Leetcode第134场周赛题目学习
1033.移动石子直到连续
题目描述
三枚石子放置在数轴上,位置分别为 a,b,c。
每一回合,我们假设这三枚石子当前分别位于位置 x, y, z 且 x < y < z。从位置 x 或者是位置 z 拿起一枚石子,并将该石子移动到某一整数位置 k 处,其中 x < k < z 且 k != y。
当你无法进行任何移动时,即,这些石子的位置连续时,游戏结束。
要使游戏结束,你可以执行的最小和最大移动次数分别是多少? 以长度为 2 的数组形式返回答案:answer = [minimum_moves, maximum_moves]
示例1:
输入:a = 1, b = 2, c = 5
输出:[1, 2]
解释:将石子从 5 移动到 4 再移动到 3,或者我们可以直接将石子移动到 3。
示例2:
输入:a = 4, b = 3, c = 2
输出:[0, 0]
解释:我们无法进行任何移动。
提示:
1 <= a <= 1001 <= b <= 1001 <= c <= 100a != b, b != c, c != a
解题思路
首先,将a,b,c按递增顺序排好。
其次,考虑最大步数。因为排序好以后,b不能移动,所以最大步数就是a,c向b靠拢的步数,即b-a-1+c-b-1。
接下来考虑最小步数。分三种情况:
a,b,c已经连续,此种情况不需要移动。b-a和c-b有一个为1,说明有一对连续,只需移动另外一个到b即可,即1步就可以了。b-a和c-b有任意一个为2,说明有一对之间只差一个位置,将另一个移到此位置即可,即1步就可以了。
其余情况,只需要2步,分别将a和c移动到b的两边。
参考代码
class Solution:
def numMovesStones(self, a: int, b: int, c: int) -> List[int]:
l=[a,b,c]
l.sort()
ansmax=l[2]-l[1]-1+l[1]-l[0]-1
if l[2]-l[1]==l[1]-l[0]==1:
return [0,ansmax]
elif l[2]-l[1]==1 or l[1]-l[0]==1:
return [1,ansmax]
elif l[2]-l[1]==2 or l[1]-l[0]==2:
return [1,ansmax]
else:
return [2,ansmax]
1036.逃离大迷宫
题目描述
在一个 10^6 x 10^6 的网格中,每个网格块的坐标为 (x, y),其中 0 <= x, y < 10^6。
我们从源方格 source 开始出发,意图赶往目标方格 target。每次移动,我们都可以走到网格中在四个方向上相邻的方格,只要该方格不在给出的封锁列表 blocked 上。
只有在可以通过一系列的移动到达目标方格时才返回 true。否则,返回 false。
示例1:
输入:blocked = [[0,1],[1,0]], source = [0,0], target = [0,2]
输出:false
解释:
从源方格无法到达目标方格,因为我们无法在网格中移动。
示例2:
输入:blocked = [], source = [0,0], target = [999999,999999]
输出:true
解释:
因为没有方格被封锁,所以一定可以到达目标方格。
提示:
0 <= blocked.length <= 200blocked[i].length == 20 <= blocked[i][j] < 10^6source.length == target.length == 20 <= source[i][j], target[i][j] < 10^6source != target
参考思路
这是一个很大的网格,常规的BFS或是DFS会超时。
此时需分析,什么情况下source到不了target?即source或者target被blocked包围(或加上边界)
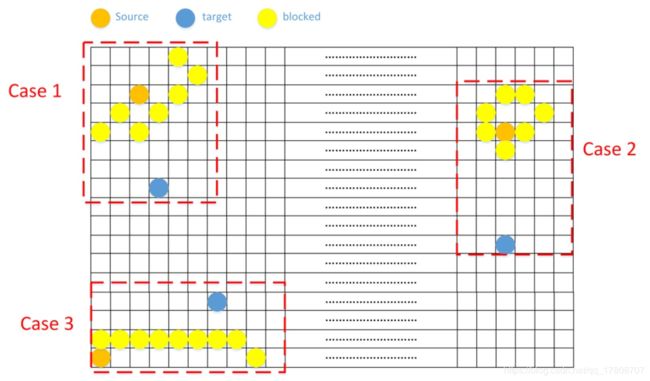
如果可以走超过blocked数量步数(最极端情况为上图的case3),说明没有被blocked包围,则必然可走出去。
参考代码
class Solution:
def isEscapePossible(self, blocked: List[List[int]], source: List[int], target: List[int]) -> bool:
from collections import deque
blocked=set(map(tuple,blocked))
def bfs(source,target):
queue=deque()
queue.appendleft((source[0],source[1],0))
visited=set()
visited.add(tuple(source))
dirs=[(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0)]
while queue:
x,y,step=queue.pop()
if x==target[0] and y==target[1]:
return True
for i,j in dirs:
tempx=i+x
tempy=j+y
if 0<=tempx<10**6 and 0<=tempy<=10**6 and (tempx,tempy) not in visited and (tempx,tempy) not in blocked:
visited.add((tempx,tempy))
queue.appendleft((tempx,tempy,step+1))
if step==len(blocked):
return True
return False
return bfs(source,target) and bfs(target,source)