hdu 3480 Division(DP-DP优化)
Division
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 999999/400000 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2999 Accepted Submission(s): 1168
Problem Description
Little D is really interested in the theorem of sets recently. There’s a problem that confused him a long time.
Let T be a set of integers. Let the MIN be the minimum integer in T and MAX be the maximum, then the cost of set T if defined as (MAX – MIN)^2. Now given an integer set S, we want to find out M subsets S1, S2, …, SM of S, such that
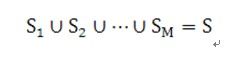
and the total cost of each subset is minimal.
Let T be a set of integers. Let the MIN be the minimum integer in T and MAX be the maximum, then the cost of set T if defined as (MAX – MIN)^2. Now given an integer set S, we want to find out M subsets S1, S2, …, SM of S, such that
and the total cost of each subset is minimal.
Input
The input contains multiple test cases.
In the first line of the input there’s an integer T which is the number of test cases. Then the description of T test cases will be given.
For any test case, the first line contains two integers N (≤ 10,000) and M (≤ 5,000). N is the number of elements in S (may be duplicated). M is the number of subsets that we want to get. In the next line, there will be N integers giving set S.
In the first line of the input there’s an integer T which is the number of test cases. Then the description of T test cases will be given.
For any test case, the first line contains two integers N (≤ 10,000) and M (≤ 5,000). N is the number of elements in S (may be duplicated). M is the number of subsets that we want to get. In the next line, there will be N integers giving set S.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing exactly one integer, the minimal total cost. Take a look at the sample output for format.
Sample Input
2 3 2 1 2 4 4 2 4 7 10 1
Sample Output
Case 1: 1 Case 2: 18
Hint
The answer will fit into a 32-bit signed integer.
首先,把数从小到大排序,你会发现,分成的M组,一定是相邻的为一组,原因:
假设有四个数,要划分两组
a b c d
相邻差: x y z
若选择:ab、cd,则花费为:x^2+z^2
若选择:ad、bc,则花费为:(x+y+z)^2+y^2
第一种选择明显比第二种选择好。
dp[i][j]表示前i个数分成j组的最小花费,则得到状态转移方程:
dp[i][j] = min(dp[k][j-1]+(a[i]-a[k+1])^2,dp[i][j]);
我们会这样枚举:
for(int j = 2; j <= M; j++){
for(int i = j; i <= N; i++){
for(int k = j-1; k < i; k++)
dp[i][j] = min(dp[k][j-1]+(a[i]-a[k+1])^2,dp[i][j]);
明显超时,需要优化。
设:k1 < k2
dp[k1][j-1]+(a[i]-a[k1+1])^2 <= dp[k2][j-1]+(a[i]-a[k2+1])^2
=>dp[k1][j-1]-dp[k2][j-1]+a[k1+1]^2-a[k2+1]^2 <= 2*a[i]*(a[k1+1]-a[k2+1])
因为a[k1+1] < a[k2+1];
=>(dp[k1][j-1]-dp[k2][j-1]+a[k1+1]^2-a[k2+1]^2 )/(2*(a[k1+1]-a[k2+1])) >= a[i]
令Q(k1,k2) = (dp[k1][j-1]-dp[k2][j-1]+a[k1+1]^2-a[k2+1]^2 )/(2*(a[k1+1]-a[k2+1]))
当Q(k1,k2) >= a[i]时,选择k1
当Q(k1,k2) <= a[i]时,选择k2
设k1 < k < k2
当Q(k , k2) <= Q(k1,k)时,无论如何都不会选择k,原因:
当a[i] <=Q(k,k2)<=Q(k1,k),选择k1
当a[i] >=Q(k,k2),选择k2
因此,维护的是斜率递增的队列,即Q(k1,k)
这题让我郁闷的是,我把数从大到小排序,然后再重新推公式,但是就是wa。。。
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10010;
int dp[maxn][maxn/2+10];
int a[maxn];
int N , M , q[maxn] , l , r;
bool cmp(int a , int b){
return a < b;
}
void readcase(){
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
scanf("%d" , &a[i]);
}
}
bool Q(int k1 , int k2 , int ai , int j){
int t1 = dp[k1][j-1]-dp[k2][j-1]+a[k1+1]*a[k1+1]-a[k2+1]*a[k2+1];
int t2 = 2*(a[k1+1]-a[k2+1])*ai;
if(t1 >= t2) return true;
return false;
}
bool fQ(int k1 , int k , int k2 , int j){
int t1 = (dp[k1][j-1]-dp[k][j-1]+a[k1+1]*a[k1+1]-a[k+1]*a[k+1])*(a[k+1]-a[k2+1]);
int t2 = (dp[k][j-1]-dp[k2][j-1]+a[k+1]*a[k+1]-a[k2+1]*a[k2+1])*(a[k1+1]-a[k+1]);
if(t1 >= t2) return true;
return false;
}
void computing(){
sort(a+1 , a+N+1 , cmp);
if(M >= N){
printf("0\n");
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) dp[i][1] = (a[i]-a[1])*(a[i]-a[1]);
for(int j = 2; j <= M; j++){
l = 0;
r = 0;
q[r] = j-1;
for(int i = j; i <= N; i++){
while(r-l > 0){
int k1 = q[l] , k2 = q[l+1];
if(Q(k1 , k2 , a[i] , j)) l++;
else break;
}
dp[i][j] = dp[q[l]][j-1]+(a[i]-a[q[l]+1])*(a[i]-a[q[l]+1]);
while(r-l > 0){
int k1 = q[r-1] , k = q[r] , k2 = i;
if(fQ(k1 , k , k2 , j)) r--;
else break;
}
q[++r] = i;
}
}
printf("%d\n" , dp[N][M]);
}
int main(){
int T;
scanf("%d" , &T);
for(int i = 1; i <= T; i++){
scanf("%d%d" , &N , &M);
readcase();
printf("Case %d: " , i);
computing();
}
return 0;
}