runtime(三)消息传递中方法找寻的过程
目录
- 从这行代码看起
- message.h
- 汇编源码
- objc_msgSend调用栈
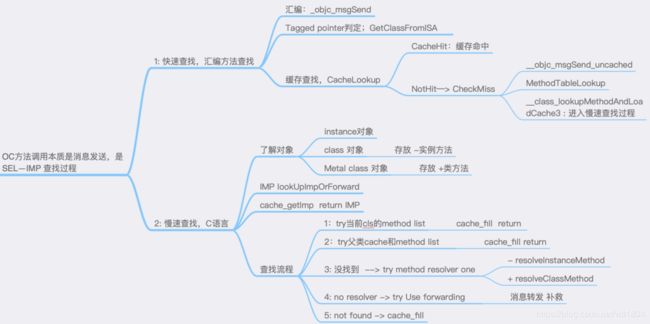
- lookUpImpOrForward源码
- 1.无锁的缓存查找
- 2.如果类没有实现(isRealized)或者初始化(isInitialized),实现或者初始化类
- 3.加锁
- 4.缓存以及当前类中方法的查找
- 5.尝试查找父类的缓存以及方法列表
- 6.没有找到实现,尝试方法解析器
- 7.进行消息转发
- 如果有了缓存
- 参考资料
从这行代码看起
object hello] -> objc_msgSend(object, @selector(hello))
众所周知,我们的消息传递会被转换成为这个函数。
生成的这个@selector(hello)叫做选择子,而且创建几个不同的类,调用这个方法,生成的还是这个选择子。
我们在这里打印俩个选择子的地址
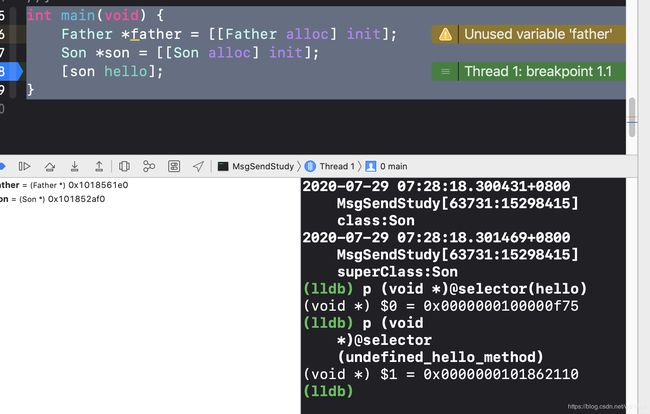
一个是@selector(hello)
一个是@selector(undefined_hello_method)
这俩个有什么区别呢?
@selector(hello) 是在编译期间就声明的选择子,而后者在编译期间并不存在,undefined_hello_method 选择子由于是在运行时生成的,所以内存地址明显比 hello 大很多
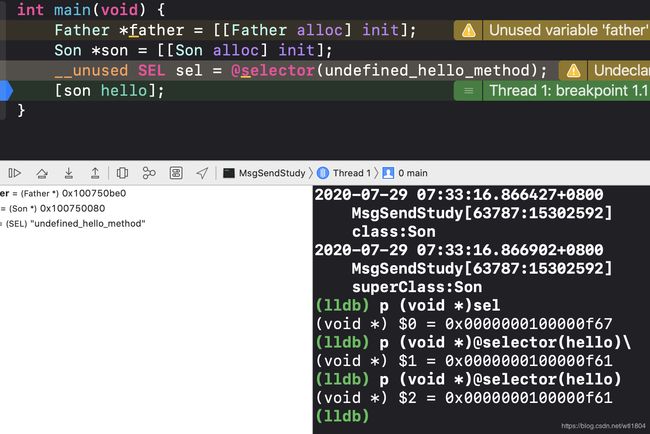
这次我们显示的声明这个选择子。再次打印地址,发现这个地址和之前的undefined_hello_method有很大出入,而这次的地址和@selector(hello)很接近。所以推测:
1.Objective-C 为我们维护了一个巨大的选择子表
2.在使用 @selector() 时会从这个选择子表中根据选择子的名字查找对应的 SEL。如果没有找到,则会生成一个 SEL 并添加到表中
3.在编译期间会扫描全部的头文件和实现文件将其中的方法以及使用 @selector() 生成的选择子加入到选择子表中
我们来验证@selecotor(hello)在运行期之前就存在的事实。

记住这个地址,在runtime初始化之前,打断点,打印hello地址。
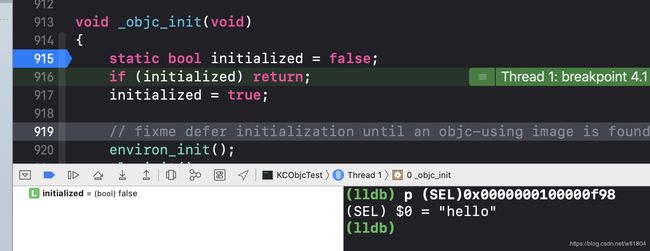
注意这里打印的方式,如果按照刚刚的方式打印

这里让我很疑惑。
然而objc_msgSend并没有开源,仅在message.h的头文件里出现
message.h
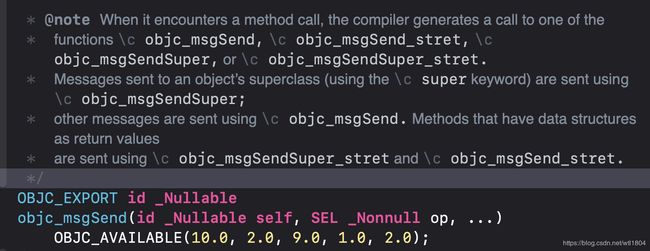
翻译一下
当遇到方法调用时,编译器生成对其中一个方法的调用
函数\c objc_msgSend, \c objc_msgSend_stret, \c objc_msgSendSuper,或\c objc_msgSendSuper_stret
发送给对象超类的消息(使用\c super关键字)使用\c objc_msgSendSuper发送;
其他消息使用\c objc_msgSend发送。以数据结构作为返回值的方法
使用\c objc_msgSendSuper_stret和\c objc_msgSend_stret发送。
汇编源码
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
cbz r0, LNilReceiver_f //判断消息接收者是否为nil
ldr r9, [r0] // r9 = self->isa
GetClassFromIsa // r9 = class
CacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSend
// cache hit, IMP in r12, eq already set for nonstret forwarding
//找到方法缓存的地址
bx r12 // call imp //调用方法
CacheLookup2 NORMAL, _objc_msgSend
// cache miss
ldr r9, [r0] // r9 = self->isa
GetClassFromIsa // r9 = class
b __objc_msgSend_uncached //没有找到缓存,就从类、父类、元类去找
LNilReceiver:
// r0 is already zero
mov r1, #0
mov r2, #0
mov r3, #0
FP_RETURN_ZERO
bx lr
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend
entry代表进入函数
下面我们就来探究一下消息发送的过程,但是这里并不对这几个方法进行区别。
objc_msgSend调用栈
先快速了解xcode左下方那几个按钮的意思。
step over、step into、step out
这三个的意思为:
单步执行下:越过子函数、进入子函数、跳出子函数。
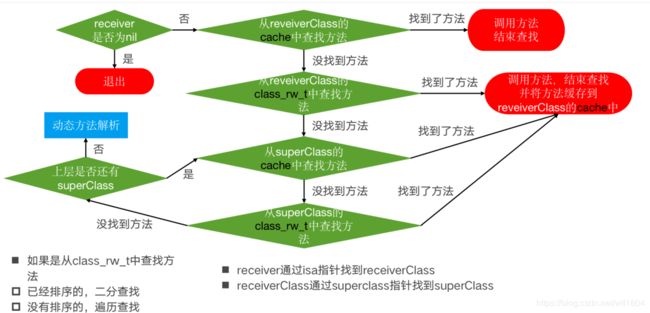
调用 objc_msgSend 时,传入了 self 以及 SEL 参数。既然要执行对应的方法,肯定要寻找选择子对应的实现。在 objc-runtime-new.mm 文件中有一个函数 lookUpImpOrForward,这个函数的作用就是查找方法的实现,于是运行程序,在运行到 hello 这一行时,激活 lookUpImpOrForward 函数中的断点
在 -> [son hello] 这里增加一个断点,当程序运行到这一行时,再向 lookUpImpOrForward 函数的第一行添加断点,确保是捕获 @selector(hello) 的调用栈,而不是调用其它选择子的调用栈。
在左下方可以看到sel确实是hello。
在左侧可以看到调用栈,这个lookUp函数已经经过修改,早期版本查看调用栈是可以看到objc_msgSend以及一个提供给派发器的函数。
就目前来看这个找寻imp的方法并不是objc_msgSend直接调用的,而是_objc_msgSend_uncached调用。
这个函数没有具体实现
下面我们来具体分析lookUpImpOrForward这个函数
lookUpImpOrForward源码
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
const IMP forward_imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
IMP imp = nil;
Class curClass;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
这里再到缓存中查找一遍,防止动态添加了方法
if (fastpath(behavior & LOOKUP_CACHE)) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done_nolock;
}
runtimeLock.lock();
checkIsKnownClass(cls);
if (slowpath(!cls->isRealized())) {
cls = realizeClassMaybeSwiftAndLeaveLocked(cls, runtimeLock);
}
if (slowpath((behavior & LOOKUP_INITIALIZE) && !cls->isInitialized())) {
cls = initializeAndLeaveLocked(cls, inst, runtimeLock);
}
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
curClass = cls;
for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) {
拿到当前类的方法列表去找sel,找到就跳到 done,
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
利用父类的指针做方法寻找
if (slowpath((curClass = curClass->superclass) == nil)) {
imp = forward_imp;
break;
}
if (slowpath(--attempts == 0)) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
查找父类的缓存
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (slowpath(imp == forward_imp)) {
break;
}
if (fastpath(imp)) {
父类中找到缓存,跳出,并缓存到自己的类中
goto done;
}
}
在缓存 父类中都没有找到方法,这个时候尝试动态方法解析
if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) {
behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;
return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
done:
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
runtimeLock.unlock();
done_nolock:
if (slowpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == forward_imp)) {
return nil;
}
return imp;
}
1.无锁的缓存查找
if (fastpath(behavior & LOOKUP_CACHE)) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done_nolock;
}
2.如果类没有实现(isRealized)或者初始化(isInitialized),实现或者初始化类
//上一篇博客里写,将类的方法列表初始化的方法就是relizedclassWithSwift(老版本是realizedClass)
if (slowpath(!cls->isRealized())) {
cls = realizeClassMaybeSwiftAndLeaveLocked(cls, runtimeLock);
}
if (slowpath((behavior & LOOKUP_INITIALIZE) && !cls->isInitialized())) {
cls = initializeAndLeaveLocked(cls, inst, runtimeLock);
}
这里初始化后,才能从方法列表里找到方法。没有初始化,类的方法都在class_ro_t中。
3.加锁
4.缓存以及当前类中方法的查找
for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) {
拿到当前类的方法列表去找sel,找到就跳到 done,
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
......
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount()这个东东的注释是
- Provides an upper bound for any iteration of classes,
- to prevent spins when runtime metadata is corrupted.
- 为类的任何迭代提供一个上限,
- 在运行时元数据被破坏时防止自旋。
由于太菜,没有看懂这个原理
来看看这个方法
static method_t *
getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
// fixme nil cls?
// fixme nil sel?
for (auto mlists = cls->data()->methods.beginLists(),
end = cls->data()->methods.endLists();
mlists != end;
++mlists)
{
// getMethodNoSuper_nolock is the hottest
// caller of search_method_list, inlining it turns
// getMethodNoSuper_nolock into a frame-less function and eliminates
// any store from this codepath.
method_t *m = search_method_list_inline(*mlists, sel);
if (m) return m;
}
return nil;
}
首先要确保类存在。
cls->data()获取了类的class_rw_t 结构体,访问methode,这个method的类型是 method_array_t,是个数组类型。这个数组类型继承了c++的map
public list_array_tt
然而我的c++并不好,只能看看注释了
A list_array_tt has one of three values:
- empty
- a pointer to a single list
- an array of pointers to lists
总之这个方法的大概就是遍历了方法列表,而且可以看到,这里列表是嵌套的,列表中还有列表。如果找到,返回了method_t类型。
返回后,赋值给了Method类型的meth,这个Method其实就是method_t,是被typedef了一下。
5.尝试查找父类的缓存以及方法列表
for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) {
。。。。
//拿到当前类的方法列表去找sel,找到就跳到 done,
。。。。
//省略上面的代码。
if (slowpath((curClass = curClass->superclass) == nil)) {
imp = forward_imp;
break;
}
从当前类的父类去找方法实现。只有NSObject的父类是nil。这里赋值如果失败了,启动消息转发。
forward_imp在第一行就被const了,现在赋值给了imp,然后跳出循环,执行方法解析。
如果赋值成功了,则执行下面的代码
if (slowpath(--attempts == 0)) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (slowpath(imp == forward_imp)) {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
if (fastpath(imp)) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
goto done;
}
此时的curClass是父类,所以先从父类的缓存中去找,如果父类的方法缓存里发现了转发入口,就停止搜索,执行方法解析,但此时不缓存。
第二个判断里,fastpath是利用汇编去找,然后去done.
6.没有找到实现,尝试方法解析器
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) {
behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;
return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
方法解析找出我们在runtime增加的方法。
7.进行消息转发
最终,父类的方法无法找到,会到NSObject中去找,还没有找到,那么会将forward_imp赋值给imp
const IMP forward_imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
返回_objc_msgForward_impcache,然后缓存。
如果有了缓存
将代码修改一下

可以看到没有执行lookUpImpOrForWard.但其实在objc_msgSend里已经找寻了方法缓存,由于本人太菜,看不懂汇编,只能看懂注释。
参考资料
从源代码看objc消息传递