经典的策略模式案例
问题描述
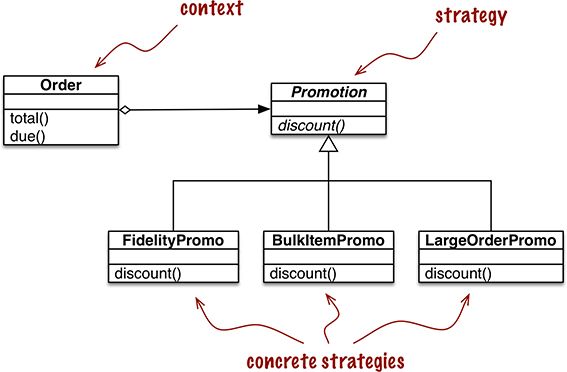
使用“策略”设计模式处理订单折扣的 UML 类图
定义一系列算法,把它们一一封装起来,并且使它们可以相互替换。本模式使得算法可以独立于使用它的客户而变化。
电商领域有个功能明显可以使用“策略”模式,即根据客户的属性或订单中的商品计算折扣。
假如一个网店制定了下述折扣规则,每个订单只能享用一个折扣:
- Customers with 1,000 or more fidelity points get a global 5% discount per order.
- A 10% discount is applied to each line item with 20 or more units in the same order.
- Orders with at least 10 distinct items get a 7% global discount.
content
把一些计算委托给实现不同算法的可互换组件,它提供服务。在这个电商示例中,上下文是 Order,它会根据不同的算法计算促销折扣。strategy
实现不同算法的组件共同的接口。在这个示例中,名为 Promotion 的抽象类扮演这个角色。concrete strategy
“策略”的具体子类。fidelityPromo、BulkPromo 和 LargeOrderPromo 是这里实现的三个具体策略。问题解决代码
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from collections import namedtuple
#--------------------------------------------------------
Customer = namedtuple('Customer', 'name fidelity') #类:(顾客, 积分)
#--------------------------------------------------------
class LineItem:
def __init__(self, product, quantity, price):
self.product = product
self.quantity = quantity
self.price = price
def total(self):
return self.price * self.quantity
#--------------------------------------------------------
class Order:
def __init__(self, customer, cart, promotion=None):
self.customer = customer
self.cart = list(cart)
self.promotion = promotion
def total(self):
if not hasattr(self, '__total'):
self.__total = sum(item.total() for item in self.cart)
return self.__total
def due(self):
if self.promotion is None:
discount = 0
else:
discount = self.promotion.discount(self)
return self.total() - discount
def __repr__(self):
fmt = ''
return fmt.format(self.total(), self.due())
#--------------------------------------------------------
class Promotion(ABC): # the Strategy: an abstract base class
@abstractmethod
def discount(self, order):
"""Return discount as a positive dollar amount"""
#--------------------------------------------------------
class FidelityPromo(Promotion): # first Concrete Strategy
"""5% discount for customers with 1000 or more fidelity points"""
def discount(self, order):
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0
#--------------------------------------------------------
class BulkItemPromo(Promotion): # second Concrete Strategy
"""10% discount for each LineItem with 20 or more units"""
def discount(self, order):
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount
#--------------------------------------------------------
class LargeOrderPromo(Promotion): # third Concrete Strategy
"""7% discount for orders with 10 or more distinct items"""
def discount(self, order):
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_items) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0 # 两个顾客:joe 的积分是 0,ann 的积分是 1100。
joe = Customer('John Doe', 0)
ann = Customer('Ann Smith', 1100)# 有三个商品的购物车
cart = [LineItem('banana', 4, .5),
LineItem('apple', 10, 1.5),
LineItem('watermellon', 5, 5.0)]# fidelityPromo 没给 joe 提供折扣
Order(joe, cart, FidelityPromo())# ann 得到了 5% 折扣,因为她的积分超过 1000
Order(ann, cart, FidelityPromo())# banana_cart 中有 30 把香蕉和 10 个苹果
banana_cart = [LineItem('banana', 30, .5),
LineItem('apple', 10, 1.5)]# BulkItemPromo 为 joe 购买的香蕉优惠了 1.50 美元
Order(joe, banana_cart, BulkItemPromo())# long_order 中有 10 个不同的商品,每个商品的价格为 1.00 美元
long_order = [LineItem(str(item_code), 1, 1.0) for item_code in range(10)]# LargerOrderPromo 为 joe 的整个订单提供了 7% 折扣
Order(joe, long_order, LargeOrderPromo())Order(joe, cart, LargeOrderPromo())案例来自《Fluent Python》Luciano Ramalho著