】
//清除单方块形状
deleteShap() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
}
}
},
2.2:我们还得再写一个单次旋转不随机的方法:change()。
因为玩游戏的时候,肯定不能随机旋转吧,肯定是按照顺时针一步一步来旋转改变shap【】的,所以就有了change()。这个时候旋转是不受控制的。
我们在旋转过程中,就要考虑到这几个问题:
- 旋转的时候,shap上次的部分不能超出all画布:x坐标的范围必须在0-380之间;y坐标必须小于780;为啥y可以小于0?因为我初始的时候shap的y坐标就已经小于0了哦~
- 旋转的时候,shap不能碰到已经堆积好的方块(all【i】【j】=1)。
先插入一个广告:
这个小方块的x,y表示的是左上角的坐标。所以x在all的范围是0-380;y是0-780。一下就是判断的方法;
for (let i = 0; i < shap1.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < shap1[i].length; j++) {
try {
if (
((shap1[i][j][0] < 0 || shap1[i][j][0] > 380||shap1[i][j][1] > 780) && shap1[i][j][2] == 1) || (this.all[this.shap[i][j][1] / 20][this.shap[i][j][0] / 20] == 1)) {
//两个同时成立退出;
return;
}
} catch (error) {
}
}
}这样我们就可以开始写change()了。
change() {
let shap1 = [];
// 深拷贝
shap1 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.shap));
//行变列。列变行,把结果先存在shap1里;
【行变列。列变行,把结果先存在shap1里。这里上面已经展示过代码了,就不复制了。】
//判断一下,改变方向以后,会不会超出墙||碰到堆积好的方块;
【改变方向以后,会不会超出墙||碰到堆积好的方块;这里上面已经展示过代码了,就不复制了。】
this.deleteShap();
//那么就把shap1的值赋给shap
this.shap = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(shap1));
this.painShap();
}
}第三步:移动:左移动,右移动,下移动;
3.1:左右移动 left()和right():每向左右移动一次,x坐标都要+-20;
以左移动为例:每次移动都要清除原来的上色shap【】哦~
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
this.shap[i][j][0] -= 20;
}
}但是我们要考虑的问题就有:
- x再怎么加都不能超过380;再怎么减都不能少于0;
- 每次左右移动的时候,如果碰到已经堆积好的方块们,就不能再左右移动了。
现在我们就可以写左移动的方法:left():
// 向左
left() {
//判断左移动的过程中是否会与下一层堆积好的方块重叠;是否会超过范围;如果会的话,就开始把shap加入this.all然后退出;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
var y = this.shap[i][j][1] / 20;
var x = this.shap[i][j][0] / 20;
try {
//因为x可能会等于0;所以用try,catch过滤掉好了。不想管。。。。
if (
(this.shap[i][j][0] < 20 || this.all[y][x - 1] == 1) && this.shap[i][j][2] == 1
) {
//左边有东西||或者靠墙了。不要向左了。
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// console.log("有bug")
}
}
}
//经过两个判断结束以后,没有符合,继续向左移动
【左移动,上面已经展示过代码,不在复制】
this.painShap();
},左右代码同理;此处就不再展示了。
3.2:下降down():向下,y坐标就是+20;
然而在下降的过程中,我们要考虑什么问题呢?
- 我下降的时候,不能再下降了,还能不能继续下降?
- 我下降的时候,会不会超出y坐标会不会超过780?或者碰到了,已经堆积好的方块们,要怎么办?
- 我下降的时候,满格了要怎么办?
现在我们就来一一解决这些问题。
解决这些问题,那么下降down()的方法也就出来来。
第一个问题:当红框要继续下降的话,这个时候,游戏就应该结束了。因为接下去新的shap的第二层就放不到all里。
所以我们我们可以看到all【0】,也就是画布的第一行橙色框框所示,只要已经存在上色的小方块。那么游戏就可以结束了。
然后我们就清空分值,清空all。清空整个400*800上色过的画布;
for (let i = 0; i < this.all[0].length; i++) {
if (this.all[0][i] == 1) {
alert("游戏结束");
this.scope = 0;
this.all.splice(0, this.all.length); //清空存放单方块的数组
//清空整个画布
this.context.clearRect(0, 0, 400, 800);
return;
}
}
第二个问题:在下降的过程中,如果碰到已经上色过的all【】,或者y要超过780的时候,那么shap【】就要停止下降了。
然后计算 不再下降的shap的位置 得到有颜色的小方块的位置,给all里对应的小方块赋值为1;
//判断下降过程中是否会与下一层堆积好的方块重叠;是否会超过范围;如果会的话,就开始把shap加入this.all然后退出;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
var y = this.shap[i][j][1] / 20;
var x = this.shap[i][j][0] / 20;
try {
if (
(this.shap[i][j][1] >= 780 || this.all[y + 1][x] == 1) && this.shap[i][j][2] == 1
) {
//会的话,那就就开始把shap加入this。all;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
var y = this.shap[i][j][1] / 20;
var x = this.shap[i][j][0] / 20;
this.all[y][x] = 1;
}
}
}
//放完以后退出
return;
}
} catch (error) {
}
}
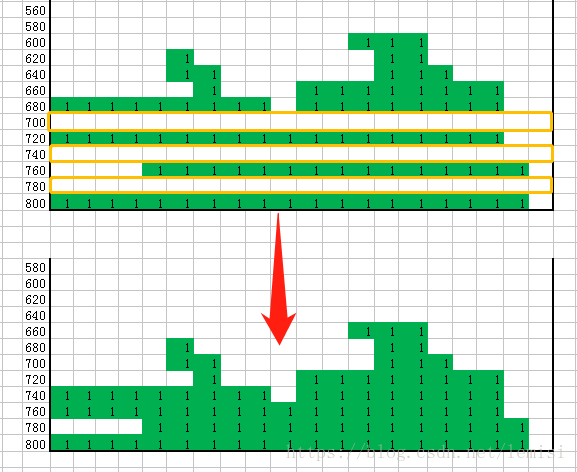
}第三个问题:如果下降的过程中满行了。那么我们就要清空这一整行的小方块们;
- 把满行的小方块的清空以后,再清空现在屏幕上所有的堆积方块。this.deletAll();
deletAll() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.all.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
if (this.all[i][j] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
j * 20,
i * 20,
20,
20
);
}
}
}
},- 这个时候整个all的值就长成这个样子了。被清空的我用黄色框框起来了。
- 被清空的部分,需要被清空行上面的集体往下移动,达到这个效果:这个方法就为allDown();代码如下:
我们从最底层往上遍历,只要有一层有一个上色的小方块,我就continue;
直到这一行都是为空,那么这行的上面所有行集体往下移动;依次类推;
最后,要记得最顶层all【0】要默认值全为0;
allDown() {
for (let i = this.all.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
var num = 0; //一整行填满的方块数量
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
//如果没有
if (this.all[i][j] == 1) {
//只有这一行有存在1的那我就不管了。
continue; //跳出本次循环;
} else {
num++;
//假如这一行都是为空的话。那么开始,这行以上的全部集体往下移动;
if (num == this.allLength) {
this.allLength = this.all[0].length;
var a0 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.all[0]));
if (i - 1 >= 0) {
for (let k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
this.all[k + 1] = this.all[k];
}
this.all[0] = a0;
}
}
}
}
}
},- 集体往下移动以后,那就在重绘堆积的方块——painAll():
//重绘堆积好的方块;
painAll() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.all.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
if (this.all[i][j] == 1) {
this.context.fillRect(
j * 20,
i * 20,
20,
20
);
} else {
this.context.clearRect(
j * 20,
i * 20,
20,
20
);
}
}
}
}- 最后我们就可以完整的写出满格的方法了:满格了那分数就加10分吧。恭喜恭喜~得了10分;
//先判断是否满格了,满格就退出;
for (let i = 0; i < this.all.length; i++) {
var num = 0; //一整行填满的方块数量
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
//如果没有
if (this.all[i][j] != 1) {
continue;
} else {
num++;
if (num == this.allLength) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
this.context.clearRect(
j * 20,
i * 20,
20,
20
);
this.all[i][j] = 0;
}
//把满的清空以后。
//清空现在屏幕上所有的堆积方块
this.deletAll();
//填满清空的区域;
this.allDown();
//重绘
this.painAll();
this.radomShap();
this.scope += 10;
continue;
}
}
}
}
好了,亲爱的朋友们,写到这里我已经心力交瘁了,很快,我们马上就要迎来最终down方法了。
在下降之前,我们只要判断一下是否存在刚才的那3个问题。如果不存在的话,ok。咱们可以往下移动了~
//向下
down() {
【判断第一个问题是否存在的代码:存在,那咱们return吧】
【判断第二个问题是否存在代码:存在,那咱们return吧】
【判断第三个问题是否存在代码:存在,那咱们return吧】
//经过3个问题的判断以后,没有符合,那么我们继续向下移动
{
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
this.shap[i][j][1] += 20;
}
}
this.painShap();
}
},开森,终于写完了耶~~
最后还是说一下:
 这个俄罗斯方块,确实还是存在一些bug。(好吧,不是一些,是很多。)
这个俄罗斯方块,确实还是存在一些bug。(好吧,不是一些,是很多。)
比如:当下降的时候,我一直让shap旋转,于是……我的shap直接就超过all这个画布了。然后就拜拜了。。。。这个问题我也不知道是什么问题。没解决好。如果你们发现了。可以跟我说下哦~
其他的我还没发现|||
还有就是……我的代码,用了不知道多少个for循环。。这肯定不是一个好的方法。尴尬了。。。。。
写到这里,咱们俄罗斯方块的各种方法已经完全结束了。就可以看着去运用这些方法啦~
感谢您的来访。谢谢。
第一次如此热诚的写下技术分析贴。语言稍有不通,如果你哪里没有看明白,请你留言,看到留言后,我会马上回复。
本人小白菜,欢迎留言~
再次最后:
我的代码主要有一下这些方法。
以下是完整js代码:
var startx, starty;
//获得角度
function getAngle(angx, angy) {
return (Math.atan2(angy, angx) * 180) / Math.PI;
}
//根据起点终点返回方向 1向上 2向下 3向左 4向右 0未滑动
function getDirection(startx, starty, endx, endy) {
var angx = endx - startx;
var angy = endy - starty;
var result = 0;
//如果滑动距离太短
if (Math.abs(angx) < 2 && Math.abs(angy) < 2) {
return result;
}
var angle = getAngle(angx, angy);
if (angle >= -135 && angle <= -45) {
result = 1;
} else if (angle > 45 && angle < 135) {
result = 2;
} else if (
(angle >= 135 && angle <= 180) ||
(angle >= -180 && angle < -135)
) {
result = 3;
} else if (angle >= -45 && angle <= 45) {
result = 4;
} else {
result = 0;
}
return result;
}
//手指接触屏幕
document.addEventListener(
"touchstart",
function (e) {
startx = e.touches[0].pageX;
starty = e.touches[0].pageY;
},
false
);
//手指离开屏幕
let timer = null;
//速度控制
document.addEventListener(
"touchend",
function (e) {
if (app.gameState == 0) {
return;
}
var endx, endy;
endx = e.changedTouches[0].pageX;
endy = e.changedTouches[0].pageY;
var direction = getDirection(startx, starty, endx, endy);
clearInterval(timer);
if (direction == 0) {
clearInterval(timer);
}
if (direction == 1) {
app.change();
timer = setInterval(() => {
app.down();
}, app.v)
}
app.downV = 100;
if (direction == 2) {
timer = setInterval(() => {
app.down();
}, app.downV)
}
if (direction == 3) {
app.left();
timer = setInterval(() => {
app.down();
}, app.v)
}
if (direction == 4) {
app.right();
timer = setInterval(() => {
app.down();
}, app.v)
}
},
false
);
var app = new Vue({
el: "#teris",
data: {
scope: 0,
v: 300,
downV: 100,
radomID: null, //图像编号
shap: [], //存放图形
all: new Array(), //存放所有已经内容
context: null, //画布
rotateID: 0, //旋转的状态,
allLength: null,
gameState: 0
},
methods: {
begin() {
if (this.gameState != 0) {
//游戏结束状态
$("#title").html("");
$("#title").html("游戏开始");
this.gameState = 0;
this.scope = 0;
this.all.splice(0, this.all.length); //清空存放单方块的数组
//清空整个画布
this.context.clearRect(0, 0, 400, 800);
}
//游戏开始状态
else {
//初始化堆积方块
for (let i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
this.all[i] = new Array(0);
for (let j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
this.all[i][j] = 0;
}
}
this.allLength = this.all[0].length;
//开始绘制单方块;
//清空整个画布
this.context.clearRect(0, 0, 400, 800);
this.radomShap();
this.gameState = 1;
//游戏开始,默认自己往下移动;
timer = setInterval(() => {
this.down();
}, this.v)
$("#title").html("");
$("#title").html("游戏结束");
}
},
//绘制
pain() {
var c = document.getElementById("stage");
this.context = c.getContext("2d");
this.context.fillStyle = "#000000";
},
//绘制图像
painShap() {
for (var i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.fillRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
}
}
},
//随机绘制单方块
radomShap() {
this.scope += 1;
this.pain();
this.radomID = parseInt(Math.random() * 7);
// this.deleteShap();
this.shap.splice(0, this.shap.length); //清空存放单方块的数组
//shap数组开始存储不同单方块
switch (this.radomID) {
case 0:
//长条
let defaultX = 200;
let defaultY = -60;
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
defaultX = 200;
if (i == 2) {
this.$set(this.shap, i, [
[defaultX, defaultY, 1],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 1],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 1],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 1],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0]
]);
} else {
this.$set(this.shap, i, [
[defaultX, defaultY, 0],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0],
[(defaultX += 20), defaultY, 0]
]);
}
defaultY += 20;
}
console.log(this.shap)
break;
case 1:
//正方形
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -40, 1],
[220, -40, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -20, 1],
[220, -20, 1]
]);
break;
case 2:
//正7
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 1],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 0],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 1],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
case 3:
//反7
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 0],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 0],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 1],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
case 4:
//正2
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 1],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 0],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 0],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
case 5:
//反2
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 0],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 1],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 0],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
case 6:
//土
this.$set(this.shap, 0, [
[200, -60, 0],
[220, -60, 1],
[240, -60, 0]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 1, [
[200, -40, 1],
[220, -40, 1],
[240, -40, 1]
]);
this.$set(this.shap, 2, [
[200, -20, 0],
[220, -20, 0],
[240, -20, 0]
]);
break;
default:
break;
}
this.rotate();
this.painShap();
},
//清除单方块形状
deleteShap() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
}
}
},
//旋转90度的方法
rotate() {
var changge = parseInt(Math.random() * 4);
console.log("变" + changge + "次")
for (i = 0; i <= changge; i++) {
let shap1 = [];
// 深拷贝
shap1 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.shap));
//行变列。列变行,把结果先存在shap1里;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = this.shap[i].length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
shap1[i][j][2] = this.shap[this.shap[i].length - 1 - j][i][2];
}
}
// //判断一下,改变方向以后,会不会超出墙||碰到堆积好的方块;
// for (let i = 0; i < shap1.length; i++) {
// for (let j = 0; j < shap1[i].length; j++) {
// try {
// if (
// ((shap1[i][j][0] < 0 || shap1[i][j][0] > 380||shap1[i][j][1] > 780) && shap1[i][j][2] == 1) || (this.all[this.shap[i][j][1] / 20][this.shap[i][j][0] / 20] == 1)) {
// //两个同时成立退出;
// return;
// }
// } catch (error) {
// }
// }
// }
this.deleteShap();
//那么就把shap1的值赋给shap
this.shap = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(shap1));
this.painShap();
}
},
change() {
let shap1 = [];
// 深拷贝
shap1 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.shap));
//行变列。列变行,把结果先存在shap1里;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = this.shap[i].length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
shap1[i][j][2] = this.shap[this.shap[i].length - 1 - j][i][2];
}
}
//判断一下,改变方向以后,会不会超出墙||碰到堆积好的方块;
for (let i = 0; i < shap1.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < shap1[i].length; j++) {
try {
if (
((shap1[i][j][0] < 0 || shap1[i][j][0] > 380||shap1[i][j][1] > 780) && shap1[i][j][2] == 1) || (this.all[this.shap[i][j][1] / 20][this.shap[i][j][0] / 20] == 1)) {
//两个同时成立退出;
return;
}
} catch (error) {
}
}
}
this.deleteShap();
//那么就把shap1的值赋给shap
this.shap = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(shap1));
this.painShap();
},
//向下
down() {
//到头了。就自杀了。
for (let i = 0; i < this.all[0].length; i++) {
if (this.all[0][i] == 1) {
alert("游戏结束");
clearInterval(timer);
$("#title").html("");
$("#title").html("游戏开始");
this.gameState = 0;
this.scope = 0;
this.all.splice(0, this.all.length); //清空存放单方块的数组
//清空整个画布
this.context.clearRect(0, 0, 400, 800);
return;
}
}
//判断下降过程中是否会与下一层堆积好的方块重叠;是否会超过范围;如果会的话,就开始把shap加入this.all然后退出;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
var y = this.shap[i][j][1] / 20;
var x = this.shap[i][j][0] / 20;
try {
if (
(this.shap[i][j][1] >= 780 || this.all[y + 1][x] == 1) && this.shap[i][j][2] == 1
) {
//会的话,那就就开始把shap加入this。all;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
var y = this.shap[i][j][1] / 20;
var x = this.shap[i][j][0] / 20;
this.all[y][x] = 1;
}
}
}
//放完以后退出
this.radomShap();
clearInterval(timer);
timer = setInterval(() => {
this.down();
}, this.v)
console.log(this.all)
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// console.log("y有bug")
}
}
}
//先判断是否满格了,满格就退出;
for (let i = 0; i < this.all.length; i++) {
var num = 0; //一整行填满的方块数量
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
//如果没有
if (this.all[i][j] != 1) {
continue;
} else {
num++;
if (num == this.allLength) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
this.context.clearRect(
j * 20,
i * 20,
20,
20
);
this.all[i][j] = 0;
}
//把满的清空以后。
//清空现在屏幕上所有的堆积方块
this.deletAll();
//填满清空的区域;
this.allDown();
//重绘
this.painAll();
this.radomShap();
this.scope += 10;
continue;
}
}
}
}
//经过两个判断结束以后,没有符合,继续向下移动
{
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
this.shap[i][j][1] += 20;
}
}
this.painShap();
}
},
// 向左
left() {
//判断左移动的过程中是否会与下一层堆积好的方块重叠;是否会超过范围;如果会的话,就开始把shap加入this.all然后退出;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
var y = this.shap[i][j][1] / 20;
var x = this.shap[i][j][0] / 20;
try {
//因为x可能会等于0;所以用try,catch过滤掉好了。不想管。。。。
if (
(this.shap[i][j][0] < 20 || this.all[y][x - 1] == 1) && this.shap[i][j][2] == 1
) {
//左边有东西||或者靠墙了。不要向左了。
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// console.log("有bug")
}
}
}
//经过两个判断结束以后,没有符合,继续向左移动
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
this.shap[i][j][0] -= 20;
}
}
this.painShap();
},
// 向右
right() {
//判断左移动的过程中是否会与右边堆积好的方块重叠;是否会超过范围;如果会的话退出;
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
var y = this.shap[i][j][1] / 20;
var x = this.shap[i][j][0] / 20;
try {
//因为x可能会等于0;所以用try,catch过滤掉好了。不想管。。。。
if (
(this.shap[i][j][0] > 360 || this.all[y][x + 1] == 1) && this.shap[i][j][2] == 1
) {
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// console.log("x太大")
}
}
}
//经过两个判断结束以后,没有符合,继续向右移动
for (let i = 0; i < this.shap.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.shap[i].length; j++) {
if (this.shap[i][j][2] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
this.shap[i][j][0],
this.shap[i][j][1],
20,
20
);
}
this.shap[i][j][0] += 20;
}
}
this.painShap();
},
deletAll() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.all.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
if (this.all[i][j] == 1) {
this.context.clearRect(
j * 20,
i * 20,
20,
20
);
}
}
}
},
//整体堆积好的方块往下;
allDown() {
for (let i = this.all.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
var num = 0; //一整行填满的方块数量
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
//如果没有
if (this.all[i][j] == 1) {
//只有这一行有存在1的那我就不管了。
continue; //跳出本次循环;
} else {
num++;
//假如这一行都是为空的话。那么开始,这行以上的全部集体往下移动;
if (num == this.allLength) {
this.allLength = this.all[0].length;
var a5 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.all[0]));
if (i - 1 >= 0) {
for (let k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
this.all[k + 1] = this.all[k];
}
this.all[0] = a5;
}
}
}
}
}
},
//重绘堆积好的方块;
painAll() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.all.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.all[i].length; j++) {
if (this.all[i][j] == 1) {
this.context.fillRect(
j * 20,
i * 20,
20,
20
);
} else {
this.context.clearRect(
j * 20,
i * 20,
20,
20
);
}
}
}
}
},
mounted() {
var c = document.getElementById("stage");
this.context = c.getContext("2d");
}
});