Java集合框架:了解ArrayList
ArrayList
基于动态数组实现的集合
目录
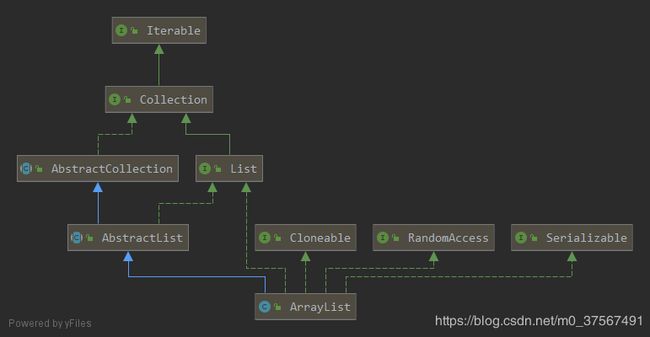
ArrayList继承关系
ArrayList源码分析
ArrayList总结
ArrayList继承关系
ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,支持序列化,可通过序列化传输
ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,覆盖了clone()方法,能被克隆
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,指示了ArrayList支持快速的随机访问
ArrayList实现了List接口和继承了Abstractlist抽象类,可进行集合相关的操作
ArrayList源码分析
私有 迭代器类Itr:(遍历集合,删除元素)
private class Itr implements Iterator {
int cursor; // 下一个元素的索引
int lastRet = -1; // 最后一个返回元素的索引,如果没有为 -1
int expectedModCount = modCount;
// 防止创建合成构造函数
Itr() {}
// 存在下一个元素
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
// 获取下一个元素
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification(); // 检查集合有无被其他迭代器修改
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) // 索引超过集合大小
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) // 数组越界
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1; // 索引指向下一个元素
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; // 记录最后返回元素的索引
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0) // 最后返回元素索引 = -1
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); // 调用ArrayList的remove方法
cursor = lastRet; // 索引更新
lastRet = -1; // 返回元素索引重置
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 从下一个索引的节点开始遍历(剩余遍历)
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (i >= es.length) // 索引越界
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && modCount == expectedModCount; i++) // 保证集合没有被其他操作修改
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} 私有 迭代器类ListItr继承自Itr:(添加,修改元素)
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.ListItr(ListItr的优化版本)
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index; // 下一个元素索引 = 当前元素索引
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
// 上一个元素
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1; // 上一个元素索引 = 下一个元素索引 - 1
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) // 索引越界
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e); // ArrayList的set方法
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e); // ArrayList的add方法
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
} 私有静态 子列表类SubList:(构造集合的子列表/子视图,添加/修改/删除元素,转换数组,SubList迭代器,SubList再次分割)
// 继承了RandomAccess,支持快速随机访问
private static class SubList extends AbstractList implements RandomAccess {
private final ArrayList root;
private final SubList parent;
private final int offset;
private int size;
/**
* 构造一个ArrayList的子列表
*/
public SubList(ArrayList root, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.root = root; // 原ArrayLsit集合
this.parent = null;
this.offset = fromIndex; // 起始索引
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex; // 集合大小
this.modCount = root.modCount;
}
/**
* 构造一个SubList的子列表
*/
private SubList(SubList parent, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.root = parent.root; // 原ArrayLsit集合
this.parent = parent; // 原SubList子列表
this.offset = parent.offset + fromIndex; // 原SubList的起始索引 + 子SubList的起始索引
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = root.modCount; // 集合修改次数
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size); // 检查索引是否越界
checkForComodification();
E oldValue = root.elementData(offset + index); // 旧值 = ArrayList.elementData:根据索引获取元素
root.elementData[offset + index] = element; // 更新新值
return oldValue;
}
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
checkForComodification();
return root.elementData(offset + index);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return size;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
root.add(offset + index, element); // 调用ArrayList的add方法
updateSizeAndModCount(1);
}
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
checkForComodification();
E result = root.remove(offset + index); // 调用ArrayList的remove方法
updateSizeAndModCount(-1);
return result;
}
/**
* 删除在索引区间内的所有元素
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
root.removeRange(offset + fromIndex, offset + toIndex); // offset:子列表subList在集合的起始位置
updateSizeAndModCount(fromIndex - toIndex);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(this.size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
root.addAll(offset + index, c); // 调用ArrayList的addAll方法
updateSizeAndModCount(cSize);
return true;
}
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator operator) {
root.replaceAllRange(operator, offset, offset + size); // 对区间内的所有元素进行操作符运算
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection c) {
return batchRemove(c, false); // 删除所有包含在c中的元素
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection c) {
return batchRemove(c, true); // 删除所有未包含在c中的元素
}
private boolean batchRemove(Collection c, boolean complement) {
checkForComodification();
int oldSize = root.size;
boolean modified =
root.batchRemove(c, complement, offset, offset + size); // 调用ArrayList的batchRemove方法
if (modified)
updateSizeAndModCount(root.size - oldSize); // 更新集合大小和计数值
return modified;
}
public boolean removeIf(Predicate filter) {
checkForComodification();
int oldSize = root.size;
boolean modified = root.removeIf(filter, offset, offset + size); // 调用ArrayList的removeIf方法
if (modified)
updateSizeAndModCount(root.size - oldSize); // 更新集合大小和计数值
return modified;
}
public Object[] toArray() {
checkForComodification();
return Arrays.copyOfRange(root.elementData, offset, offset + size); // 将制定范围的数组复制到新数组中
}
/**
* 转换成指定类型的数组
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
checkForComodification();
if (a.length < size)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOfRange(
root.elementData, offset, offset + size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(root.elementData, offset, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof List)) {
return false;
}
boolean equal = root.equalsRange((List)o, offset, offset + size); // 区间范围内比较
checkForComodification();
return equal;
}
public int hashCode() {
int hash = root.hashCodeRange(offset, offset + size); // ArrayList的hashCode方法
checkForComodification();
return hash;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = root.indexOfRange(o, offset, offset + size); // 顺序索引
checkForComodification();
return index >= 0 ? index - offset : -1;
}
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = root.lastIndexOfRange(o, offset, offset + size); // 逆序索引
checkForComodification();
return index >= 0 ? index - offset : -1;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public Iterator iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
// 返回一个从索引开始的子列表迭代器
public ListIterator listIterator(int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListIterator() { // 一个匿名内部类实现了ListIterator接口
int cursor = index;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = root.modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != SubList.this.size;
}
/**
* 返回集合的下一个元素
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
/**
* 返回集合的上一个元素
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
/**
* 从下一个索引的节点开始遍历(剩余元素遍历)
*/
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = SubList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = root.elementData;
if (offset + i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && modCount == expectedModCount; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, offset + i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
SubList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = root.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
root.set(offset + lastRet, e); // 上面的都是调用SubList的方法,为啥这里调用ArrayList的方法?
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
SubList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = root.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (root.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
};
}
/**
* 对SubList子列表再次分割
*/
public List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); // 校验参数
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size;
}
private void checkForComodification() {
if (root.modCount != modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
private void updateSizeAndModCount(int sizeChange) {
SubList slist = this;
do {
slist.size += sizeChange;
slist.modCount = root.modCount;
slist = slist.parent;
} while (slist != null);
}
public Spliterator spliterator() {
checkForComodification();
// 匿名内部类, 由于动态绑定(运行时根据具体对象的类型进行绑定), 此处未使用ArrayListSpliterator
return new Spliterator() {
private int index = offset; // 当前索引
private int fence = -1; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // 迭代器修改次数,
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
hi = fence = offset + size;
}
return hi;
}
/**
* 对迭代器进行分割
*/
public ArrayList.ArrayListSpliterator trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
// ArrayListSpliterator can be used here as the source is already bound
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
root.new ArrayListSpliterator(lo, index = mid, expectedModCount);
}
/**
* 对当前元素进行操作
*/
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)root.elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
if (root.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
ArrayList lst = root;
Object[] a;
if ((a = lst.elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = modCount;
hi = offset + size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (lst.modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return getFence() - index;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
};
}
}
不可变 的基于二分索引,延迟初始化的Spliterator:
final class ArrayListSpliterator implements Spliterator {
/*
* 若ArrayList是不可变的(无添加/删除操作),则可用Arrays.spliterator实现可分割迭代器
* ArrayListSpliterator :
* 1.主要依靠modCounts:不能保证检测到并发冲突,且有时对线程内干扰过于保守,但可以检测到足够多的问题
* 2.延迟初始化fence和expectedModCount:于需要提交到要检查的状态的最新点时初始化,从而提高精度
* 3.在ForEach末尾只执行一次ConcurrentModificationException检查:简化lambda-resolution
*/
private int index; // 当前索引, 集合操作时修改
private int fence; // 最后一个索引:使用时初始化, 默认为-1
private int expectedModCount; // 设置时初始化
/**
* 创建指定范围的可分割迭代器
*/
ArrayListSpliterator(int origin, int fence, int expectedModCount) {
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
private int getFence() { // initialize fence to size on first use
int hi; // (a specialized variant appears in method forEach)
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
hi = fence = size;
}
return hi;
}
public ArrayListSpliterator trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small
new ArrayListSpliterator(lo, index = mid, expectedModCount);
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) {
index = i + 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)elementData[i];
action.accept(e);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((a = elementData) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = modCount;
hi = size;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
if (modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return getFence() - index;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
} ArrayList构造方法:
/**
* 指定初始容量的初始化
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* 创建一个初始容量=10的集合
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* 创建一个包含指定元素的集合
*/
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// defend against c.toArray (incorrectly) not returning Object[]
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // 集合初始化一个空数组
}
}ArrayList数组容量操作:
/**
* 将集合数组的容量 = 集合元素数量大小
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) { // 列表当前大小 < 数组容量
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA // 空数组
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
/**
* 扩容以容纳所需的最小容量
*
* @param minCapacity 所需最小容量
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 所需最小容量 > 数组当前容量 && 数组 != null && 所需最小容量 > 默认容量
if (minCapacity > elementData.length
&& !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA && minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) {
modCount++;
grow(minCapacity); // elementData扩容
}
}
/**
* 增加容量以容纳所需的最小容量
*
* @param minCapacity 所需最小容量
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity < 0
*/
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity(minCapacity));
}
/**
* 容量 + 1
*/
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
/**
* 返回容量 >= minCapacity
* 如果满足, 返回容量 = 当前容量 + 当前容量 * 50%
* 若 minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE:返回容量 = minCapacity
* 否则 返回容量 <= MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
*
* @param minCapacity 所需最小容量
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity < 0
*/
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 新容量 = 1.5 * 原容量
if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); // 返回默认容量和所需最小容量中最大值
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return minCapacity;
}
return (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE <= 0) // 新容量 <= 最大容量 ? 新容量 : hugeCapacity(minCapacity)
? newCapacity
: hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) // 所需最小容量 > 最大容量 ? 整数的最大值 : 最大容量
? Integer.MAX_VALUE
: MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
/**
* 返回集合的元素个树
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* 集合是否为空
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}ArrayList索引查找:
/**
* 集合中是否存在元素
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
/**
* 返回元素第一次出现的索引
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
/**
* 返回元素在区间内的首次出现的索引
*/
int indexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
Object[] es = elementData;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (es[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (o.equals(es[i])) { // 返回第一次匹配的索引(顺序)
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 返回元素最后一次出现的索引
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
/**
* 返回元素在区间内的最后一次出现的索引
*/
int lastIndexOfRange(Object o, int start, int end) {
Object[] es = elementData;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = end - 1; i >= start; i--) {
if (es[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = end - 1; i >= start; i--) {
if (o.equals(es[i])) { // 返回第一次匹配的索引(逆序)
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}ArrayList增加/删除/修改操作:
/**
* 返回数组指定位置的元素
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
/**
* 返回特定数组的对应的元素
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static E elementAt(Object[] es, int index) {
return (E) es[index];
}
/**
* 返回数组指定位置的元素
*
* @param index 要返回元素的索引
* @return 指定位置的元素
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* 用指定元素替换数组中指定位置的元素。
*
* @param index 要返回元素的索引
* @param element 要替换的元素
* @return 被替换的元素
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method
* bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value),
* which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop.
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow(); // 存储数组空间已满:扩容数组 -> 容量 + 1
elementData[s] = e; // 元素加到列表末尾
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* 指定元素加到列表末尾
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
/**
* 特定位置插入元素, 将当前位置及其右边元素右移
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow(); // 存储数组空间已满:扩容数组 -> 容量 + 1
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index); // 将index位置及其右边的元素右移
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* 删除数组中指定的元素(删除的元素右方元素左移)
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
final Object[] es = elementData;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[index];
fastRemove(es, index);
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))}
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = this.size;
int i = 0;
found: {
if (o == null) {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (es[i] == null)
break found;
} else {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(es[i]))
break found;
}
return false;
}
fastRemove(es, i);
return true;
}
/**
* 专用的删除方法, 无返回值, 无边界检查
*/
private void fastRemove(Object[] es, int i) {
modCount++;
final int newSize;
if ((newSize = size - 1) > i)
System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i); // 被删元素右方元素左移一位
es[size = newSize] = null; // 最后一个元素清空
}
/**
* 清空列表
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
final Object[] es = elementData;
for (int to = size, i = size = 0; i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
/**
* 按照新增集合c的迭代器返回顺序, 将c中所有元素追加到列表末尾
* 若在操作进行过程中修改了c, 则此行为结果不确定
* (意味着若c是列表本身, 并且列表非空, 则此行为结果不确定)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray(); // 转换成数组
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size)) // 新增元素数量 > 数组剩余可添加容量 = (数组最大容量 - 列表当前元素数量)
elementData = grow(s + numNew); // 数组需要 s(已有的元素) + numNew(新增的元素) 个位置
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, s, numNew); // 新元素添加到列表(从列表size的位置开始)
size = s + numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* 从指定位置开始, 将指定集合插入列表中
* 指定集合的显示顺序为迭代器返回顺序
* 指定位置及其后续元素右移
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size)) // 新增元素数量 > 数组剩余可添加容量
elementData = grow(s + numNew); // 数组需要 s + numNew 个位置
int numMoved = s - index; // 后移元素数量
if (numMoved > 0) // 索引开始的元素右移numNew个位置
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); // 指定集合元素从index位置开始添加到列表中
size = s + numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* 删除列表在fromIndex <= index < toIndex 之间的元素
* 后续元素索引左移
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex} or
* {@code toIndex} is out of range
* ({@code fromIndex < 0 ||
* toIndex > size() ||
* toIndex < fromIndex})
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
outOfBoundsMsg(fromIndex, toIndex));
}
modCount++;
shiftTailOverGap(elementData, fromIndex, toIndex); // 通过移动数组元素进行删除
}
/**
* 从列表中删除指定集合包含的元素
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException 若列表的类与指定集合的类不兼容
* @throws NullPointerException 若列表包含null, 且指定集合不允许null, 或指定集合为null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection c) {
return batchRemove(c, false, 0, size);
}
/**
* 保留列表中在指定集合出现的元素
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException 若列表的类与指定集合的类不兼容
* @throws NullPointerException 若列表包含null, 且指定集合不允许null, 或指定集合为null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
*/
public boolean retainAll(Collection c) {
return batchRemove(c, true, 0, size);
}
boolean batchRemove(Collection c, boolean complement,
final int from, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
final Object[] es = elementData;
int r;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (r = from;; r++) {
if (r == end)
return false;
if (c.contains(es[r]) != complement)
break;
}
int w = r++;
try {
for (Object e; r < end; r++)
if (c.contains(e = es[r]) == complement) // complemen:true-> 匹配指定集合中的元素, false-> 匹配指定集合外的元素
es[w++] = e;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
System.arraycopy(es, r, es, w, end - r);
w += end - r;
throw ex;
} finally {
modCount += end - w;
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end); // 删除区间内元素
}
return true;
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate filter) {
return removeIf(filter, 0, size);
}
/**
* 索引区间 i<= index < end 内删除所有满足给定谓词的元素
*/
boolean removeIf(Predicate filter, int i, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (; i < end && !filter.test(elementAt(es, i)); i++)
;
// Tolerate predicates that reentrantly access the collection for
// read (but writers still get CME), so traverse once to find
// elements to delete, a second pass to physically expunge.
if (i < end) {
final int beg = i;
final long[] deathRow = nBits(end - beg);
deathRow[0] = 1L; // set bit 0
for (i = beg + 1; i < end; i++)
if (filter.test(elementAt(es, i)))
setBit(deathRow, i - beg);
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
modCount++;
int w = beg;
for (i = beg; i < end; i++)
if (isClear(deathRow, i - beg))
es[w++] = es[i];
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end);
return true;
} else {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator operator) {
replaceAllRange(operator, 0, size);
modCount++;
}
/**
* 根据操作符运算替换区间内所有元素
*/
private void replaceAllRange(UnaryOperator operator, int i, int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final Object[] es = elementData;
for (; modCount == expectedModCount && i < end; i++)
es[i] = operator.apply(elementAt(es, i)); // 对每个元素执行操作
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
/**
* 将索引hi的右方元素左移到lo来删除区间内元素
*/
private void shiftTailOverGap(Object[] es, int lo, int hi) {
System.arraycopy(es, hi, es, lo, size - hi); // 将被删区间元素lo-hi右方元素左移到lo
for (int to = size, i = (size -= hi - lo); i < to; i++)
es[i] = null;
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
private static String outOfBoundsMsg(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return "From Index: " + fromIndex + " > To Index: " + toIndex;
} ArrayList总结
ArrayList底层通过维护一个Object数组实现
ArrayList初始的默认容量是10,容量不足时扩容:新的容量 = 1.5 * 原始容量
ArrayList支持高效的随机访问
ArrayList是线程不安全的