NestJS 最早在 2017.1 月立项,2017.5 发布第一个正式版本,它是一个基于 Express,使用 TypeScript 开发的后端框架。设计之初,主要用来解决开发 Node.js 应用时的架构问题,灵感来源于 Angular。在本文中,我将粗略介绍 NestJS 中的一些亮点。
组件容器
NestJS 采用组件容器的方式,每个组件与其他组件解耦,当一个组件依赖于另一组件时,需要指定节点的依赖关系才能使用:
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CatsController } from './cats.controller';
import { CatsService } from './cats.service';
import { OtherModule } from '../OtherModule';
@Module({
imports: [OtherModule],
controllers: [CatsController],
providers: [CatsService],
})
export class CatsModule {}依赖注入(DI)
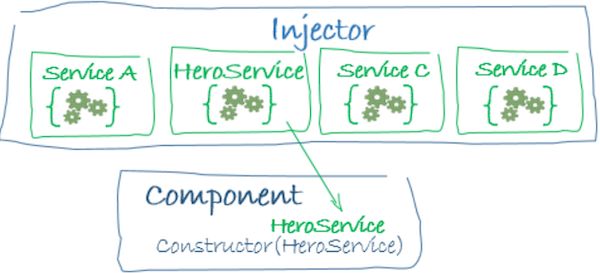
与 Angular 相似,同是使用依赖注入的设计模式开发
当使用某个对象时,DI 容器已经帮你创建,无需手动实例化,来达到解耦目的:
// 创建一个服务
@Inject()
export class TestService {
public find() {
return 'hello world';
}
}
// 创建一个 controller
@Controller()
export class TestController {
controller(
private readonly testService: TestService
) {}
@Get()
public findInfo() {
return this.testService.find()
}
}为了能让 TestController 使用 TestService 服务,只需要在创建 module 时,作为 provider 写入即可:
@Module({
controllers: [TestController],
providers: [TestService],
})
export class TestModule {}当然,你可以把任意一个带 @Inject() 的类,注入到 module 中,供此 module 的 Controller 或者 Service 使用。
背后的实现基于 Decorator + Reflect Metadata,详情可以查看 深入理解 TypeScript - Reflect Metadata。
细粒化的 Middleware
在使用 Express 时,我们会使用各种各样的中间件,譬如日志服务、超时拦截,权限验证等。在 NestJS 中,Middleware 功能被划分为 Middleware、Filters、Pipes、Grards、Interceptors。
例如使用 Filters,来捕获处理应用中抛出的错误:
@Catch()
export class AllExceptionsFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: any, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse();
const request = ctx.getRequest();
const status = exception.getStatus();
// 一些其他做的事情,如使用日志
response
.status(status)
.json({
statusCode: status,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url,
});
}
}使用 interceptor,拦截 response 数据,使得返回数据格式是 { data: T } 的形式:
import { Injectable, NestInterceptor, ExecutionContext } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { map } from 'rxjs/operators';
export interface Response {
data: T;
}
@Injectable()
export class TransformInterceptor
implements NestInterceptor> {
intercept(
context: ExecutionContext,
call$: Observable,
): Observable> {
return call$.pipe(map(data => ({ data })));
}
} 使用 Guards,当不具有 'admin' 角色时,返回 401:
import { ReflectMetadata } from '@nestjs/common';
export const Roles = (...roles: string[]) => ReflectMetadata('roles', roles);
@Post()
@Roles('admin')
async create(@Body() createCatDto: CreateCatDto) {
this.catsService.create(createCatDto);
}数据验证
得益于 class-validator 与 class-transformer 对传入参数的验证变的非常简单:
// 创建 Dto
export class ContentDto {
@IsString()
text: string
}
@Controller()
export class TestController {
controller(
private readonly testService: TestService
) {}
@Get()
public findInfo(
@Param() param: ContentDto // 使用
) {
return this.testService.find()
}
}当所传入参数 text 不是 string 时,会出现 400 的错误。
GraphQL
GraphQL 由 facebook 开发,被认为是革命性的 API 工具,因为它可以让客户端在请求中指定希望得到的数据,而不像传统的 REST 那样只能在后端预定义。
NestJS 对 Apollo server 进行了一层包装,使得能在 NestJS 中更方便使用。
在 Express 中使用 Apollo server 时:
const express = require('express');
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require('apollo-server-express');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`;
// Provide resolver functions for your schema fields
const resolvers = {
Query: {
hello: () => 'Hello world!',
},
};
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
const app = express();
server.applyMiddleware({ app });
const port = 4000;
app.listen({ port }, () =>
console.log(`Server ready at http://localhost:${port}${server.graphqlPath}`),
);在 NestJS 中使用它:
// test.graphql
type Query {
hello: string;
}
// test.resolver.ts
@Resolver()
export class {
@Query()
public hello() {
return 'Hello wolrd';
}
}使用 Decorator 的方式,看起来也更 TypeScript。
其他
除上述一些列举外,NestJS 实现微服务开发、配合 TypeORM、以及 Prisma 等特点,在这里就不展开了。
参考
- 深入理解 TypeScript - Reflect Metadata
- Egg VS NestJS
- NestJS 官网