python画图
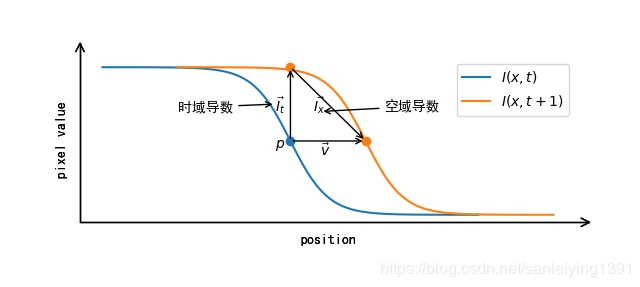
光流法原理图
双曲正切函数等于双曲正弦函数与双曲余弦函数的商.即
t a n h = s i n h c o s h tanh =\frac{sinh}{cosh} tanh=coshsinh
其中 s i n h ( x ) = e x − e − x 2 sinh(x)=\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{2} sinh(x)=2ex−e−x, c o s h ( x ) = e x + e − x 2 cosh(x)=\frac{e^{x}+e^{-x}}{2} cosh(x)=2ex+e−x,所以 t a n h ( x ) = e x − e − x e x + e − x tanh(x)=\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}} tanh(x)=ex+e−xex−e−x。
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mpl_toolkits.axisartist as axisartist
def tanh(x):
exp_x = math.exp(x)
exp_mx = math.exp(-x)
deno = exp_x + exp_mx
nume = exp_x - exp_mx
return nume/deno
if __name__=='__main__':
x1 = np.linspace(-5,5,100)
x2 = x1 + 2
# 使画布能显示汉字
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
y = [-tanh(e) for e in x1]
# 创建画布
fig = plt.figure()
# 使用axisartist.Subplot方法创建一个绘图区对象
ax = axisartist.Subplot(fig, 211)
# 把绘图区对象添加到画布中
fig.add_axes(ax)
# 通过set_axisline_style方法设置绘图区的底部及左侧坐标轴样式
# "-|>"代表实心箭头:"->"代表空心箭头
ax.axis["bottom"].set_axisline_style("->", size=1.5)
ax.axis["left"].set_axisline_style("->", size=1.5)
# 通过set_visible方法关闭上边框和右边框
ax.axis['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.axis['right'].set_visible(False)
# 在画布上画箭头
ax.annotate("", xy=(2, 0), xytext=(0, 0), arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
ax.annotate("", xy=(0, 1), xytext=(0, 0), arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
ax.annotate("", xy=(2, 0), xytext=(0, 1), arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
# 隐藏坐标轴刻度
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
# 在画布上写字符
plt.text(-0.4,-0.1,r'$p$')
plt.text(0.8, -0.2, r'$\vec{v}$')
plt.text(-0.4, 0.4, r'$\vec{I_{t}}$')
ax.annotate("时域导数", xy=(-0.4, 0.5), xytext=(-3, 0.4), arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
plt.text(0.6, 0.4, r'$\vec{I_{x}}$')
ax.annotate("空域导数", xy=(0.8, 0.4), xytext=(2.5, 0.4), arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
plt.xlabel('position')
plt.ylabel('pixel value')
plt.plot(x1,y,label=r'$I(x,t)$')
plt.plot(x2, y, label=r'$I(x,t + 1)$')
plt.legend()
plt.scatter(0,0)
plt.scatter([0,2], [1,0])
plt.show()