2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> ![]()
事务管理是应用系统开发中必不可少的一部分。Spring 为事务管理提供了丰富的功能支持。Spring 事务管理分为编程式和声明式的两种方式。编程式事务指的是通过编码方式实现事务;声明式事务基于 AOP,将具体业务逻辑与事务处理解耦。声明式事务管理使业务代码逻辑不受污染, 因此在实际使用中声明式事务用的比较多。声明式事务有两种方式,一种是在配置文件(xml)中做相关的事务规则声明,另一种是基于 @Transactional 注解的方式。本文将着重介绍基于 @Transactional 注解的事务管理。
需要明确几点:
- 默认配置下 Spring 只会回滚运行时、未检查异常(继承自 RuntimeException 的异常)或者 Error。参考这里
@Transactional注解只能应用到 public 方法才有效。参考这里 Method visibility and @Transactional
以下的示例使用的是 mybatis,所以 spring boot 会自动配置一个 DataSourceTransactionManager,我们只需在方法(或者类)加上 @Transactional 注解,就自动纳入 Spring 的事务管理了。
简单的使用方法
只需在方法加上 @Transactional 注解就可以了。
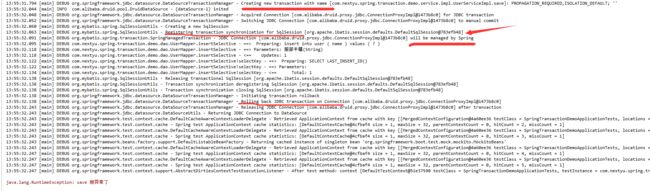
如下有一个保存用户的方法,加入 @Transactional 注解,使用默认配置,抛出异常之后,事务会自动回滚,数据不会插入到数据库。
@Transactional
@Override
public void save() {
User user = new User("服部半藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("save 抛异常了");
}
}
我们可以从日志里面看出这些信息
@Transactional 注解的属性介绍
下面分别介绍一下 @Transactional 的几个属性。
value 和 transactionManager 属性
它们两个是一样的意思。当配置了多个事务管理器时,可以使用该属性指定选择哪个事务管理器。
propagation 属性
事务的传播行为,默认值为 Propagation.REQUIRED。
可选的值有:
-
Propagation.REQUIRED
如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务,如果当前不存在事务,则创建一个新的事务。
-
Propagation.SUPPORTS
如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前不存在事务,则以非事务的方式继续运行。
-
Propagation.MANDATORY
如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前不存在事务,则抛出异常。
-
Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW
重新创建一个新的事务,如果当前存在事务,暂停当前的事务。
-
Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED
以非事务的方式运行,如果当前存在事务,暂停当前的事务。
-
Propagation.NEVER
以非事务的方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
-
Propagation.NESTED
和 Propagation.REQUIRED 效果一样。
这些概念理解起来实在是有点儿抽象,后文会用代码示例解释说明。
isolation 属性
事务的隔离级别,默认值为 Isolation.DEFAULT。
可选的值有:
-
Isolation.DEFAULT
使用底层数据库默认的隔离级别。
-
Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED
-
Isolation.READ_COMMITTED
-
Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ
-
Isolation.SERIALIZABLE
timeout 属性
事务的超时时间,默认值为-1。如果超过该时间限制但事务还没有完成,则自动回滚事务。
readOnly 属性
指定事务是否为只读事务,默认值为 false;为了忽略那些不需要事务的方法,比如读取数据,可以设置 read-only 为 true。
rollbackFor 属性
用于指定能够触发事务回滚的异常类型,可以指定多个异常类型。
noRollbackFor 属性
抛出指定的异常类型,不回滚事务,也可以指定多个异常类型。
@Transactional 的 propagation 属性代码示例
比如如下代码,save 方法首先调用了 method1 方法,然后抛出了异常,就会导致事务回滚,如下两条数据都不会插入数据库。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Override
public void save() {
method1();
User user = new User("服部半藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("save 抛异常了");
}
}
public void method1() {
User user = new User("宫本武藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
}
现在有需求如下,就算 save 方法的后面抛异常了,也不能影响 method1 方法的数据插入。或许很多人的想法如下,给 method1 页加入一个新的事务,这样 method1 就会在这个新的事务中执行,原来的事务不会影响到新的事务。比如 method1 方法上面再加入注解 @Transactional,设置 propagation 属性为 Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW,代码如下。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Override
public void save() {
method1();
User user = new User("服部半藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("save 抛异常了");
}
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void method1() {
User user = new User("宫本武藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
}
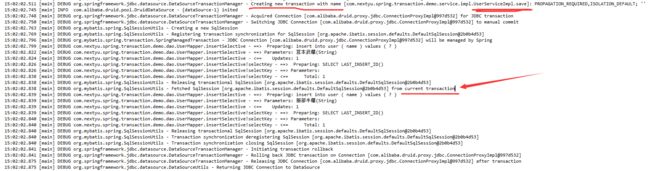
运行之后,发现然并卵,数据也是没有插入数据库。怎么肥四,看起来很不科学。我们先来看看日志内容。
从日志内容可以看出,其实两个方法都是处于同一个事务中,method1 方法并没有创建一个新的事务。
这就得看看 Spring 官方文档了。
![]()
In proxy mode (which is the default), only external method calls coming in through the proxy are intercepted. This means that self-invocation, in effect, a method within the target object calling another method of the target object, will not lead to an actual transaction at runtime even if the invoked method is marked with @Transactional.
大概意思:在默认的代理模式下,只有目标方法由外部调用,才能被 Spring 的事务拦截器拦截。在同一个类中的两个方法直接调用,是不会被 Spring 的事务拦截器拦截,就像上面的 save 方法直接调用了同一个类中的 method1方法,method1 方法不会被 Spring 的事务拦截器拦截。可以使用 AspectJ 取代 Spring AOP 代理来解决这个问题,但是这里暂不讨论。
为了解决这个问题,我们可以新建一个类。
@Service
public class OtherServiceImpl implements OtherService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
@Override
public void method1() {
User user = new User("风魔小太郎");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
}
}
然后在 save 方法中调用 otherService.method1 方法
@Autowired
private OtherService otherService;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Override
public void save() {
otherService.method1();
User user = new User("服部半藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("save 抛异常了");
}
}
这下,otherService.method1 方法的数据插入成功,save 方法的数据未插入,事务回滚。
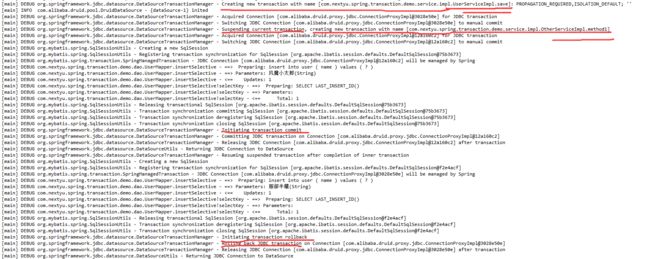
继续看一下日志内容
从日志可以看出,首先创建了 save 方法的事务,由于 otherService.method1 方法的 @Transactional 的 propagation 属性为 Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW ,所以接着暂停了 save 方法的事务,重新创建了 otherService.method1 方法的事务,接着 otherService.method1 方法的事务提交,接着 save 方法的事务回滚。这就印证了只有目标方法由外部调用,才能被 Spring 的事务拦截器拦截。
还有几个示例如下。
接着把 save 方法的 @Transactional 注解去掉,otherService.method1 的 @Transactional 注解保持不变,从日志就可以看出,只会创建一个 otherService.method1 方法的事务,两条数据都会插入。
@Autowired
private OtherService otherService;
// @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Override
public void save() {
otherService.method1();
User user = new User("服部半藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("save 抛异常了");
}
}
接着把 save 方法的 @Transactional 注解去掉,save 方法改为调用内部的 method1 方法,从日志就可以看出,完全没有创建任何事务,两条数据都会插入。
// @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Override
public void save() {
method1();
User user = new User("服部半藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("save 抛异常了");
}
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void method1() {
User user = new User("宫本武藏");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
}
这样,其他的几个 propagation 属性值也就比较好理解了。
@Transactional 事务实现机制
在应用系统调用声明了 @Transactional 的目标方法时,Spring Framework 默认使用 AOP 代理,在代码运行时生成一个代理对象,根据 @Transactional 的属性配置信息,这个代理对象决定该声明 @Transactional 的目标方法是否由拦截器 TransactionInterceptor 来使用拦截,在 TransactionInterceptor 拦截时,会在目标方法开始执行之前创建并加入事务,并执行目标方法的逻辑, 最后根据执行情况是否出现异常,利用抽象事务管理器 AbstractPlatformTransactionManager 操作数据源 DataSource 提交或回滚事务。
Spring AOP 代理有 CglibAopProxy 和 JdkDynamicAopProxy 两种,以 CglibAopProxy 为例,对于 CglibAopProxy,需要调用其内部类的 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor 的 intercept 方法。对于 JdkDynamicAopProxy,需要调用其 invoke 方法。
![]()
正如上文提到的,事务管理的框架是由抽象事务管理器 AbstractPlatformTransactionManager 来提供的,而具体的底层事务处理实现,由 PlatformTransactionManager 的具体实现类来实现,如事务管理器 DataSourceTransactionManager。不同的事务管理器管理不同的数据资源 DataSource,比如 DataSourceTransactionManager 管理 JDBC 的 Connection。
![]()
源码地址
- https://github.com/nextyu/spring-transaction-demo
参考资料
- Spring 官方文档
- Spring boot 官方文档
- Mybatis
- 资料
- 资料
- 资料
结语
由于本人知识和能力有限,文中如有没说清楚的地方,希望大家能在评论区指出,以帮助我将博文写得更好。