Educational Codeforces Round 90 (Rated for Div. 2) CF1373 E,F,G题解
E:
首先考虑第一位的 f ( ) = m f()=m f()=m,枚举m,后面的k个的 f ( ) f() f()为 ( m + 1 , m + 2 , m + 3... m + k ) (m+1,m+2,m+3...m+k) (m+1,m+2,m+3...m+k)(不考虑进位)。
对于这些m,直接贪心选择数:越靠后的数字尽可能大。
如果要进位,最多只可能进一次,也就变成了:
m , m + 1 , m + 2 , m + 3... m + i − j ∗ 9... m + k − j ∗ 9 m,m+1,m+2,m+3...m+i-j*9...m+k-j*9 m,m+1,m+2,m+3...m+i−j∗9...m+k−j∗9
对于这类情况直接枚举进位的个数就行了。
代码:
O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3)
#include
#define KEEP while(1)
#define SRAND mt19937 rng(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count())
#define random(a) rng()%a
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define POB pop_back
#define ff fflush(stdout)
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define debug_pair(A) cerr<
using namespace std;
const LL INF=1e18;
typedef pair<int,int> mp;
typedef pair<mp,mp> superpair;
#define int LL
int n,k;
int check(int num){
// int cnt=0;
if(num%9==0){
return num/9;
}
return 0;//
// while(num){
// if(num%10==9) cnt++;
// else{
// return 0;
// }
// num/=10;
// }
// return cnt;
}
int check2(int num,int k){
int res=0;
rb(i,num,num-1+k){
int tmp=i;
while(tmp){
res+=tmp%10;
// cout<
tmp/=10;
}
// cout<
}
return res;
}
string Min(string s1,string s2){
if(s1==":"){
return s2;
}
else{
if(s1.length()<s2.length()){
return s1;
}
if(s1.length()>s2.length()){
return s2;
}
return min(s1,s2);
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>k;
string res=":";
k++;
rb(i,0,n){
int save=n;
n-=(k*(i+i+k-1))/2;
if(n>0){
n=save;
continue;
}
if(n==0){
LL base=1;
string tmp="";
int rest=i;
while(rest){
if(rest+k-1<10&&base==1){
tmp+=char('0'+rest);
rest=0;
break;
}
if(base==1){
tmp+=char('0'+9-k+1);
base*=10;
rest-=9-k+1;
}
else{
tmp=char('0'+min(9ll,rest))+tmp;
base*=10;
rest-=min(9ll,rest);
}
// cout<
}
if(tmp==""){
tmp="0";
}
res=Min(res,tmp);
}
else{//
// if(i==23){
// cout<
// }
n=-n;
rb(j,1,n-1){
if(j>k-1) continue;
if(n%j==0&&check(n/j)){
int tmp=check(n/j);
tmp--;
int fi=k-j;
fi--;
int rest=i;
rest-=tmp*9;
rest-=9-fi;
if(rest>=0){
LL base=10;
string tt="";
tt+=char('0'+9-fi);
rb(I,1,tmp){
tt='9'+tt;
base*=10;
}
bool ok=1;
while(rest){
tt=char('0'+min(rest,9ll-ok))+tt;
rest-=min(rest,9ll-ok);
base*=10;
ok=0;
}
res=Min(res,tt);
}
}
}
}
n=save;
}
if(res[0]==':'){
res="-1";
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
signed main(){
fastio;
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
/*
1
123 2
1
26 4
896 897 898 899 900
*/
F:
两种做法:
第一种:
类似于"HMT"如果连续的一段基站的值<他们之间的房子的需要值则不可以,否则ok。
可以看一下这个证明。
第二种
假设第1个基站分给了第一个城市里的 x x x个房子的网。
那么剩下的那么多怎么分配?
首先贪心考虑,由于 第一个基站分给了第一个城市 x x x个则剩下 b 1 − x b_1-x b1−x个,由于这些只能分给第2个城市了则就把它们全部分给第二个城市。设第 i i i房子还需要的值位 n e e d i need_i needi。这样 n e e d 2 = n e e d 2 − ( b [ 1 ] − x ) need_2=need_2-(b[1]-x) need2=need2−(b[1]−x)…也就是对于基站 i ( i ≥ 2 ) i(i\geq2) i(i≥2),先补完前面一个,然后把所有的都分给后面的一个。
这样也就是只要固定了 x x x最优的策略也就固定了。
设 f ( x ) f(x) f(x)表示如果给第一个基站分给第一个城市x个之后,为了满足所有的城市,还差 f ( x ) f(x) f(x)个。
显然如果存在一个 x ( 0 ≤ x ≤ m i n ( a 1 , b 1 ) , f ( x ) = 0 ) x(0\leq x\leq min(a_1,b_1),f(x)=0) x(0≤x≤min(a1,b1),f(x)=0),则答案位 Y E S YES YES,否则位 N O NO NO.。
显然如果第一个基站给第一个城市 x x x个后。
- 如果 x x x给多了,那么 f ( x ) ≤ f ( x + 1 ) ≤ f ( x ) + 1 f(x)\leq f(x+1)\leq f(x)+1 f(x)≤f(x+1)≤f(x)+1也就是 f ( x ) , f ( x + 1 ) . . . . . . f ( m i n ( a 1 , b 1 ) ) f(x),f(x+1)......f(min(a_1,b_1)) f(x),f(x+1)......f(min(a1,b1))是递增的
- 如果 x x x给少了,那么 f ( x ) ≤ f ( x − 1 ) ≤ f ( x ) + 1 f(x)\leq f(x-1)\leq f(x)+1 f(x)≤f(x−1)≤f(x)+1也就是 f ( x ) , f ( x − 1 ) . . . . . . f ( 0 ) f(x),f(x-1)......f(0) f(x),f(x−1)......f(0)是递增的。
则是一个这样的图像:
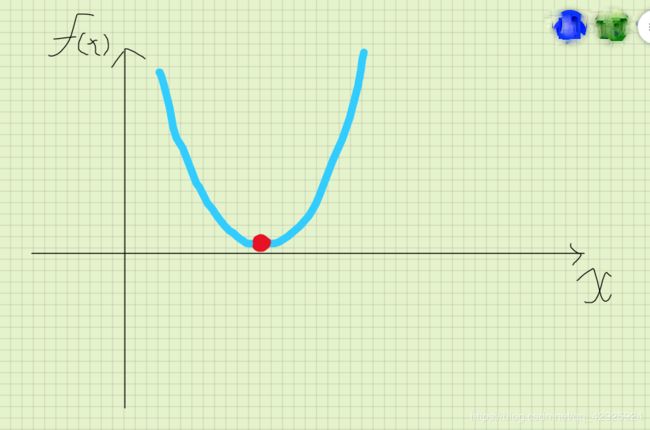
那么只要这个红点(最低点)在x轴上则答案为 Y E S YES YES
code:
O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)
#include
#define KEEP while(1)
#define SRAND mt19937 rng(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count())
#define random(a) rng()%a
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define POB pop_back
#define ff fflush(stdout)
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define debug_pair(A) cerr<
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef pair<int,int> mp;
typedef pair<mp,mp> superpair;
int tmp[1000000+2],n,a[1000000+2],b[1000000+2];
LL check2(int x)
{
rb(i,1,n){
tmp[i]=a[i];
}
tmp[1]-=x;
LL res=0;
rb(i,2,n){
int rest=b[i-1];
if(i!=2)rest-=tmp[i-1];
else rest-=x;
if(rest<0){
res+=-rest;
// cerr<
rest=0;
}
tmp[i]-=min(tmp[i],rest);
}
// cerr<
res+=max(0,tmp[1]+tmp[n]-b[n]);
// cerr<<"#"<
return res;
}
bool check(int x){
return check2(x-1)>=check2(x);
}
void mian(){
bool ok=1;
cin>>n;
rb(i,1,n)
cin>>a[i];
rb(i,1,n)
cin>>b[i];
// check2(1);
// return ;
if(check2(0)){
int l=1,r=min(b[1],a[1])+1;
while(l<r-1){
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(check(mid)){
l=mid;
}
else{
r=mid;
}
}
// cerr<<"#"<
if(check2(l)){
ok=0;
}
}
cout<<(ok? "YES":"NO")<<endl;
}
int main(){
fastio;
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
mian();
}
return 0;
}
/*
10
2 3 2 1 1 6 3 9 2 1
1 2 1 3 8 5 8 7 2 3
*/
G
首先可以贪心如果一个数在(x,y)要走到k列则,至少要走到 ( k , y + ∣ k − x ∣ ) (k,y+|k-x|) (k,y+∣k−x∣)这样可以给每一个在棋盘上的棋子附上一个士兵(x,y) 一个 v a l = y + ∣ k − x ∣ val=y+|k-x| val=y+∣k−x∣也就是至少走到的行数。
把所有val从小到大排序:
v a l 1 , v a l 2 , v a l 3 . . . v a l m val_1,val_2,val_3...val_m val1,val2,val3...valm
由于每一个格子最多有一个士兵,所以在纸上推一下就可以发现如果把每一个数 v a l i val_i vali加上 m − i m-i m−i:
v a l 1 + m − 1 , v a l 2 + m − 2 , v a l 3 + m − 3... v a l m + 0 val_1+m-1,val_2+m-2,val_3+m-3...val_m+0 val1+m−1,val2+m−2,val3+m−3...valm+0
答案就是:
m a x ( 0 , m a x ( v a l 1 + m − 1 , v a l 2 + m − 2 , v a l 3 + m − 3... v a l m + 0 ) − n ) max(0,max(val_1+m-1,val_2+m-2,val_3+m-3...val_m+0)-n) max(0,max(val1+m−1,val2+m−2,val3+m−3...valm+0)−n)
维护这个东西可以用fhq-treap,非常方便
code:
O ( m l o g m ) O(mlogm) O(mlogm)
#include
#define KEEP while(1)
//#define SRAND mt19937 rng(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count())
#define random(a) rand()%a
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define POB pop_back
#define ff fflush(stdout)
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define debug_pair(A) cerr<
using namespace std;
//const LL INF=23333333333333333;
typedef pair<int,int> mp;
typedef pair<mp,mp> superpair;
struct node{
int maxi,add,val,block;
int size,l,r,fix;
bool flag;
}v[200000+20];
void update(int index)
{
// v[index].mini=v[index].block;
v[index].maxi=v[index].val;
v[index].size=1;
if(v[index].l){
// v[index].mini=mini(v[index].mini,v[v[index].l].mini);
v[index].size+=v[v[index].l].size;
v[index].maxi=max(v[index].maxi,v[v[index].l].maxi+v[index].add);
}
if(v[index].r){
// v[index].mini=mini(v[index].mini,v[v[index].r].mini);
v[index].size+=v[v[index].r].size;
v[index].maxi=max(v[index].maxi,v[v[index].r].maxi+v[index].add);
}
}
void push_down(int index){
if(v[index].flag){
//this must be reversed
if(v[index].l){
v[v[index].l].flag^=1;
swap(v[v[index].l].l,v[v[index].l].r);
}
if(v[index].r){
v[v[index].r].flag^=1;
swap(v[v[index].r].l,v[v[index].r].r);
}
v[index].flag=0;
}
if(v[index].l){
v[v[index].l].add+=v[index].add;
v[v[index].l].maxi+=v[index].add;
v[v[index].l].val+=v[index].add;
// update(v[index].l);
}
if(v[index].r){
v[v[index].r].add+=v[index].add;
v[v[index].r].maxi+=v[index].add;
v[v[index].r].val+=v[index].add;
}
v[index].add=0;
// update(index);
}
int cnt=0;
int getnewnode(int val,int block){
node tmp;
tmp.maxi=val;
tmp.val=val;
tmp.add=tmp.flag=0;
tmp.size=1;
tmp.l=tmp.r=0;
tmp.block=block;
// tmp.mini=b,lock;
tmp.fix=random(1234567890);
cnt++;
v[cnt]=tmp;
return cnt;
}
void split(int base,int& x,int& y,int boundary){
if(!base){
x=y=0;
return;
}
if(v[base].size==boundary){
x=base;
y=0;
update(x);
}
if(!boundary){
x=0;
y=base;
update(y);
}
push_down(base);
if(v[v[base].l].size>=boundary){
y=base;
v[y]=v[base];
split(v[base].l,x,v[y].l,boundary);
update(y);
}
else{
x=base;
v[x]=v[base];
split(v[base].r,v[x].r,y,boundary-v[v[base].l].size-1);
update(x);
}
}
void split2(int base,int& x,int& y,int boundary){//=boundary
if(!base){
x=y=0;
return;
}
push_down(base);
if(v[base].block>=boundary){
y=base;
// v[y]=v[base];
split2(v[base].l,x,v[y].l,boundary);
update(y);
}
else{
x=base;
// v[x]=v[base];
split2(v[base].r,v[x].r,y,boundary);
update(x);
}
}
int merge(int x,int y){
if((!x)||(!y)){
if(x+y){
update(x+y);
}
return x+y;
}
if(v[x].fix>v[y].fix){
push_down(x);
v[x].r=merge(v[x].r,y);
update(x);
return x;
}
else{
push_down(y);
v[y].l=merge(x,v[y].l);
update(y);
return y;
}
}
int root=1;
map <mp,bool> M;
int main(){
srand(19260817);
fastio;
int n,k,m;
cin>>n>>k>>m;
int cnt=0;
rb(i,1,m){
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
int val=y+abs(x-k);
// cerr<<"#"<
if(M[II(x,y)]){
cnt--;
if(cnt==0){
cnt=0;
M[II(x,y)]=0;
cout<<0<<endl;
continue;
}
else{
int L,R;
split2(root,L,R,val);
int MID;
split(R,MID,R,1);
v[L].add--;
v[L].val--;
v[L].maxi--;
root=merge(L,R);
}
}
else{
cnt++;
if(cnt==1){
root=getnewnode(val,val);
}
else{
int L,R;
split2(root,L,R,val);
if(L){
v[L].add++;
v[L].val++;
v[L].maxi++;
}
// cerr<<"@"<
int Add=0;
if(R)
Add+=v[R].size;
int MID=getnewnode(Add+val,val);
L=merge(L,MID);
root=merge(L,R);
}
}
cout<<max(0,v[root].maxi-n)<<endl;
M[II(x,y)]^=1;
}
return 0;
}