IO(输入、输出)数据流(Java小白进阶day12)
IO流
1、IO->Input Output
具体底层架构图
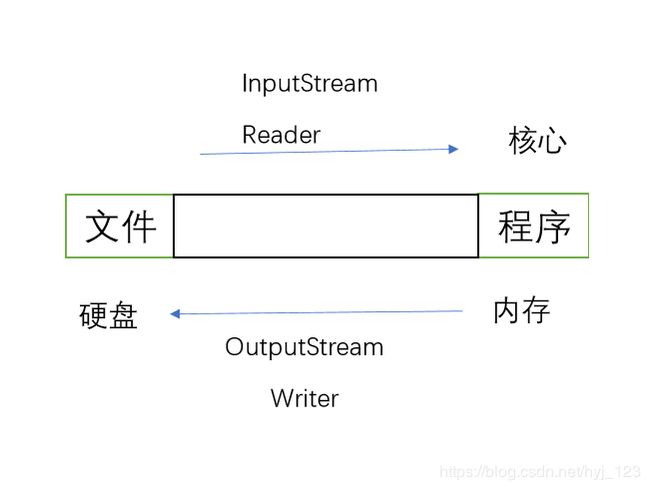
2、按照流的读写方式:字节流和字符流
字节流–传输过程中,传输数据的最基本单位是字节的流。
字符流–传输过程中,传输数据的最基本单位是字符的流。
3、按照流的放向:输入流和输出流
InputStream abstract
Reader abstract
OutputStream abstract
Writer abstract
4、输入流的核心方法:read()
输出流的核心方法:write()
5、操作的数组类型
字节流:byte 类型
字节流:char类型
6、FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
使用步骤
1> 选择流类(输入或者输出)
2> 确定方法(read还是write)
3> 关闭流close
public class Demo1 {
//文件的写操作,将字符串写入到a.txt文件中,write()方法
public static void test1() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("a.txt");//FileNotFoundException异常
//若无a.txt可自动创建
out.write("hello".getBytes());//IOException
out.close();
}
//文件的读操作,从a.txt里面读取数据,read()方法
public static void test2() throws IOException {
File file = new File("a.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();//如果文件不存在,创建
}
//创建文件输入流对象
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
byte[] buf = new byte[(int) file.length()];//file.length()为long型
input.read(buf);//把数据读到数组中
System.out.println(new String(buf));//把数组转换为字符串
input.close();
}
public static void test3() throws IOException{
File file = new File("a.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
//创建输入流对象
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
int n =0;
//while((n=input.read())!=-1) {
//System.out.print((char)n);
//utf-8汉字3字节,gbk汉字2字节,字母数字占一位
byte[] b = new byte[3];
while ((n=input.read(b))!=-1) {
System.out.print(new String(b));
}
input.close();
}
//追加文本
public static void test() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("a.txt",true);
outputStream.write("hello\n".getBytes());
outputStream.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
test1();
}
7、对象的输入流和输出流
对象的序列化:把对象转化为二进制的流,写到数据文件中
//Serializable标识性接口,表示类为序列化的类
//创建的对象是一个序列化对象
public class Student implements Serializable{
/**
* serialVersionUID 序列化的版本号
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//serialVersionUID为序列化的版本号
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name,int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
public class Demo {
//写对象到数据文件oo.txt
public static void test1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("oos.txt",true));
Student stu1 = new Student("admin", 18);
Student stu2 = new Student("张三", 18);
oos.writeObject(stu1);
oos.writeObject(stu2);
oos.close();
}
public static void test2() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file = new File("oos.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Student stu1 = (Student)ois.readObject();
Student stu2 = (Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(stu1);
System.out.println(stu2);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
test2();
}
}
对象的反序列化:把数据文件中的二进制的流代表的数据,恢复为对象
8、按照流是否能直接操作数据文件:节点流和处理流
节点流:直接在构造方法中传入要读写的文件对象或文件名
处理流:不能直接在构造方法中传入要读写的文件对象或文件名
9、FileReader和FileWriter
public class Demo3 {
public static void test() throws IOException {
//
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");
fw.write("hello韩");
fw.close();
}
public static void test1() throws IOException {
File file = new File("fw.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
char[] buf = new char[(int) file.length()];
fr.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf));
}
//复制fw.txt的内容到fw1.txt文件中
public static void test2() throws IOException {
File f1 = new File("fw.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(f1);
char[] buf = new char[(int) f1.length()];
fr.read(buf);//将数据放入
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw1.txt");
fw.write(buf);
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
test2();
}
}
10、BufferReader和BufferWriter效率高 \n
readLine()
11、转换流:
InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter
public class Demo4 {
public static void test1() throws IOException {
PrintWriter pWriter = new PrintWriter("pw.txt");
pWriter.println("张三 132332 [email protected]");
pWriter.println("李四 165877 [email protected]");
pWriter.close();
}
public static void test2() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("pw.txt"));
String string = "";
while ((string = br.readLine())!=null) {
String[] value = string.split("\\s");
String nameString = value[0];
String phoneString = value[1];
String emailString = value[2];
System.out.println("name:"+nameString+",phone:"+phoneString);
}
br.close();
}
//连接InputStream与BufferedReader
public static void test3() throws IOException{
InputStream ins = new FileInputStream("ins.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(ins));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
test2();
}
}
12、输入流和输出流是一个流对象:
RandomAccessFile类
小结 File FileInputStream FileOutputStream
ObjectInputStream ObjectOutputStreamFileReader FileWriter BuffferedReader PrintWriter
InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter
复习:
1、Math
final,构造方法是私有的,方法由static修饰 ceil,floor,min,max,round,random[0,1) double
Random类
next(10)[0,10)+1
2、日期相关的类
Data
SimpleDateFormt
format():data->字符串
parse():字符串->data Calendar
getInstance()
月份:0-11 +1
getTime():Data LocalTime
LocalTime.now() LocalData LocalDateTime
3、异常类
继承关系:Throwable:Error,Exception
Exception:
RuntimeException:运行时
其它:编译时
处理异常(运行时异常,不强制处理):
throws Exception
try-catch try-catch:
try后跟catch或者finally
自定义异常
标识异常类:继承任意异常类
异常信息:super(msg)
throw和throws
4、File
new File("d:\\a.text");
new File("d:\\","a.txt");
new File(new File("d:\\","a.txt"));
//mkdir() mkdirs() delete()//一个一个删 exists()
if(!file.exists()){
file.creatNewFile();
}
//length() isFile(),isDirectory() getName(),getParents(),getPath(),getAbsolutePath()