【小项目】注释风格转换(从C语言注释风格转换到C++注释风格)
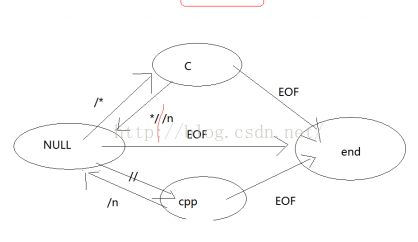
我们设置四种状态,这是状态之间的转换图。
那在从C到C++的转换过程中,我们大概能遇到几种情况呢。先来看看的我们的测试文件
// 1.一般情况
/* int i = 0; */
// 2.换行问题
/* int i = 0; */int j = 0;
/* int i = 0; */
int j = 0;
// 3.匹配问题
/*int i = 0;/*xxxxx*/
// 4.多行注释问题
/*
int i=0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
*/int k = 0;
// 5.连续注释问题
/**//**/
// 6.连续的**/问题
/***/
// 7.C++注释问题
// /*xxxxxxxxxxxx*/
这个程序,我觉得最难的部分就是把逻辑弄清楚,之后再慢慢的实现,在程序没有语法错误的时候,根据结果文件output.c来查找是哪里的问题就比较容易了。
接下来看看我的实现,先看主函数部分,主要功能就是打开两个文件
#include"CommentConvert.h"
int main()
{
FILE *pfRead = NULL;
FILE *pfWrite = NULL;
printf("转换开始\n");
pfRead = fopen(INPUTFILENAME, "r");
if (NULL == pfRead)
{
perror("open file for read");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
pfWrite = fopen(OUTPUTFILENAME, "w");
if (NULL == pfWrite)
{
fclose(pfRead);
perror("open file for write");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
CommentConvert(pfRead, pfWrite);
printf("转换结束\n");
fclose(pfRead);
fclose(pfWrite);
getchar();
return 0;
}#include"CommentConvert.h"
void CommentConvert(FILE *pfRead, FILE *pfWrite)
{
state = NUL_STATE;
while (state != END_STATE)
{
switch (state)
{
case NUL_STATE:
Do_NUL_State(pfRead, pfWrite);
break;
case C_STARE:
Do_C_State(pfRead, pfWrite);
break;
case CPP_STATE:
Do_Cpp_State(pfRead, pfWrite);
break;
case END_STATE:
break;
}
}
}
void Do_NUL_State(FILE *pfRead, FILE *pfWrite)
{
int first = 0;
int second = 0;
first = fgetc(pfRead);
switch (first)
{
case '/':
second = fgetc(pfRead);
if (second == '*')
{
fputc('/', pfWrite);
fputc('/', pfWrite);
state = C_STARE;
}
else if (second == '/')
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
fputc(second, pfWrite);
state = CPP_STATE;
}
else
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
fputc(second, pfWrite);
}
break;
case EOF:
fputc(first, pfWrite);
state = END_STATE;
break;
default:
fputc(first, pfWrite);
break;
}
}
void Do_C_State(FILE *pfRead, FILE *pfWrite)
{
int first = 0;
int second = 0;
first = fgetc(pfRead);
switch (first)
{
case '\n':
fputc('\n', pfWrite);
fputc('/', pfWrite);
fputc('/', pfWrite);
break;
case'*':
second = fgetc(pfRead);
if (second == '/')
{
state = NUL_STATE;
first = fgetc(pfRead);
if (first != '\n')
{
fputc('\n', pfWrite);
ungetc(first, pfRead);
}
else
{
fputc('\n', pfWrite);
}
}
else if (second == '*')
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
ungetc(second,pfRead);
//first = fgetc(pfRead);
/*if (first == '/')
{
fputc('\n', pfWrite);
state = NUL_STATE;
}*/
}
else
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
fputc(second, pfWrite);
}
break;
case EOF:
fputc(first, pfWrite);
state = END_STATE;
break;
default:
fputc(first, pfWrite);
break;
}
}
void Do_Cpp_State(FILE *pfRead, FILE *pfWrite)
{
int first = 0;
int second = 0;
first = fgetc(pfRead);
switch (first)
{
case'/':
second = fgetc(pfRead);
if (second == '*')
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
fputc(second, pfWrite);
}
else if (second == '/')
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
fputc(second, pfWrite);
state = NUL_STATE;
}
else
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
fputc(second, pfWrite);
}
break;
case'\n':
fputc(first, pfWrite);
state = NUL_STATE;
break;
case'*':
second = fgetc(pfRead);
if (second == '/')
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
fputc(second, pfWrite);
}
else if (second == '*')
{
fputc(first, pfWrite);
ungetc(second, pfRead);
}
break;
case EOF:
/*fputc(first, pfWrite);*/
state = END_STATE;
break;
default:
fputc(first, pfWrite);
break;
}
}#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#ifndef _COMCON_
#define _COMCON_
#include
#include
#define INPUTFILENAME "input.c"
#define OUTPUTFILENAME "output.c"
enum STATE
{
NUL_STATE,
C_STARE,
CPP_STATE,
END_STATE
};
enum STATE state;
void CommentConvert(FILE *pfRead, FILE *pfWrite);
void Do_NUL_State(FILE *pfRead, FILE *pfWrite);
void Do_C_State(FILE *pfRead, FILE *pfWrite);
void Do_Cpp_State(FILE *pfRead, FILE *pfWrite);
#endif // 1.一般情况
// int i = 0;
// 2.换行问题
// int i = 0;
int j = 0;
// int i = 0;
int j = 0;
// 3.匹配问题
//int i = 0;/*xxxxx
// 4.多行注释问题
//
//int i=0;
//int j = 0;
//int k = 0;
//
int k = 0;
// 5.连续注释问题
//
//
// 6.连续的**/问题
//*
// 7.C++注释问题
// /*xxxxxxxxxxxx*/