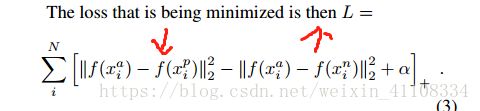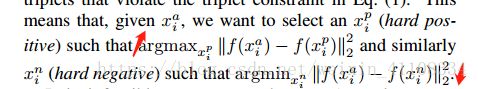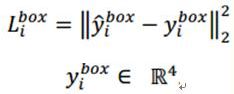深度学习:人脸识别Facenet_cvpr2015+MTcnn
论文_2015cvpr:FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering
facenet史上最全代码详解:https://blog.csdn.net/u013044310/article/details/79556099
triplet loss 代码解析:https://blog.csdn.net/u011918382/article/details/79006782
三元组博客 :https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/35560666
一、MTCNN
一、主要思想:
embedding映射关系:将特征从原来的特征空间映射到一个新的特征空间上,新的特征就称原来的特征嵌入,卷积末端全连接层输出为的特征映射到一个超球面上,使其特征二范数归一化。
通过 CNN人脸图像特征映射到欧式空间的特征向量上,计算不同图片人脸特征的距离,通过相同个体的人脸的距离,总是小于不同个体的人脸这一先验知识训练网络。测试时只需要计算人脸特征,然后计算距离使用阈值即可判定两张人脸照片是否属于相同的个体。识别:如每个人抽取512或者256维度,将维度上的值进行欧式距离计算,小于一个阈值则判定是同一个人,否者不是同一人。
亮点: embedding 嵌入层 特征提取 128 256 512 特征向量
triplet loss 用于粒度比较小的粒度。
二、网络结构:
网络结构:传统的卷积神经网络,然后在求L2范数之前进行归一化,就建立了这个嵌入空间(512/256/128维),最后损失函数。
triplet loss 将嵌入层输出 例如:40postive 5个negative mini-batch 选出一个 hard 三元组 然后计算损失 反复 更新参数 更新 嵌入层embedding
三、triplet loss
1、三元组概念
triplet loss 损失函数,用于训练差异性较小的样本
在有监督的机器学习领域,通常有固定的类别,这时就可以使用基于softmax的交叉熵损失函数进行训练。但有时,类别是一个变量,此时使用triplet loss就能解决问题。在人脸识别,Quora question pair任务中,triplet loss的优势在于细节区分,即当两个输入相似时,triplet loss能够更好地对细节进行建模,相当于加入了两个输入差异性差异的度量,学习到输入的更好表示,从而在上述两个任务中有出色的表现。当然,triplet loss的缺点在于其收敛速度慢,有时不收敛。
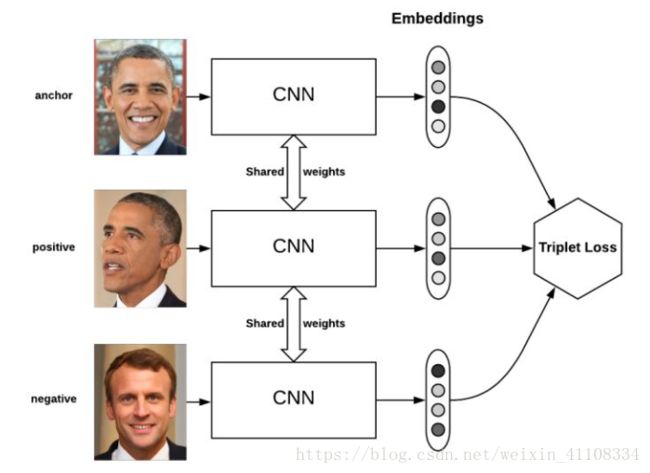
Triplet loss的motivation是要让属于同一个人的人脸尽可能地“近”(在embedding空间里),而与其他人脸尽可能地“远”。
anchor 为锚点 negative positive,经过learning使得离positive正 距离变小,negative负 距离变大,用于训练差异性较小的样本,
2、三元组定义
triplet loss的目标是:
两个具有同样标签的样本,他们在新的编码空间里距离很近。
两个具有不同标签的样本,他们在新的编码空间里距离很远。
进一步,我们希望两个positive examples和一个negative example中,negative example与positive example的距离,大于positive examples之间的距离,或者大于某一个阈值:margin。
3、LOSS function
4、三元组分类 :
为了保证训练的收敛速度,选择距离最远的相同人像hard-positive,和最近的不同人像训练hard negative,在mini-batch中进行选择.
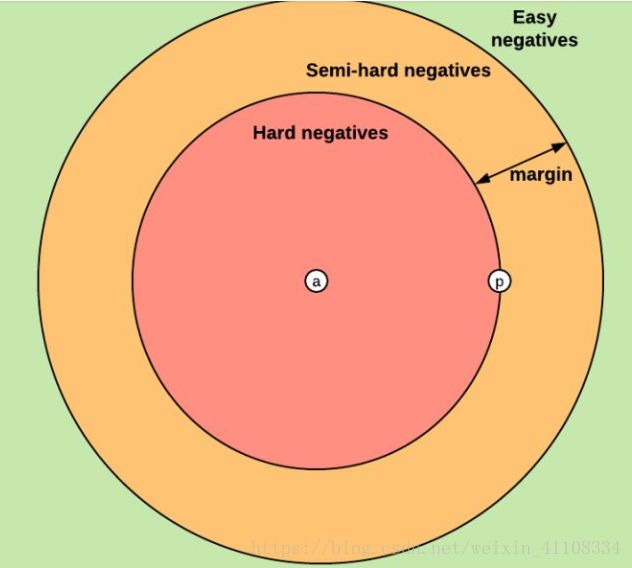
- easy triplets(简单三元组): triplet对应的损失为0的三元组,形式化定义为d(a,n)>d(a,p)+margin。
- hard triplets(困难三元组): negative example 与anchor距离小于anchor与positive example的距离,形式化定义为 d(a,n)
- semi-hard triplets(一般三元组): negative example 与anchor距离大于anchor与positive example的距离,但还不至于使得loss为0,即d(a,p)
- semi-hard triplets(一般三元组): negative example 与anchor距离大于anchor与positive example的距离,但还不至于使得loss为0,即d(a,p)
上述三种概念都是基于negative example与anchor和positive距离定义的。类似的,可以根据上述定义将negative examples分为3类:hard negatives, easy negatives, semi-hard negatives。如下图所示,这个图构建了编码空间中三种negative examples与anchor和positive example之间的距离关系。
如何选择triplet或者negative examples,对模型的效率有很大影响。在上述Facenet论文中,采用了随机的semi-hard negative构建triplet进行训练,取得了不错的效果。
5、offline /online triplet mining
通过上面的分析,可以看到,easy negative example比较容易识别,没必要构建太多由easy negative example组成的triplet,否则会严重降低训练效率。若都采用hard negative example,又可能会影响训练效果。这时,就需要一定的方法进行triplet的挑选,也就是“mine the triplets”。
5.1 Offline triplet mining
离线方式的triplet mining将所有的训练数据喂给神经网络,得到每一个训练样本的编码,根据编码计算得到negative example与anchor和positive example之间的距离,根据这个距离判断semi-hard triplets,hard triplets还是easy triplets。offline triplet mining 仅仅选择select hard or semi-hard triplets,因为easy triplet太容易了,没有必要训练。
总得来说,这个方法不够高效,因为最初要把所有的训练数据喂给神经网络,而且每过1个或几个epoch,可能还要重新对negative examples进行分类。
5.2 Online triplet mining
Google的研究人员为解决上述问题,提出了online triplet mining的方法。该方法的motivation比较简单,将B张图片(一个batch)喂给神经网络,得到B张图片的embedding,将triplet的组合一共最多$B^3$个triplets,其中包含很多没用的triplet(比如,三个negative examples和三个positive examples,这种称作invalid triplets)。哪些是valid triplets呢?假设一个triplet$(B_i,B_j,B_k)$,如果样本i和j有相同的label且不是同一个样本,而样本k具有不同的label,则称其为valid triplet。
假设一个batch的数据包含P*K张人脸,P个人,每人K张图片。
针对valid triplet的“挑选”,有以下两个策略(来自论文[1703.07737] In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification):
- batch all: 计算所有的valid triplet,对6hard 和 semi-hard triplets上的loss进行平均。
- 不考虑easy triplets,因为easy triplets的损失为0,平均会把整体损失缩小
- 将会产生PK(K-1)(PK-K)个triplet,即PK个anchor,对于每个anchor有k-1个可能的positive example,PK-K个可能的negative examples
- batch hard: 对于每一个anchor,选择hardest positive example(距离anchor最大的positive example)和hardest negative(距离anchor最小的negative example),
- 由此产生PK个triplet
- 这些triplet是最难分的
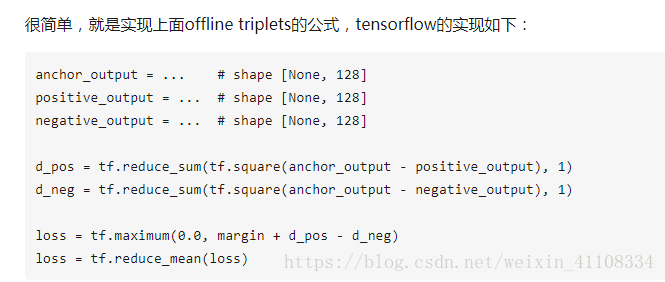
4. 那如何用tensorflow实现triplet loss呢?
4.1 offline triplets
4.2 online triplets
4.2.1 batch all的实现方式
- batch all: 计算所有的valid triplet,对6hard 和 semi-hard triplets上的loss进行平均。
- 不考虑easy triplets,因为easy triplets的损失为0,平均会把整体损失缩小
- 将会产生PK(K-1)(PK-K)个triplet,即PK个anchor,对于每个anchor有k-1个可能的positive example,PK-K个可能的negative examples
def batch_all_triplet_loss(labels, embeddings, margin, squared=False):
"""Build the triplet loss over a batch of embeddings.
We generate all the valid triplets and average the loss over the positive ones.
Args:
labels: labels of the batch, of size (batch_size,)
embeddings: tensor of shape (batch_size, embed_dim)
margin: margin for triplet loss
squared: Boolean. If true, output is the pairwise squared euclidean distance matrix.
If false, output is the pairwise euclidean distance matrix.
Returns:
triplet_loss: scalar tensor containing the triplet loss
"""
# Get the pairwise distance matrix
pairwise_dist = _pairwise_distances(embeddings, squared=squared)
anchor_positive_dist = tf.expand_dims(pairwise_dist, 2)
anchor_negative_dist = tf.expand_dims(pairwise_dist, 1)
# Compute a 3D tensor of size (batch_size, batch_size, batch_size)
# triplet_loss[i, j, k] will contain the triplet loss of anchor=i, positive=j, negative=k
# Uses broadcasting where the 1st argument has shape (batch_size, batch_size, 1)
# and the 2nd (batch_size, 1, batch_size)
triplet_loss = anchor_positive_dist - anchor_negative_dist + margin
# Put to zero the invalid triplets
# (where label(a) != label(p) or label(n) == label(a) or a == p)
mask = _get_triplet_mask(labels)
mask = tf.to_float(mask)
triplet_loss = tf.multiply(mask, triplet_loss)
# Remove negative losses (i.e. the easy triplets)
triplet_loss = tf.maximum(triplet_loss, 0.0)
# Count number of positive triplets (where triplet_loss > 0)
valid_triplets = tf.to_float(tf.greater(triplet_loss, 1e-16))
num_positive_triplets = tf.reduce_sum(valid_triplets)
num_valid_triplets = tf.reduce_sum(mask)
fraction_positive_triplets = num_positive_triplets / (num_valid_triplets + 1e-16)
# Get final mean triplet loss over the positive valid triplets
triplet_loss = tf.reduce_sum(triplet_loss) / (num_positive_triplets + 1e-16)
return triplet_loss, fraction_positive_triplets
4.2.2 batch hard的实现方式
- batch hard: 对于每一个anchor,选择hardest positive example(距离anchor最大的positive example)和hardest negative(距离anchor最小的negative example),
- 由此产生PK个triplet
- 这些triplet是最难分的
def batch_hard_triplet_loss(labels, embeddings, margin, squared=False):
"""Build the triplet loss over a batch of embeddings.
For each anchor, we get the hardest positive and hardest negative to form a triplet.
Args:
labels: labels of the batch, of size (batch_size,)
embeddings: tensor of shape (batch_size, embed_dim)
margin: margin for triplet loss
squared: Boolean. If true, output is the pairwise squared euclidean distance matrix.
If false, output is the pairwise euclidean distance matrix.
Returns:
triplet_loss: scalar tensor containing the triplet loss
"""
# Get the pairwise distance matrix
pairwise_dist = _pairwise_distances(embeddings, squared=squared)
# For each anchor, get the hardest positive
# First, we need to get a mask for every valid positive (they should have same label)
mask_anchor_positive = _get_anchor_positive_triplet_mask(labels)
mask_anchor_positive = tf.to_float(mask_anchor_positive)
# We put to 0 any element where (a, p) is not valid (valid if a != p and label(a) == label(p))
anchor_positive_dist = tf.multiply(mask_anchor_positive, pairwise_dist)
# shape (batch_size, 1)
hardest_positive_dist = tf.reduce_max(anchor_positive_dist, axis=1, keepdims=True)
# For each anchor, get the hardest negative
# First, we need to get a mask for every valid negative (they should have different labels)
mask_anchor_negative = _get_anchor_negative_triplet_mask(labels)
mask_anchor_negative = tf.to_float(mask_anchor_negative)
# We add the maximum value in each row to the invalid negatives (label(a) == label(n))
max_anchor_negative_dist = tf.reduce_max(pairwise_dist, axis=1, keepdims=True)
anchor_negative_dist = pairwise_dist + max_anchor_negative_dist * (1.0 - mask_anchor_negative)
# shape (batch_size,)
hardest_negative_dist = tf.reduce_min(anchor_negative_dist, axis=1, keepdims=True)
# Combine biggest d(a, p) and smallest d(a, n) into final triplet loss
triplet_loss = tf.maximum(hardest_positive_dist - hardest_negative_dist + margin, 0.0)
# Get final mean triplet loss
triplet_loss = tf.reduce_mean(triplet_loss)
return triplet_loss
在minist等数据集上的效果都是棒棒哒。
5. 总结
triplet loss的实现不是很简单,比较tricky的地方是如何计算embedding的距离,以及怎样识别并抛弃掉invalid和easy triplet。当然,如果您使用的是tensorflow,可以直接移步至[github repository](omoindrot/tensorflow-triplet-loss),有一份写好的triplet loss在等着你。。。
可能有人会有疑惑,siamese network, triplet network的输入都是成对的,或者triplet的三元组,怎么对一个样本进行分类啊?神经网络的优势在于表示学习,自动的特征提取,所以,成对或者triplet的输入能让神经网络学到输入的更好的表示,后面再接svm, logtistic regression就可以啦。
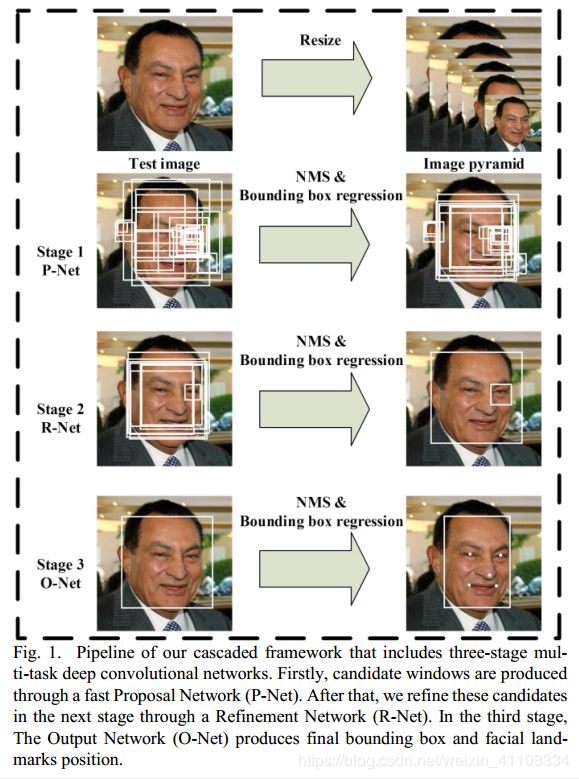
二、MTCNN
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/38520597
Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks - 原文
- 知乎专栏:MTCNN人脸检测---PNet网络训练
- 知乎专栏:MTCNN人脸检测---RNet网络训练
- 知乎专栏:MTCNN人脸检测---ONet网络训练
同时进行人脸检测和人脸对齐
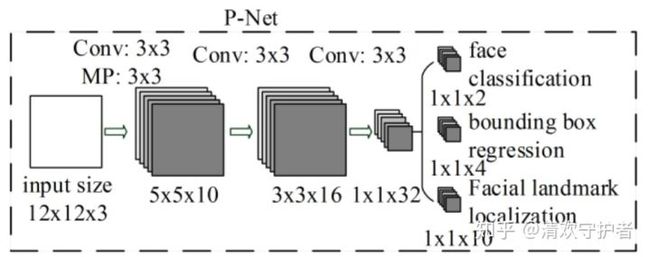
1、模型结构
2、细节详解
- Proposal Network(P-Net):
使用全卷积网络FCN,用来生成候选框和边框回归向量(bounding box regression vectors),使用bounding box regression 的方法来校正这些候选框,使用非大值抑制(nms)合并重叠的候选框。
- 输入:原始图片resize到不同尺寸,作为输入。
- 使用FCN的思想,每
12*12*3作为一个bbox作为输入,预测预测的分类信息、bbox信息、landmark localization信息。 - 为什么要将原始图片resize到不同尺寸?
- 原始图片上人脸大小可能不一致,最开始都是通过
12*12*3预测人脸信息。 - resize到不同尺寸图片,可以对检测不同大小的人脸信息。
- 原始图片上人脸大小可能不一致,最开始都是通过
- Refine Network(R-Net):
使用N-Net改善候选窗。将通过P-Net的候选窗输入R-Net中,拒绝掉大部分false的窗口,继续使用Bounding box regression和NMS合并。
- 输入:以P-Net预测的bbox信息作为基础,对原始图片进行切片,并resize到固定尺寸。
- 预测预测的分类信息、bbox信息、landmark localization信息,并对bbox进行NMS筛选。
- Output Network(O-Net):
最后使用O-Net输出最终的人脸框和特征点位置。和第二步类似,但是不同的是生成5个特征点位置。
- 输入:以R-Net预测的bbox信息作为基础,对原始图片进行切片,并resize到固定尺寸。
- 预测预测的分类信息、bbox信息、landmark localization信息,并对bbox进行NMS筛选。
- 训练:
算法实现三个任务的学习:人脸和非人脸的分类(2),bounding box regression(4),人脸特征点定位(10)
2.3. 损失函数介绍
MTCNN 特征描述3个部分,人脸、非人脸分类器,边界框回归,地标定位
- 人脸分类误差,模型预测是否是人脸:人脸分类交叉熵损失函数,pi是人脸的概率,yidet是背景真实标签
![]()
- 边界框bbox 回归误差,模型预测的是offset(偏移量),而非bbox本身:欧氏距离计算回归损失,y是真是坐标,y帽网络预测,y(x左上角,y右上角,长,宽)组成的四元组
- landmark localization 地标定位 误差,预测人脸以下几个关键点:双眼、鼻子、两个嘴角。5*2=10 (x,y)
预测与真实的欧式距离,最小化该距离,
![]()
2.4. 多任务训练,损失
- 对于每一层来说,都有三类误差,但对于不同的训练数据,三类误差应该有不同的权值,因此提出了以下公式:
- 其中 alpha 是每类误差的权重,每一层权重不同。
多个输入源训练:
![]()
整个的训练学习过程就是最小化上面的这个函数,其中,N为训练样本数量,aj表示任务的重要性,bj为样本标签,Lj为上面的损失函数。
在训练过程中,为了取得更好的效果,作者每次只后向传播前70%样本的梯度,这样来保证传递的都是有效的数字。有点类似latent SVM,只是作者在实现上更加体现了深度学习的端到端。
2.5. Online Hard Sample mining
- 作用:构建训练数据的方法。
- 流程:传统的难例处理方法是检测过一次以后,手动检测哪些困难的样本无法被分类,本文采用online hard sample mining的方法。具体就是在每个mini-batch中,取loss最大的70%进行反向传播,忽略那些简单的样本。
- 在每个mini-batch中,计算所有loss,并降序排序。
- 获取钱获取前70%的sample进行梯度下降训练。
2.6. 训练数据构建
在训练过程中,y尖和y的交并集IoU(Intersection-over-Union)比例:
0-0.3:非人脸
0.65-1.00:人脸
0.4-0.65:Part人脸
0.3-0.4:地标
训练样本的比例,负样本:正样本:part样本:地标=3:1:1:2
- 分类:
- positives:与 ground truth 的IOU高于阈值。
- negatives:与 ground truth 的IOU低于阈值。
- part faces:与 ground truth 的IOU处于上述两个阈值之间。
- landmark faces:拥有landmark的标签。
- 使用:
- 分类任务使用 positives & negatives。
- bbox预测使用 potitives & part faces。
- landmark localization预测使用 landmark faces。
2.7. 如何进行 face alignment ?
- 可以参考:知乎提问:MTCNN人脸对齐得到关键点的坐标后,下一步人脸矫正应该怎么做呢?
3.实验
数据集:FDDB,Wider Face,AFLW
A、训练数据
本文将数据分成4种:
Negative:非人脸
Positive:人脸
Part faces:部分人脸
Landmark face:标记好特征点的人脸
分别用于训练三种不同的任务。Negative和Positive用于人脸分类,positive和part faces用于bounding box regression,landmark face用于特征点定位。
B、效果
本文的人脸检测和人脸特征点定位的效果都非常好。关键是这个算法速度很快,在2.6GHZ的CPU上达到16fps,在Nvidia Titan达到99fps。
4.其他细节
4.1.bounding box regression
http://www.caffecn.cn/?/question/160
简单而言就是将预测的框移动到实际的框,输入特征是候选区域提取的特征,目标是两个框的变化值。
4.2.IoU重叠度
物体检测需要定位出物体的bounding box,就像下面的图片一样,我们不仅要定位出车辆的bounding box 我们还要识别出bounding box 里面的物体就是车辆。
![]()
对于bounding box的定位精度,有一个很重要的概念: 因为我们算法不可能百分百跟人工标注的数据完全匹配,因此就存在一个定位精度评价公式:IOU。 它定义了两个bounding box的重叠度,如下图所示
![]()
就是矩形框A、B的重叠面积占A、B并集的面积比例。
4.3非极大值抑制NMS
RCNN会从一张图片中找出n个可能是物体的矩形框,然后为每个矩形框为做类别分类概率:
![]()
就像上面的图片一样,定位一个车辆,最后算法就找出了一堆的方框,我们需要判别哪些矩形框是没用的。非极大值抑制的方法是:先假设有6个矩形框,根据分类器的类别分类概率做排序,假设从小到大属于车辆的概率 分别为A、B、C、D、E、F。
(1)从最大概率矩形框F开始,分别判断A~E与F的重叠度IOU是否大于某个设定的阈值;
(2)假设B、D与F的重叠度超过阈值,那么就扔掉B、D;并标记第一个矩形框F,是我们保留下来的。
(3)从剩下的矩形框A、C、E中,选择概率最大的E,然后判断E与A、C的重叠度,重叠度大于一定的阈值,那么就扔掉;并标记E是我们保留下来的第二个矩形框。
就这样一直重复,找到所有被保留下来的矩形框。
非极大值抑制(NMS)顾名思义就是抑制不是极大值的元素,搜索局部的极大值。这个局部代表的是一个邻域,邻域有两个参数可变,一是邻域的维数,二是邻域的大小。这里不讨论通用的NMS算法,而是用于在目标检测中用于提取分数最高的窗口的。例如在行人检测中,滑动窗口经提取特征,经分类器分类识别后,每个窗口都会得到一个分数。但是滑动窗口会导致很多窗口与其他窗口存在包含或者大部分交叉的情况。这时就需要用到NMS来选取那些邻域里分数最高(是行人的概率最大),并且抑制那些分数低的窗口。
详情参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41108334/article/details/82897572
三、代码解析
代码解析:https://blog.csdn.net/u013044310/article/details/79556099
检测+识别
检测mtcnn :人脸对齐align ,detect_face.py(网络构建p,r,o)==>align_dataset_mtcnn.py (扣出检测到的人脸)