2020.07.17-Binder机制
文章目录
- 1.Binder机制综述:
- 2.Binder Driver 实现及作用机制
- 2.1 Binder init
- 3.ServiceManager 实现与作用机制
- 4.Server端
- 5.Client端
1.Binder机制综述:
BInder可以实现native层或者hal层的跨进程间的服务调用/通信,采用C/S架构,通过注册服务和获取服务来链接Server和Client两端,Client可以同调用服务接口远程调用Server接口实现相应功能。
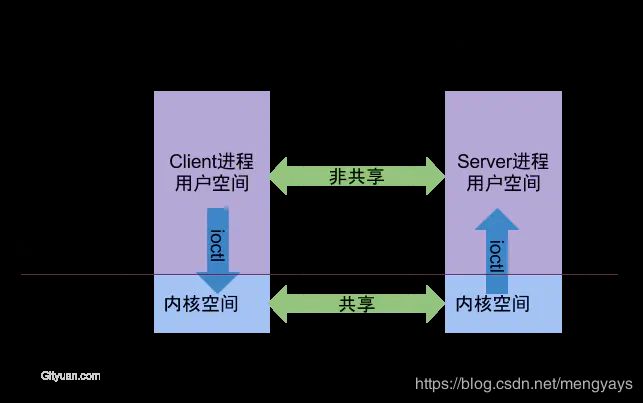
Binder可以作为跨进程通信手段(IPC,Inter-Process Communication)。,也可以作为远程过程调用手段(RPC,Remote Procedure Call)。从实现的角度来说,Binder核心被实现成一个Linux驱动程序,并运行于内核态。这样它才能具有强大的跨进程访问能力。Android系统在Linux内核讲Binder作为一个虚拟字符设备,通过载入内核驱动将BInder Driver ,加载进内核。
为什么要以内核驱动的形式实现Binder的的底层实现原理?我的理解是目前现有的IPC/RPC,包括管道,消息队列,共享内存,socket都没有办法很好的支持Android这种需要C/S架构,讲服务与调用分离的需求,同时又要很好的保证通信的实时性和一致性。因此采用mmap内存映射的机制,同时通过内核驱动的方式,可以实现Android下的IPC需求:1,实时性,mmap机制的数据访问/同步速率比较快;2,通过讲Binder看做虚拟字符设备,将BInder Driver加载内核,可以有效解决Client和Server进程在用户空间的内存空间隔离问题,通过各个进程相同的内核空间,通过copy_from_kernel
/copy_from_user等系统调用可以实现不同的进程之间的数据通信。

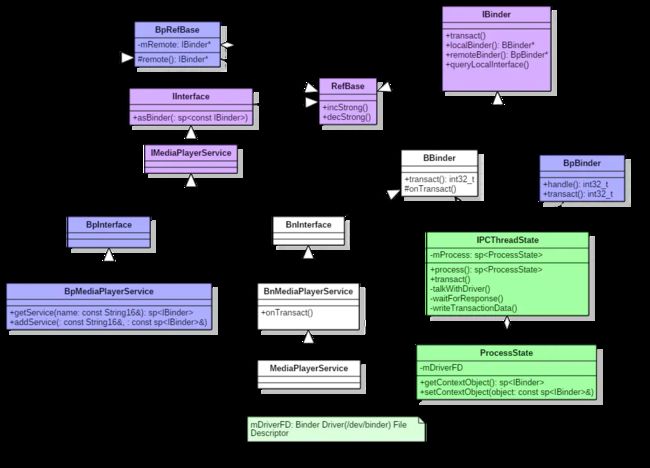
而在hal以及native层,由ServiceManager统一管理相应的Client端和Server端,同一功能的Server端通过注册服务将服务注册到ServiceManager中,相应的Client端就可以根据Server的注册信息获取到该Server,就可以使用该Server,包括想用的功能接口。
Binder Driver负责Binder的底层IPC,可以高效快速准确进行进程间的数据通信,而在上层通过ServiceManager服务管理器的方式可以统一管理各个Server和Client。已经从原理上对binder进行了说明分析,接下来我们对BInder的具体模块进行细致的分析研究,以及通过阅读源码对Binder进行更深入的理解。
2.Binder Driver 实现及作用机制
下列是binder虚拟字符设备驱动的文件操作结构体,也即文件操作句柄,定义了一下接口信息,包括open接口,mmap接口,万能的ioctl及接口,这些接口即为设备文件在执行open,write等操作时,通过系统调用将调用驱动定义的的对应的接口。

6040 static const struct file_operations binder_fops = {
6041 .owner = THIS_MODULE,
6042 .poll = binder_poll,
6043 .unlocked_ioctl = binder_ioctl,
6044 .compat_ioctl = binder_ioctl,
6045 .mmap = binder_mmap,
6046 .open = binder_open,
6047 .flush = binder_flush,
6048 .release = binder_release,
6049 };
6050
6051 BINDER_DEBUG_ENTRY(state);
6052 BINDER_DEBUG_ENTRY(stats);
6053 BINDER_DEBUG_ENTRY(transactions);
6054 BINDER_DEBUG_ENTRY(transaction_log);
2.1 Binder init
在加载驱动时进行对驱动执行初始化,
6084 static int __init binder_init(void)
6085 {
6086 int ret;
6087 char *device_name, *device_names, *device_tmp;
6088 struct binder_device *device;
6089 struct hlist_node *tmp;
6090 //申请内存 初始化shrinker
6091 ret = binder_alloc_shrinker_init();
6092 if (ret)
6093 return ret;
6094 //原子操作,赋值
6095 atomic_set(&binder_transaction_log.cur, ~0U);
6096 atomic_set(&binder_transaction_log_failed.cur, ~0U);
6097
6098 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root = debugfs_create_dir("binder", NULL);
6099 if (binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root)
6100 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_proc = debugfs_create_dir("proc",
6101 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root);
6102
6103 if (binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root) {
6104 debugfs_create_file("state",
6105 0444,
6106 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root,
6107 NULL,
6108 &binder_state_fops);
6109 debugfs_create_file("stats",
6110 0444,
6111 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root,
6112 NULL,
6113 &binder_stats_fops);
6114 debugfs_create_file("transactions",
6115 0444,
6116 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root,
6117 NULL,
6118 &binder_transactions_fops);
6119 debugfs_create_file("transaction_log",
6120 0444,
6121 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root,
6122 &binder_transaction_log,
6123 &binder_transaction_log_fops);
6124 debugfs_create_file("failed_transaction_log",
6125 0444,
6126 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root,
6127 &binder_transaction_log_failed,
6128 &binder_transaction_log_fops);
6129 }
6130
6131 /*
6132 * Copy the module_parameter string, because we don't want to
6133 * tokenize it in-place.
6134 *///申请设备空间
6135 device_names = kzalloc(strlen(binder_devices_param) + 1, GFP_KERNEL);
6136 if (!device_names) {
6137 ret = -ENOMEM;
6138 goto err_alloc_device_names_failed;
6139 }
6140 strcpy(device_names, binder_devices_param);
6141
6142 device_tmp = device_names;
6143 while ((device_name = strsep(&device_tmp, ","))) {//初始化设备
6144 ret = init_binder_device(device_name);
6145 if (ret)
6146 goto err_init_binder_device_failed;
6147 }
6148
6149 return ret;
6150
6151 err_init_binder_device_failed:
6152 hlist_for_each_entry_safe(device, tmp, &binder_devices, hlist) {
6153 misc_deregister(&device->miscdev);
6154 hlist_del(&device->hlist);
6155 kfree(device);
6156 }
6157
6158 kfree(device_names);
6159
6160 err_alloc_device_names_failed:
6161 debugfs_remove_recursive(binder_debugfs_dir_entry_root);
6162
6163 return ret;
6164 }
6165
6166 device_initcall(binder_init);
6167
6168 #define CREATE_TRACE_POINTS
6169 #include "binder_trace.h"
6170
6171 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
6172
下面是kernel中比较重要的list的实现函数:
21 #define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
22
23 #define LIST_HEAD(name) \
24 struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
25
26 static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
27 {
28 WRITE_ONCE(list->next, list);
29 list->prev = list;
30 }
31
32 #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
33 extern bool __list_add_valid(struct list_head *new,
34 struct list_head *prev,
35 struct list_head *next);
36 extern bool __list_del_entry_valid(struct list_head *entry);
37 #else
38 static inline bool __list_add_valid(struct list_head *new,
39 struct list_head *prev,
40 struct list_head *next)
41 {
42 return true;
43 }
44 static inline bool __list_del_entry_valid(struct list_head *entry)
45 {
46 return true;
47 }
48 #endif
49
50 /*
51 * Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
52 *
53 * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
54 * the prev/next entries already!
55 */
56 static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
57 struct list_head *prev,
58 struct list_head *next)
59 {
60 if (!__list_add_valid(new, prev, next))
61 return;
62
63 next->prev = new;
64 new->next = next;
65 new->prev = prev;
66 WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, new);
67 }
68
69 /**
70 * list_add - add a new entry
71 * @new: new entry to be added
72 * @head: list head to add it after
73 *
74 * Insert a new entry after the specified head.
75 * This is good for implementing stacks.
76 */
77 static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
78 {
79 __list_add(new, head, head->next);
80 }
81
82
83 /**
84 * list_add_tail - add a new entry
85 * @new: new entry to be added
86 * @head: list head to add it before
87 *
88 * Insert a new entry before the specified head.
89 * This is useful for implementing queues.
90 */
91 static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
92 {
93 __list_add(new, head->prev, head);
94 }
95
96 /*
97 * Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
98 * point to each other.
99 *
100 * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
101 * the prev/next entries already!
102 */
103 static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
104 {
105 next->prev = prev;
106 WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, next);
107 }
108
109 /**
110 * list_del - deletes entry from list.
111 * @entry: the element to delete from the list.
112 * Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is
113 * in an undefined state.
114 */
115 static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry)
116 {
117 if (!__list_del_entry_valid(entry))
118 return;
119
120 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
121 }
122
123 static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
124 {
125 __list_del_entry(entry);
126 entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
127 entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
128 }
binder_open()函数是Binder设备的open函数的底层接口,Binder Driver还有更多的函数接口,其中比较重要的是binder_transaction函数,可以实现进程间的数据通信功能。
5206 static int binder_open(struct inode *nodp, struct file *filp)
5207 {
5208 struct binder_proc *proc;
5209 struct binder_device *binder_dev;
5210
5211 binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_OPEN_CLOSE, "%s: %d:%d\n", __func__,
5212 current->group_leader->pid, current->pid);
5213
5214 proc = kzalloc(sizeof(*proc), GFP_KERNEL);
5215 if (proc == NULL)
5216 return -ENOMEM;
5217 spin_lock_init(&proc->inner_lock);
5218 spin_lock_init(&proc->outer_lock);
5219 get_task_struct(current->group_leader);
5220 proc->tsk = current->group_leader;
5221 mutex_init(&proc->files_lock);
5222 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&proc->todo);
5223 if (binder_supported_policy(current->policy)) {
5224 proc->default_priority.sched_policy = current->policy;
5225 proc->default_priority.prio = current->normal_prio;
5226 } else {
5227 proc->default_priority.sched_policy = SCHED_NORMAL;
5228 proc->default_priority.prio = NICE_TO_PRIO(0);
5229 }
5230
5231 binder_dev = container_of(filp->private_data, struct binder_device,
5232 miscdev);
5233 proc->context = &binder_dev->context;
5234 binder_alloc_init(&proc->alloc);
5235
5236 binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_PROC);
5237 proc->pid = current->group_leader->pid;
5238 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&proc->delivered_death);
5239 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&proc->waiting_threads);
5240 filp->private_data = proc;
5241
5242 mutex_lock(&binder_procs_lock);
5243 hlist_add_head(&proc->proc_node, &binder_procs);
5244 mutex_unlock(&binder_procs_lock);
5245
5246 if (binder_debugfs_dir_entry_proc) {
5247 char strbuf[11];
5248
5249 snprintf(strbuf, sizeof(strbuf), "%u", proc->pid);
5250 /*
5251 * proc debug entries are shared between contexts, so
5252 * this will fail if the process tries to open the driver
5253 * again with a different context. The priting code will
5254 * anyway print all contexts that a given PID has, so this
5255 * is not a problem.
5256 */
5257 proc->debugfs_entry = debugfs_create_file(strbuf, 0444,
5258 binder_debugfs_dir_entry_proc,
5259 (void *)(unsigned long)proc->pid,
5260 &binder_proc_fops);
5261 }
5262
5263 return 0;
5264 }
3.ServiceManager 实现与作用机制
ServiceManager是Binder IPC通信过程中的守护进程,本身也是一个Binder服务,通过打开初始化binder 设备文件,开启进程池,然后创建ServiceManager对象,开启ServiceManager,然后循环遍历,等待设备注册服务。
ServiceManager本身工作相对简单,其功能:查询和注册服务。 对于Binder IPC通信过程中,其实更多的情形是BpBinder和BBinder之间的通信,比如ActivityManagerProxy和ActivityManagerService之间的通信等。

116 int main(int argc, char** argv) {
117 if (argc > 2) {
118 LOG(FATAL) << "usage: " << argv[0] << " [binder driver]";
119 }
120 //打开Binder 字符设备
121 const char* driver = argc == 2 ? argv[1] : "/dev/binder";
122
123 sp<ProcessState> ps = ProcessState::initWithDriver(driver);
//设置进程池
124 ps->setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(0);
//回调注册
125 ps->setCallRestriction(ProcessState::CallRestriction::FATAL_IF_NOT_ONEWAY);
126 // 创建新的ServiceManager
127 sp<ServiceManager> manager = new ServiceManager(std::make_unique<Access>());
// 将管理器添加到管理服务器中
128 if (!manager->addService("manager", manager, false /*allowIsolated*/, IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT).isOk()) {
129 LOG(ERROR) << "Could not self register servicemanager";
130 }
131
132 IPCThreadState::self()->setTheContextObject(manager);
133 ps->becomeContextManager(nullptr, nullptr);
134 //创建便利器
135 sp<Looper> looper = Looper::prepare(false /*allowNonCallbacks*/);
136 //设置回调的
137 BinderCallback::setupTo(looper);
138 ClientCallbackCallback::setupTo(looper, manager);
139 //遍历
140 while(true) {
141 looper->pollAll(-1);//遍历
142 }
143
144 // should not be reached
145 return EXIT_FAILURE;
146 }
下面是进程池和looper的具体路径:
system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp
frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
4.Server端
在介绍binder在native层的具体的作用机制时我们将以boot control service 为例,介绍该服务的ServiceManager和Client的相互配合的工作原理。
在bootcontrol server中创建[email protected]的服务进程来启动IBootControl的 Server,注册bootcontrol服务,返回一个implement interface service,通过android.hardware.boot
@1.1-service.rc 脚本开机启动booconyrol service。
21 using android::hardware::defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation;
22 using IBootControl_V1_0 = android::hardware::boot::V1_0::IBootControl;
23 using IBootControl_V1_1 = android::hardware::boot::V1_1::IBootControl;
24
25 int main(int /* argc */, char* /* argv */[]) {
26 return defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation<IBootControl_V1_0, IBootControl_V1_1>();
27 }
66 __attribute__((warn_unused_result)) status_t defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation(
67 const std::string& name, size_t maxThreads = 1) {
68 configureRpcThreadpool(maxThreads, true);
69 status_t result = registerPassthroughServiceImplementation<Interface, ExpectInterface>(name);
70
71 if (result != OK) {
72 return result;
73 }
74
75 joinRpcThreadpool();
76 return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
77 }
注册服务的具体实现函数:
31 __attribute__((warn_unused_result)) status_t registerPassthroughServiceImplementation(
32 const std::string& interfaceName, const std::string& expectInterfaceName,
33 RegisterServiceCb registerServiceCb, const std::string& serviceName) {
34 sp<IBase> service =
35 getRawServiceInternal(interfaceName, serviceName, true /*retry*/, true /*getStub*/);
36
37 if (service == nullptr) {
38 ALOGE("Could not get passthrough implementation for %s/%s.", interfaceName.c_str(),
39 serviceName.c_str());
40 return EXIT_FAILURE;
41 }
42 if (service->isRemote()) {
43 ALOGE("Implementation of %s/%s is remote!", interfaceName.c_str(), serviceName.c_str());
44 return EXIT_FAILURE;
45 }
46
47 std::string actualName;
48 Return<void> result = service->interfaceDescriptor(
49 [&actualName](const hidl_string& descriptor) { actualName = descriptor; });
50 if (!result.isOk()) {
51 ALOGE("Error retrieving interface name from %s/%s: %s", interfaceName.c_str(),
52 serviceName.c_str(), result.description().c_str());
53 return EXIT_FAILURE;
54 }
55 if (actualName != expectInterfaceName) {
56 ALOGE("Implementation of %s/%s is actually %s, not a %s!", interfaceName.c_str(),
57 serviceName.c_str(), actualName.c_str(), expectInterfaceName.c_str());
58 return EXIT_FAILURE;
59 }
60
61 status_t status = registerServiceCb(service, serviceName);
62 if (status == OK) {
63 ALOGI("Registration complete for %s/%s.", interfaceName.c_str(), serviceName.c_str());
64 } else {
65 ALOGE("Could not register service %s/%s (%d).", interfaceName.c_str(), serviceName.c_str(),
66 status);
67 }
68
69 return status;
70 }
71
72 } // namespace details
创建应用层BootControl的实现实例,然后对该实例进行初始化,初始化过程采用的libboot_control库,实现具体的实现功能,boot的implement库对HAL接口库[email protected]的实现。
具体的实现关系为:
[email protected]——>[email protected]——>libboot_control——>boot control
^
getService()
118 IBootControl* HIDL_FETCH_IBootControl(const char* /* hal */) {
119 auto module = std::make_unique<BootControl>();
120 if (!module->Init()) {
121 ALOGE("Could not initialize BootControl module");
122 return nullptr;
123 }
124 return module.release();
125 }
34 bool BootControl::Init() {
35 return impl_.Init();
36 }
196 bool BootControl::Init() {
197 if (initialized_) return true;
198
199 // Initialize the current_slot from the read-only property. If the property
200 // was not set (from either the command line or the device tree), we can later
201 // initialize it from the bootloader_control struct.
202
203 //Later initialize the slot_suffix proterty,so it be commented out.
204 std::string suffix_prop = android::base::GetProperty("ro.boot.slot_suffix", "");
205 if (suffix_prop.empty()) {
206 LOG(ERROR) << "Slot suffix property is not set";
207 return false;
208 }
209 current_slot_ = SlotSuffixToIndex(suffix_prop.c_str());
210
211 std::string err;
212 std::string device = get_bootloader_message_blk_device(&err);
213 if (device.empty()) {
214 LOG(ERROR) << "Could not find bootloader message block device: " << err;
215 return false;
216 }
217
218 bootloader_control boot_ctrl;
219 if (!LoadBootloaderControl(device.c_str(), &boot_ctrl)) {
220 LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to load bootloader control block";
221 return false;
222 }
223
224 // Note that since there isn't a module unload function this memory is leaked.
225 // We use `device` below sometimes, so it's not moved out of here.
226 misc_device_ = device;
227 initialized_ = true;
228
229 // Validate the loaded data, otherwise we will destroy it and re-initialize it
230 // with the current information.
231 uint32_t computed_crc32 = BootloaderControlLECRC(&boot_ctrl);
232 if (boot_ctrl.crc32_le != computed_crc32) {
233 LOG(WARNING) << "Invalid boot control found, expected CRC-32 0x" << std::hex << computed_crc32
234 << " but found 0x" << std::hex << boot_ctrl.crc32_le << ". Re-initializing.";
235 InitDefaultBootloaderControl(this, &boot_ctrl);
236 UpdateAndSaveBootloaderControl(device.c_str(), &boot_ctrl);
237 }
238
239 if (!InitMiscVirtualAbMessageIfNeeded()) {
240 return false;
241 }
242
243 num_slots_ = boot_ctrl.nb_slot;
244 return true;
245 }
5.Client端
Client端的主要功能是调用Server端的接口实现相应的功能,或者有其他程序创建一个Binder Service的Client,作为Client来通过getService获取服务,然后调用Sercer端的接口。