Python网络爬虫《七》
案例一:淘宝商品信息定向爬虫实例编写
功能描述:
1、目标:获取淘宝搜索页面的信息,提取其中的商品名称和价格;
2、理解:淘宝的搜索接口;翻页的处理;
3、技术路线:request-re
4、可行性:User-agent:*Dissallow
观察:
https://s.taobao.com/search?q=%E4%B9%A6%E5%8C%85&imgfile=&commend=all&ssid=s5-e&search_type=item&sourceId=tb.index&spm=a21bo.2017.201856-taobao-item.1&ie=utf8&initiative_id=tbindexz_20170306&bcoffset=4&ntoffset=4&p4ppushleft=1%2C48&s=0
https://s.taobao.com/search?q=%E4%B9%A6%E5%8C%85&imgfile=&commend=all&ssid=s5-e&search_type=item&sourceId=tb.index&spm=a21bo.2017.201856-taobao-item.1&ie=utf8&initiative_id=tbindexz_20170306&bcoffset=4&ntoffset=4&p4ppushleft=1%2C48&s=44
https://s.taobao.com/search?q=%E4%B9%A6%E5%8C%85&imgfile=&commend=all&ssid=s5-e&search_type=item&sourceId=tb.index&spm=a21bo.2017.201856-taobao-item.1&ie=utf8&initiative_id=tbindexz_20170306&bcoffset=4&ntoffset=4&p4ppushleft=1%2C48&s=88
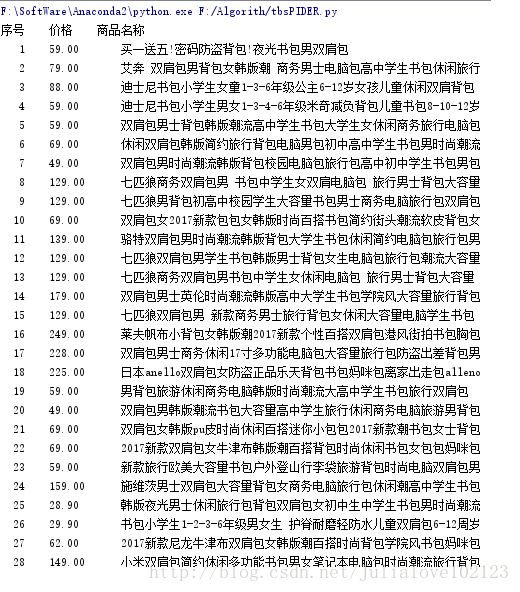
第一个商品 :view_price":"59.00","raw_title":"迪士尼书包小学生男女1-3-4-6年级米奇减负背包儿童书包8-10-12岁"
代码练习:
#/usr/bin/env.python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import requests
import re
#1、提交商品搜索请求,循环获取页面;
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text #返回的类型是 str(object='') -> string
except:
return ""
#2、对于每个页面,提取商品名称和价格信息;
def parsePage(ilt,html):
try:
plt = re.findall(r'\"view_price\"\:\"[\d\.]*\"', html) #商品价格“view_price”:"price"
tlt = re.findall(r'\"raw_title\"\:\".*?\"', html) #商品名称,一定注意中英文格式,还有转义符
for i in range(len(plt)):
price = eval(plt[i].split(':')[1]) #eval去掉单双引号, list of strings
title = eval(tlt[i].split(':')[1])
ilt.append([price,title]) #注意[]列表
except:
print ""
#3、将信息输出到屏幕上;
def printInfoList(ilt):
tplt = "{:4}\t{:8}\t{:16}"
print tplt.format("序号", "价格", "商品名称")
count = 0
for g in ilt:
count = count + 1
print tplt.format(count,g[0],g[1])
def main():
goods ="书包"
depth = 2
#https://s.taobao.com/search?q=书包
start_url = 'https://s.taobao.com/search?q=' + goods
infolist=[]
for i in range(depth):
try:
url =start_url+'&s='+str(44*i)
#print getHTMLText(url)
parsePage(infolist,getHTMLText(url))
except:
continue
printInfoList(infolist)
main()补充:
1、eval
功能:将字符串str当成有效的表达式来求值并返回计算结果。
语法: eval(source[, globals[, locals]]) -> value
参数:
source:一个Python表达式或函数compile()返回的代码对象
globals:可选。必须是dictionary
locals:可选。任意map对象
实例展示:
1 可以把list,tuple,dict和string相互转化。
2 #################################################
3 字符串转换成列表 4 >>>a = "[[1,2], [3,4], [5,6], [7,8], [9,0]]" 5 >>>type(a) 6 'str'> 7 >>> b = eval(a) 8 >>> print b 9 [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8], [9, 0]] 10 >>> type(b) 11 'list'> 12 ################################################# 13 字符串转换成字典 14 >>> a = "{1: 'a', 2: 'b'}" 15 >>> type(a) 16 'str'> 17 >>> b = eval(a) 18 >>> print b 19 {1: 'a', 2: 'b'} 20 >>> type(b) 21 'dict'> 22 ################################################# 23 字符串转换成元组 24 >>> a = "([1,2], [3,4], [5,6], [7,8], (9,0))" 25 >>> type(a) 26 'str'> 27 >>> b = eval(a) 28 >>> print b 29 ([1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8], (9, 0)) 30 >>> type(b) 31 'tuple'>
2、split():通常用于将字符串切片并转换为列表。
<一>、函数说明:
split():语法:str.split(str="",num=string.count(str))[n]
拆分字符串。通过制定分隔符将字符串进行切片,并返回分割后的字符串列表[list]
参数:str:分隔符,默认为空格,但不能为空("")
num: 表示分割次数。如果指定num,则分割成n+1个子字符串,并可将每个字符串赋给新的变量
[n]: 选取第n个分片,即第n个字符串,从0开始算。
<二>、例子:
u = "www.google.com"
print u.split('.') --> ['www','google','com']
print u.split('.',1)-->['www','google.com']
print u.split('.',2)[1]-->google
u1,u2,u3 = u.split('.')
结果展示: