自定义TextView实现
前言
文本展示在Android开发中非常常见,大部分都是用TextView来实现,不过有些文本展示必须要手动调用Canvas来绘制,如果不了解绘制文本的原理很难把展示的文本对齐,这里就来记录一下文本绘制的各种技巧。
文本测量
在Android中调用Canvas绘制图形图像提供的坐标都代表对象的左上角位置,但绘制文本的坐标却不是左上角而是文本基线的左下角,下面的图详细展示了文本各个位置的对应关系。

图中的各个变量的值都是以基线baseLine作为坐标轴确定的,其中向上为负数,向下为正数,我们可以使用Paint对象的FontMetrics对象查看它的各个属性部分对应的数值,可以看到bottom和desc是正数而top和asc则是负数。
fontMetricsInt.top = -96
fontMetricsInt.ascent = -83
fontMetricsInt.descent = 22
fontMetricsInt.bottom = 25通常文本都是竖向填满整个控件的内容,而Canvas.drawText方法的x,y却是文本的基线左边位置,x轴防线的左边很容器确定就是getPaddingLeft()左边补白的部分,但竖向的位置还需要仔细的做计算。考虑做一条从View横向平分分割线,那么个这条分割线的y值就是getHeight() / 2, 而baseLine和横向平分线的距离还有一个dy的差值,getHeight() / 2 + dy就是基线的竖直坐标值。
横向分割线其实和(Math.abs(bottom) + Math.abs(top)) / 2处在同一个位置,而基线到bottom之间的距离就是bottom,所以可以得知dy = (bottom - top) / 2 - bottom,最终基线的位置就是:
int dy = (fontMetricsInt.bottom - fontMetricsInt.top) / 2 - fontMetricsInt.bottom;
int baseLine = getHeight() / 2 + dy;变色TextView实现
TextView经常作为Tab来展示,有些控件能够监听不同Tab切换的进度,这时需要根据进度展示不同的TextView颜色。这种通常都是使用clipPath裁剪一块展示区域专门展示一种颜色的文本,再使用clipPath裁剪另外一块区域展示另外一种颜色的文本,裁剪范围的确定和progress存在关系。

public class CustomTextView extends AppCompatTextView {
private Paint mInnerPaint;
private Paint mOuterPaint;
private float mProgress;
private int colorDefault = Color.BLACK;
private int colorNew = Color.RED;
public CustomTextView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
setTextSize(20);
mInnerPaint = new Paint();
mInnerPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mInnerPaint.setDither(true);
mInnerPaint.setTextSize(dp2sp(20));
mInnerPaint.setColor(colorDefault);
mOuterPaint = new Paint();
mOuterPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mOuterPaint.setDither(true);
mOuterPaint.setTextSize(dp2sp(20));
mOuterPaint.setColor(colorNew);
mProgress = 0.5f;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
Paint.FontMetricsInt fontMetricsInt = mOuterPaint.getFontMetricsInt();
int dy = (fontMetricsInt.bottom - fontMetricsInt.top) / 2 - fontMetricsInt.bottom;
int baseLine = getHeight() / 2 + dy;
// 根据当前进度值计算需要clip的矩形大小,展示红色文本
canvas.save();
canvas.clipRect(0, 0, mProgress * getWidth(), getHeight());
canvas.drawText(getText().toString(), getPaddingLeft(), baseLine, mInnerPaint);
canvas.restore();
// 根据当前进度值计算需要clip的矩形大小,展示黑色文本
canvas.save();
canvas.clipRect(mProgress * getWidth(), 0, getWidth(), getHeight());
canvas.drawText(getText().toString(), getPaddingLeft(), baseLine, mOuterPaint);
canvas.restore();
}
public int dp2sp(int dp) {
return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, dp, getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
public void setProgress(float progress) {
this.mProgress = progress;
invalidate();
}
}
探照灯效果
有些TextView的文按为了能够吸引用户的注意,通常会加入动态元素,探照灯效果就是不停地扫描文本部分内容让它与别的区域展示不同,它主要是利用Shader的内部matrix来实现颜色效果改变。

public class BlinkTextView extends AppCompatTextView {
private Paint mPaint;
private LinearGradient mGradient;
private Matrix mMatrix;
private String mText = "Hello World, Good Morning to you!!";
private ValueAnimator mValueAnimator;
public BlinkTextView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public BlinkTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public BlinkTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
setBackgroundColor(Color.BLACK);
setText(mText);
setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
mPaint = getPaint();
mPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.colorAccent));
// 定义渐变颜色,并且指定其本地Matrix
mGradient = new LinearGradient(0, 0, CommonUtils.dp2px(40), 0,
new int[] { 0x33ffffff, 0xffffffff, 0x33ffffff },
new float[] { 0.1f, 0.5f, 0.9f }, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
mMatrix = new Matrix();
mGradient.setLocalMatrix(mMatrix);
mPaint.setTextSize(50);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setDither(true);
mPaint.setShader(mGradient);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
float width = mPaint.measureText(mText);
mValueAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat((w - width) / 2, w / 2 + width / 2);
mValueAnimator.setDuration(1000);
mValueAnimator.setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.REVERSE);
mValueAnimator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
mValueAnimator.addUpdateListener(animation -> {
float current = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
// 做属性动画操作不断改变本地matrix的偏移值,实现探照灯效果
mMatrix.setTranslate(current, 0);
mGradient.setLocalMatrix(mMatrix);
invalidate();
});
mValueAnimator.start();
}
}数据加载控件
有些加载控件需要能够展示自定义的文本,这些文本和当前用户正在执行的应用紧密相关,这就要求能够在自定义的View内部准确绘制文案,保证文案对齐效果,这就需要前面提到的文本测量方法准确计算文本的展示基线。
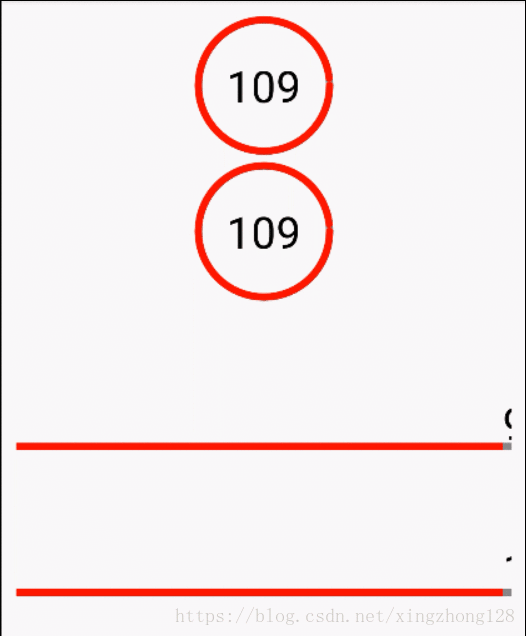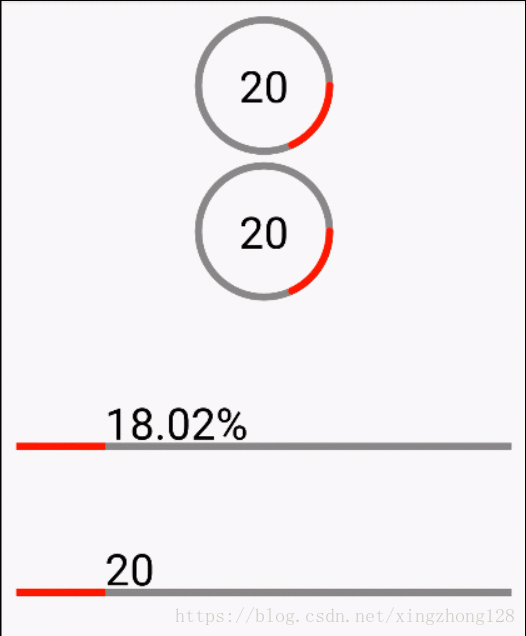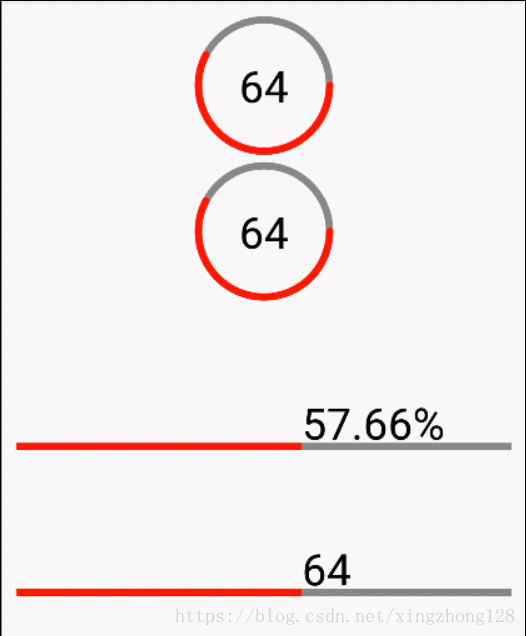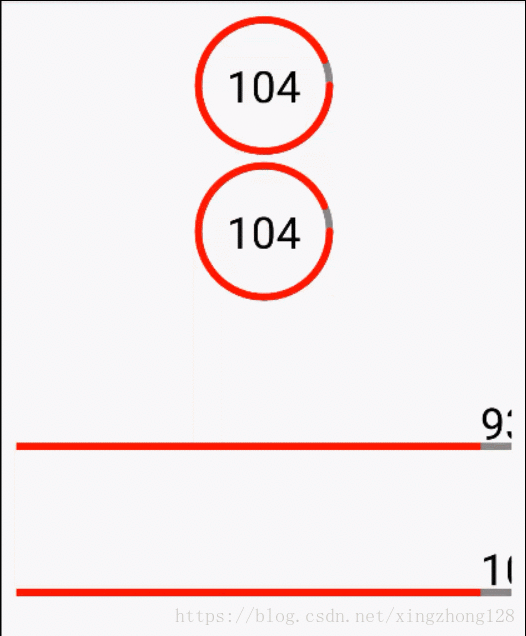
public class ProgressView extends View {
// 加载分成圆形和线性展示
private static final int ROUND = 0;
private static final int LINE = 1;
// 文本按照数字或者百分比展示
private static final int PERCENT = 0;
private static final int TEXT = 1;
private int mShape = ROUND;
private int mType = TEXT;
private Paint mShapePaint;
private Paint mTextPaint;
@ColorInt
private int mColorUnprocessed = Color.GRAY;
@ColorInt
private int mColorProcessed = Color.RED;
@ColorInt
private int mColorText = Color.BLACK;
private int mMaxCount = 111;
private int mCurrent = 0;
private RectF mTmpRectF;
public ProgressView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public ProgressView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public ProgressView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
if (attrs != null) {
TypedArray array = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ProgressView);
mMaxCount = array.getInt(R.styleable.ProgressView_progress_max_count, mMaxCount);
mCurrent = array.getInt(R.styleable.ProgressView_progress_current, mCurrent);
mShape = array.getInt(R.styleable.ProgressView_progress_shape, ROUND);
mType = array.getInt(R.styleable.ProgressView_progress_type, TEXT);
array.recycle();
}
mShapePaint = new Paint();
mShapePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mShapePaint.setDither(true);
mShapePaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint.setDither(true);
mTextPaint.setTextSize(dp2px(30));
mTextPaint.setColor(mColorText);
mTmpRectF = new RectF();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
float progress = mCurrent * 1.0f / mMaxCount;
if (mShape == ROUND) {
int radius = (int) Math.min(getWidth() / 2 - dp2px(5), getHeight() / 2 - dp2px(5));
mShapePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mShapePaint.setStrokeWidth(dp2px(5));
mShapePaint.setColor(mColorUnprocessed);
// 绘制底部圆形
canvas.drawCircle(getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2, radius, mShapePaint);
mTmpRectF.set(getWidth() / 2 - radius, getHeight() / 2 - radius, getWidth() / 2 + radius,
getHeight() / 2 + radius);
mShapePaint.setColor(mColorProcessed);
// 绘制当前进度圆形
canvas.drawArc(mTmpRectF, 0, progress * 360, false, mShapePaint);
// 计算处于中间位置的文案baseLine
Paint.FontMetricsInt fontMetricsInt = mTextPaint.getFontMetricsInt();
int dy = (fontMetricsInt.bottom - fontMetricsInt.top) / 2 - fontMetricsInt.bottom;
String text = mType == PERCENT ? String.format("%.2f%%", progress * 100f) : String.valueOf(mCurrent);
int x = (int) (getWidth() / 2 - mTextPaint.measureText(text) / 2);
int y = getHeight() / 2 + dy;
canvas.drawText(text, x, y, mTextPaint);
} else {
mShapePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mShapePaint.setColor(mColorUnprocessed);
mTmpRectF.set(getPaddingLeft(), getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() - dp2px(5),
getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), getHeight() - getPaddingBottom());
canvas.drawRect(mTmpRectF, mShapePaint);
mTmpRectF.set(getPaddingLeft(), getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() - dp2px(5),
getPaddingLeft() + (getWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) * progress,
getHeight() - getPaddingBottom());
mShapePaint.setColor(mColorProcessed);
canvas.drawRect(mTmpRectF, mShapePaint);
String text = mType == PERCENT ? String.format("%.2f%%", progress * 100f) : String.valueOf(mCurrent);
int x = (int) (getPaddingLeft() + (getWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) * progress);
Paint.FontMetricsInt fontMetricsInt = mTextPaint.getFontMetricsInt();
// 计算当文案贴着横条时的baseLine位置
int y = getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() - fontMetricsInt.descent;
canvas.drawText(text, x, y, mTextPaint);
}
}
private float dp2px(int dp) {
return TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, dp, getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
public void setCurrent(int current) {
this.mCurrent = current;
invalidate();
}
public void setMaxCount(int maxCount) {
if (maxCount == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("mMaxCount must be positive!");
}
this.mMaxCount = maxCount;
invalidate();
}
public int getMax() {
return mMaxCount;
}
}