彷徨 | Hive的SQL--DDL详细操作
Hive的简介与安装见另一篇文章 : https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_35353187/article/details/82154151
Hive的三种使用方式 :
方式一 : bin/hive 交互式查询
方式二 : 启动Hive的网络服务 , 然后通过客户端beeline去连接服务进行查询 :
启动服务 : bin/hiveserver2
启动客户端去连接Hive服务 : bin/beeline -u jdbc:hive2://hadoop01:10000 -n root
方式三 : shell脚本方式查询
#!/bin/bash
HIVE_HOME=/root/apps/hive-1.2.2
$HIVE_HOME/bin/hive -e 'insert into table t_avg as select skuid,avg(amount) from t_2 group by skuid'
$HIVE_HOME/bin/hive -e 'create table t_result as select skuid,sum(amount) from t_2 group by skuid'
补充一 :bin/hive -f /root/etl.sql (把sql语句写到一个专门的文件里), Linux 会去执行SQL文件里面的所有语句
新建一个test.sql文件 , 里面放俩条SQL语句 :
执行 hive -f /root/test.sql 命令
补充二 : 在Linux窗口hive -e '' SQL语句 '' 也可以执行SQL语句
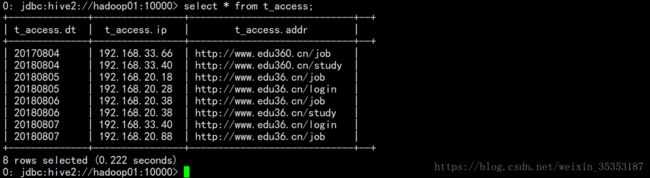
hive -e 'select * from t_access'
可以看出查询结果是一样的
补充三 : SQL是一种面向集合的编程语言
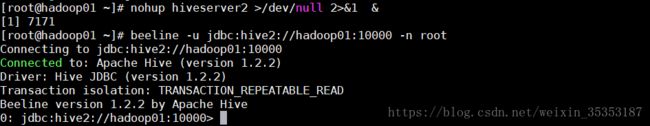
1 以服务的形式启动Hive :
nohup hiveserver2 >/dev/null 2>&1 &
2 客户端连接 :
方式一:
beeline
!connect jdbc:hive2://hadoop01:10000
root
方式二:
beeline -u jdbc:hive2://hadoop01:10000 -n root
查看端口是否被监听 : netstat -nltp
如果10000端口被监听 , hive服务就启动了 .
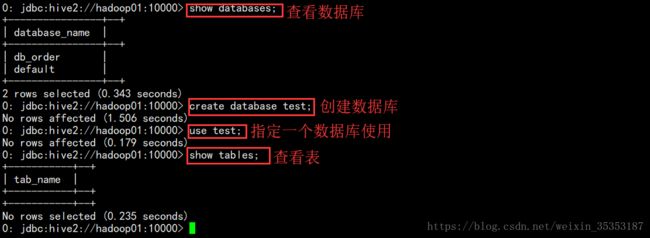
3 基本操作语句
3.1 创建内部表
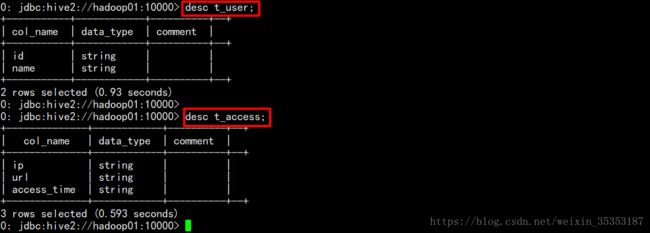
create table t_user(id string,name string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ',';
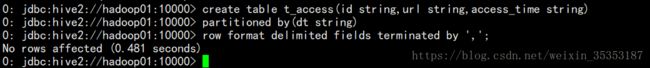
3.2 创建外部表
create external table t_access(ip String,url String,access_time String)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
location "/data/acc";
内部表直接把数据上传到hdfs对应的目录(/user/hive/warehouse)上,就能够关联起来 . 外部表跟内部表的区别,内部表放在warehouse下面,删除表的时候会把数据删除掉,外部表示需要自己制定目录,删除表的时候,不会删除数据
3.3 查看表结构.
desc tablename
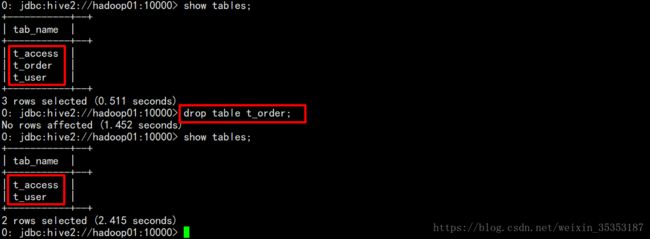
3.4 删除表
drop table t_order;
删除表的效果是:
hive会从元数据库中清除关于这个表的信息;
hive还会从hdfs中删除这个表的表目录;
3.5 分区表
3.5.1 一个分区建表
注意:分区字段,不能出现在表字段里面 , 不同的分区数据存放在不同的目录下面
create table t_access(id string,url string,access_time string)
partitioned by(dt string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
日志文件 :
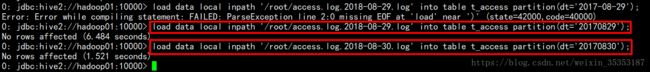
向分区中导入数据 :
load data local inpath '/root/access.log.2018-08-29.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170829');
load data local inpath '/root/access.log.2018-08-30.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170830');
针对分区进行查询 :
A : 统计8月30号的总量:实质:就是将分区字段当成表字段来用,就可以使用where子句指定分区了
select count(*) from t_access where dt='20180829';
B : 统计表中所有数据总量:实质:不指定分区条件即可
select count(*) from t_access;
3.5.2 多个分区建表
3.5.2.1 内部表分区
建表 :
CREATE TABLE t_2(id int,skuid string,price float,amount int)
partitioned by (day string,city string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
导数据 :
t 2.1 数据 :2018-04-15 北京
t 2.2 数据 :2018-04-15 上海
![]()
t 2.3 数据 :
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/root/t2.1' into TABLE t_2 PARTITION(day='2018-04-15',city='beijing');
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/root/t2.2' into TABLE t_2 PARTITION(day='2018-04-15',city='shanghai');
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/root/t2.3' into TABLE t_2 PARTITION(day='2018-04-16',city='beijing');
查询 :
1 : select * from t_2;
2 : select sum(price*amount) from t_2;
3 : select sum(price*amount) from t_2 where day = "2018-04-15" and city = "beijing";
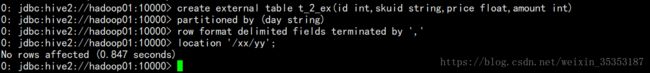
3.5.2.2 外部表分区
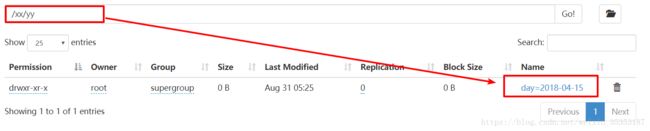
建表 :注:外部表建表时,最后需要制定一个目录 location '/xx/yy';
导数据 :
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/root/t2.1' into TABLE t_2_ex PARTITION(day='2018-04-15');
查询 :
注 : 给外部表添加分区
已经存在一个目录 , 但是不在外部表的指定目录下 , 我们可以修改表 , 给这个表添加一个目录 .即将一个已存在的文件夹 , 作为表的一个分区 .
此时,根目录下面有一个2018-04-16的文件夹,里面有一个名为 t2.1 的文件
我们将其添加到外部表的指定目录 /xx/yy 下 , 以便一起查询 . 此时只是Hive记录了那个文件的位置 , 并没有将文件复制或剪贴到外部表的指定目录.
alter table t_2_ex add partition (day = '2018-04-16') location '/2018-04-16';
查询 :
select * from t_2_ex;
我们将其添加到外部表的指定目录 /xx/yy 下 , 以便一起查询 . 此时只是Hive记录了那个文件的位置 , 并没有将文件复制或剪贴到外部表的指定目录 . 可以看到外部表的指定目录 /xx/yy下只有2018-04-15一个文件夹 , 并没有我们刚才添加的2018-04-16文件夹 ,但是查询的时候 , 会查询到里面的内容 .
此方法也适用于内部表 , 可以将一个已存在的文件夹作为内部表的一个分区
3.6 CTAS建表语法
3.6.1 可以通过已存在表来建表:
create table t_user_2 like t_user;
新建的t_user_2表结构定义与源表t_user一致,但是没有数据
查看表数据 : 并没有数据
3.6.2 在建表的同时插入数据
create table t_user_3
as
select id,name from t_user;
t_user_3会根据select查询的字段来建表,同时将查询的结果插入新表中
查询新表数据 :
3.7 数据的导入与导出
3.7.1 将数据文件导入hive的表
方式1:导入数据的一种方式:手动用hdfs命令,将文件放入表目录;
方式2:在hive的交互式shell中用hive命令来导入本地数据到表目录 ( 将本地文件导入 Hive 中的表 )
hive>load data local inpath '/root/order.data.2' into table t_order;
方式3:用hive命令导入hdfs中的数据文件到表目录 ( 将 HDFS 中的文件导入Hive中 )
hive>load data inpath '/access.log.2017-08-06.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170806');
注意:导本地文件和导HDFS文件的区别:
本地文件导入表:复制
hdfs文件导入表:移动
注 :Hive不会对用户所导入的数据做任何的检查和约束;想导什么数据就导什么数据,但是字段不匹配会出现问题.
3.7.2 将hive表中的数据导出到指定路径的文件
将hive表中的数据导入HDFS的文件
insert overwrite directory '/root/access-data'
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
select * from t_access;
将hive表中的数据导入本地磁盘文件
insert overwrite local directory '/root/access-data'
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
select * from t_access limit 100000;
3.7.3 hive文件格式
HIVE支持很多种文件格式: SEQUENCE FILE | TEXT FILE | PARQUET FILE | RC FILE
create table t_pq(movie string,rate int) stored as textfile;
create table t_pq(movie string,rate int) stored as sequencefile;
create table t_pq(movie string,rate int) stored as parquetfile;
3.8 时间类型
TIMESTAMP (时间戳) (包含年月日时分秒的一种封装)
DATE (日期)(只包含年月日)
示例,假如有以下数据文件:
| 1,zhangsan,1985-06-30 2,lisi,1986-07-10 3,wangwu,1985-08-09 |
那么,就可以建一个表来对数据进行映射
create table t_customer(id int,name string,birthday date)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
然后导入数据
load data local inpath '/root/customer.dat' into table t_customer;
然后,就可以正确查询
3.9 复合类型
3.9.1 array数组类型
示例:array类型的应用
假如有如下数据需要用hive的表去映射:
| 战狼2,吴京:吴刚:龙母,2017-08-16 三生三世十里桃花,刘亦菲:痒痒,2017-08-20 |
设想:如果主演信息用一个数组来映射比较方便
建表:
create table t_movie(moive_name string,actors array
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':';
导入数据:
load data local inpath '/root/movie.dat' into table t_movie;
查询:
select * from t_movie;
我也不知道为啥没对齐,很尴尬
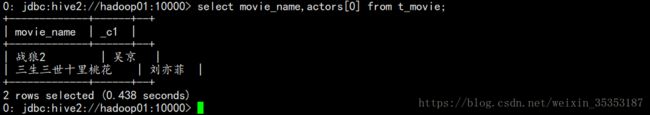
select moive_name,actors[0] from t_movie;
select movie_name,actors from t_movie where array_contains(actors,'吴刚');
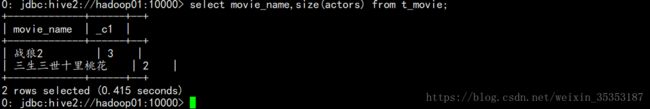
select movie_name,size(actors) from t_movie;
3.9.2 Map类型
maps: MAP
假如有以下数据:
| 1,zhangsan,father:xiaoming#mother:xiaohuang#brother:xiaoxu,28 2,lisi,father:mayun#mother:huangyi#brother:guanyu,22 3,wangwu,father:wangjianlin#mother:ruhua#sister:jingtian,29 4,mayun,father:mayongzhen#mother:angelababy,26 |
可以用一个map类型来对上述数据中的家庭成员进行描述
建表语句:
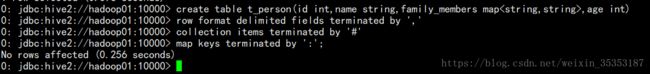
create table t_person(id int,name string,family_members map
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by '#'
map keys terminated by ':';
导入数据:
load data local inpath '/root/person.dat' into table t_person;
查询
select * from t_person;
取map字段的指定key的值
select id,name,family_members['father'] as father from t_person;
注 : as father 为设置一个别名
取map字段的所有key
select id,name,map_keys(family_members) as relation from t_person;
取map字段的所有value
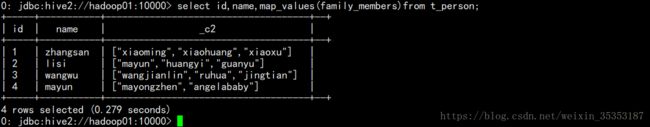
select id,name,map_values(family_members) from t_person;
select id,name,map_values(family_members)[0] from t_person;
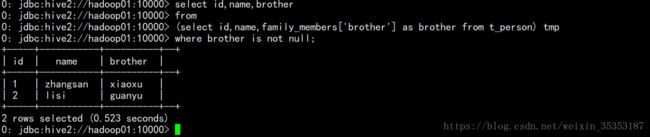
综合:查询有brother的用户信息
select id,name,brother
from
(select id,name,family_members['brother'] as brother from t_person) tmp
where brother is not null;
3.9.3 struct类型
structs: STRUCT
假如有如下数据:
| 1,zhangsan,18:male:beijing 2,lisi,28:female:shanghai |
其中的用户信息包含:年龄:整数,性别:字符串,地址:字符串
设想用一个字段来描述整个用户信息,可以采用struct
建表:
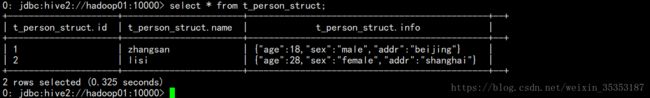
create table t_person_struct(id int,name string,info struct
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':';
导入数据:
load data local inpath '/root/person_struct.dat' into table t_person_struct;
查询
select * from t_person_struct;
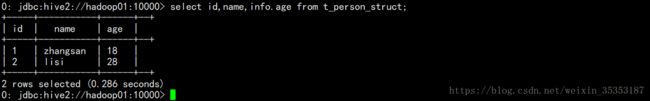
select id,name,info.age from t_person_struct;
select id,name,info.sex from t_person_struct;
3.10 修改表定义
仅修改Hive元数据,不会触动表中的数据,用户需要确定实际的数据布局符合元数据的定义。
修改表名:
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name
示例:alter table t_zhang rename to t_junjie;
修改分区名:
alter table t_partition partition(department='xiangsheng',sex='male',howold=20)
rename to partition(department='1',sex='1',howold=20);
添加分区:
alter table t_partition add partition (department='2',sex='0',howold=40);
删除分区:
alter table t_partition drop partition (department='2',sex='2',howold=24);
修改表的文件格式定义:
ALTER TABLE table_name [PARTITION partitionSpec] SET FILEFORMAT file_format
alter table t_partition partition(department='2',sex='0',howold=40 ) set fileformat sequencefile;
修改列名定义:
ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE [COLUMN] col_old_name col_new_name column_type [COMMENTcol_comment] [FIRST|(AFTER column_name)]
alter table t_user change price jiage float first;
price为之前的列名 , jiage为新的列名 , float 为字段的类型 ,first 可加可不加 , 加的话该列修改以后会放到第一列 .
增加/替换列:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD|REPLACE COLUMNS (col_name data_type[COMMENT col_comment], ...)
alter table t_user add columns (sex string,addr string);
添加列 , 一次可以添加多个列 . (sex,addr)即为新添加的列 , 需要跟上字段类型
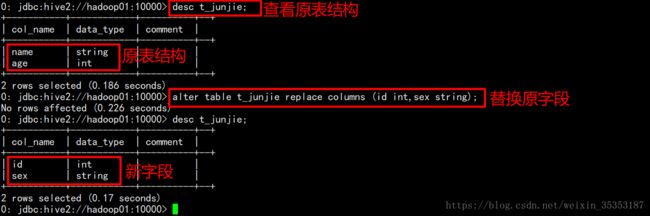
alter table t_user replace columns (id string,age int,price float);
替换 ,直接将原字段替换掉
alter table t_junjie replace columns (id int,sex string);
3.11 hive查询语法
sql是一门面向集合的编程语言;
select 1;
提示:在做小数据量查询测试时,可以让hive将mrjob提交给本地运行器运行,可以在hive会话中设置如下参数:
hive> set hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true;
hive> set hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true;
hive> set hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true;
基本查询示例
select * from t_access;
select count(*) from t_access;
select max(ip) from t_access;
条件查询
select * from t_access where access_time<'2017-08-06 15:30:20'
select * from t_access where access_time<'2017-08-06 16:30:20' and ip>'192.168.33.3';
3.12 join关联查询示例
注 : Hive中 join 不支持不等值连接 , 只支持等值连接 , 其他 SQL 支持不等值 join 连接 .
假如有a.txt文件
a,1
b,2
c,3
d,4假如有b.txt文件
a,aa
b,bb
d,cc
e,dd创建 t_a 表和 t_b 表 :
导入数据 :
3.12.1 内连接
select * from t_a a join t_b b on a.name = b.name;![]()
结果:
3.12.2 左外连接
select * from t_a a left join t_b b on a.name = b.name;
![]()
结果 :
3.12.3 右外连接
select * from t_a a right join t_b b on a.name = b.name;
![]()
结果:
3.12.4 全外连接 full outer join
select * from t_a a full join t_b b on a.name = b.name;
![]()
结果:
3.12.5 左半连接 left semi join
Left semi join :相当于join连接两个表后产生的数据中的左半部分
注意: left semi join的 select子句中,不能有右表的字段
select * from t_a a left semi join t_b b on a.name = b.name;
![]()
结果:
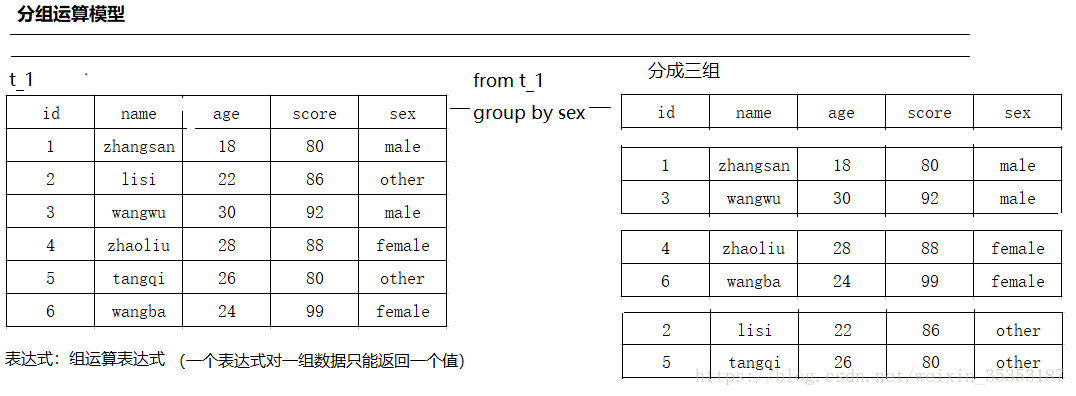
3.13 group by分组聚合
注意: 一旦有group by子句,那么,在select子句中就不能有 (分组字段,聚合函数) 以外的字段
(说的简单通俗一点就是 , 分组以后的查询只能查询分组的字段 , 以及分组以后可以聚合的字段 , 比如最大值 , 最小值 , 求和 , 求平均值等等的答案只有一个的字段 , 如果按性别分组 , 会有 male这种结果 , 我们可以求成绩的最大值 , 或者年龄的平均值 , 又或是年龄的最小值 , 但是不能求姓名 , 因为对应的 male 只有一行 , 而姓名有俩个 , 就会出现俩行 ) .
为什么where必须写在group by的前面,为什么group by后面的条件只能用having
因为,where是用于在真正执行查询逻辑之前过滤数据用的
having是对group by聚合之后的结果进行再过滤;
有如下数据 :
创建一个表 :
create table t_user(id int,name string,age int,score int,sex string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
![]()
导数据 :
load data local inpath '/root/user.txt' into table t_user;
![]()
分组查询 :
1 按性别分组 , 并查询性别以及年龄的最大值
select max(age),sex from t_user group by sex ;
2 求每一种性别的平均成绩 , 但请过滤掉平均年龄 >25岁的性别
select sex,avg(score) from t_user group by sex having avg(age)<=25;
3 . 求每一种性别的平均成绩 , 但是性别平均年龄>25的不要 , 而且性别平均成绩低于85分的不要
select sex,avg(score) from t_user group by sex having avg(age)<=25 and avg(score)>=85;
4 求每种性别的平均成绩 , 但是成绩低于82分不计入统计 , 并且最后结果中 , 去除性别平均年龄>25岁的;
select sex,avg(score) from t_user where score>82 group by sex having avg(age)<25;
查询过程图 :
上述语句的执行逻辑:
where过滤不满足条件的数据
用聚合函数和group by进行数据运算聚合,得到聚合结果
用having条件过滤掉聚合结果中不满足条件的数据