球面坐标系
本文主要解决在球面上一点A,经纬度为( θ , ϕ \theta,\phi θ,ϕ), 朝着与经线成 ψ \psi ψ角转动,走了 ℓ \ell ℓ长度之后的新坐标系( θ ′ , ϕ ′ \theta',\phi' θ′,ϕ′), 求新坐标系的值以及跟新经线的新夹角是多少。
(一)球面正弦定理余弦定理
在球面上画一个三角形,如下图 Δ A B C \Delta ABC ΔABC


∠A对应的边为 a a a,(弧度单位),假设球半径为 r r r,则满足如下的余弦定理:

以及正弦定理:
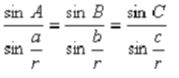
如果是单位球,即半径等于1,则正弦定理和余弦定理如下:

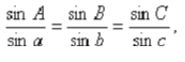
(二)新坐标的求解
如图,已经知道点 A ( θ , ϕ ) A(\theta, \phi) A(θ,ϕ), AB是经线,沿着与AB经线成一个角度 ψ \psi ψ的方向AC线(不一定是经线)走动距离 ℓ \ell ℓ到点C,求点C的经纬度( θ ′ , ϕ ′ \theta',\phi' θ′,ϕ′),以及BC经线与球面上的线AC的夹角 α \alpha α.
求解过程如下:

两次利用余弦定理即可把夹角 α \alpha α求出来
接下来要求经纬度( θ ′ , ϕ ′ \theta',\phi' θ′,ϕ′),这里需要考虑到点A是东经还是西经,南纬还是北纬的问题,先在这里不考虑,接下来一节再讨论这个问题

程序实现如下
import numpy as np
def point_change(init_longi,init_lati,r,psi):
psi = np.deg2rad(psi)
ang_c = np.pi/2-np.deg2rad(init_lati)
cos_a = np.cos(r)*np.cos(ang_c)+np.sin(r)*np.sin(ang_c)*np.cos(psi)
new_lati = np.abs(90-np.rad2deg(np.arccos(cos_a)))
new_longi = np.abs(init_longi-np.rad2deg(np.arcsin(np.sin(psi)*np.sin(r)/np.sqrt(1-cos_a**2))))
angle_change = np.rad2deg(np.arccos((np.cos(ang_c)-cos_a*np.cos(r))/(np.sqrt(1-cos_a**2)*np.sin(r))))
angle_change = 180 - angle_change
return angle_change, new_longi, new_lati
if __name__ == "__main__":
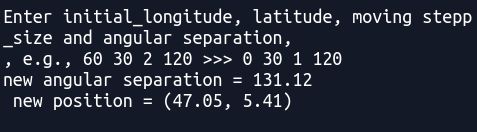
init_longitude, init_latitude, move_step_size, init_included_angle = map(int,input('Enter initial_longitude, latitude, moving stepp\
_size and angular separation,\n, e.g., 60 30 2 120 >>> ').split())
# The unit of r is rad
#included_angle, new_longi, new_lati = point_change(60,30,2,120)
included_angle, new_longi, new_lati = point_change(init_longitude, init_latitude, move_step_size, init_included_angle)
print("new angular separation = %.2f \n new position = (%.2f, %.2f) \n" %(included_angle, new_longi, new_lati))
(三)讨论点A东经西经南北纬问题
上面的程序是在没有考虑东西经度,南北纬度的情况。
东西经度的划分:面对一个地球仪经线0度,上方为北极,则左边是西经(经度往左逐渐增大),右边是东经(经度往右逐渐增大),下方是南纬,上方是北纬。
1)讨论经度
假设转动的角 ψ ≤ 180 \psi \leq 180 ψ≤180, 表明移动后的点C是在点A的左边。
- 点A初始点在西经,则在求得∠B之后,需要用 θ ′ = θ + ∠ B \theta'=\theta+\angle B θ′=θ+∠B得到的还是西经;然而需要注意的是如果 θ + ∠ B > 180 \theta+\angle B>180 θ+∠B>180, 则变成了东经,大小为abs ( θ + ∠ B − 360 ) (\theta+\angle B-360) (θ+∠B−360),
- 点A初始点在东经, 则在求得∠B之后,需要用 θ ′ = θ − ∠ B \theta'=\theta-\angle B θ′=θ−∠B得到的还是东经;然而需要注意的是如果 θ − ∠ B ≤ 0 \theta-\angle B \leq 0 θ−∠B≤0, 则变成了西经,大小为abs ( θ − ∠ B ) (\theta-\angle B) (θ−∠B)
假设转动的角 ψ > 180 \psi > 180 ψ>180, 表明移动后的点C是在点A的右边。
- 点A初始点在西经,则在求得∠B之后,需要用 θ ′ = θ − ∠ B \theta'=\theta-\angle B θ′=θ−∠B得到的还是西经;然而需要注意的是如果 θ − ∠ B ≤ 0 \theta-\angle B\leq 0 θ−∠B≤0, 则变成了东经,大小为abs ( θ − ∠ B ) (\theta-\angle B) (θ−∠B),
- 点A初始点在东经, 则在求得∠B之后,需要用 θ ′ = θ + ∠ B \theta'=\theta+\angle B θ′=θ+∠B得到的还是东经;然而需要注意的是如果 θ + ∠ B > 180 \theta+\angle B > 180 θ+∠B>180, 则变成了西经,大小为abs ( θ + ∠ B − 360 ) (\theta+\angle B - 360) (θ+∠B−360)
因此伪代码如下:
begin
if psi <= 180:
if theta is west longitude:
if theta + B <=180:
theta' = theta+B (west longitude)
else: theta' = abs(theta+B - 360) (east longitude)
else:
if theta - B > 0:
theta' = theta-B (east longitude)
else: theta' = abs(theta-B) (west longitude)
elif psi > 180:
if theta is east longitude:
if theta + B <=180:
theta' = theta+B (east longitude)
else: theta' = abs(theta+B - 360) (west longitude)
else:
if theta - B > 0:
theta' = theta-B (west longitude)
else: theta' = abs(theta-B) (east longitude)
end
由于往右边走,即 ψ > 180 \psi>180 ψ>180时, ∠B是负数,因此上面的两者可以结合起来,
无论夹角是否大于180度
- 点A初始点在西经,则在求得∠B之后,需要用 θ ′ = θ + ∠ B \theta'=\theta+\angle B θ′=θ+∠B得到的还是西经;然而需要注意的是如果 θ + ∠ B > 180 \theta+\angle B>180 θ+∠B>180, 则变成了东经,大小为abs ( θ + ∠ B − 360 ) (\theta+\angle B-360) (θ+∠B−360), 如果 θ + ∠ B < 0 \theta+\angle B<0 θ+∠B<0, 则值变为abs( θ + ∠ B \theta+\angle B θ+∠B), 东经
- 点A初始点在东经, 则在求得∠B之后,需要用 θ ′ = θ − ∠ B \theta'=\theta-\angle B θ′=θ−∠B得到的还是东经;然而需要注意的是如果 θ − ∠ B ≤ 0 \theta-\angle B \leq 0 θ−∠B≤0, 则变成了西经,大小为abs ( θ − ∠ B ) (\theta-\angle B) (θ−∠B),如果 θ − ∠ B < 0 \theta-\angle B<0 θ−∠B<0, 则值变为abs( θ − ∠ B \theta-\angle B θ−∠B), 西经
2)讨论纬度
因为我们计算的点B是位于北极点(无论点A在南纬还是北纬),所以以BC的边长a作为判断依据
如果A是北纬
- 如果 π / 2 − \pi/2- π/2−a > 0, 则是北纬rad2deg( π / 2 − \pi/2- π/2−a)度; #弧度化为度
- 如果 π / 2 − \pi/2- π/2−a < 0, 则是南纬rad2deg(abs( π / 2 − \pi/2- π/2−a))度;
如果A是南纬
- 如果 π / 2 − \pi/2- π/2−a > 0, 则是北纬rad2deg( π / 2 − \pi/2- π/2−a)度; #弧度化为度
- 如果 π / 2 − \pi/2- π/2−a < 0, 则是南纬rad2deg(abs( π / 2 − \pi/2- π/2−a))度;
因此对于南北纬都是一样的结论(因为是以a为判据,B在北极点)
伪代码:
if pi/2-a>0:
theta' = np.rad2deg(pi/2-a) (North latitude)
else: theta' = np.rad2deg(abs(pi/2-a)) (south latitude)
由于三角函数本身的限制,比如图中49°和131°的sin值是一样的,都是0.75,即
sin ( 49 ° ) = sin ( 131 ° ) = 0.75 \sin(49°)=\sin(131°)=0.75 sin(49°)=sin(131°)=0.75
当反推时arcsin(0.75)程序上只能给小值49.

因此在上面的过程中有以下要求:
- 在球面上移动的步长不能超过90度,即弧度值不能超过1.5
源码如下:
import numpy as np
def point_change(init_lon,w_e,init_lat,s_n,r,psi):
psi = np.deg2rad(psi)
ang_c = np.pi/2-np.deg2rad(init_lat)
cos_a = np.cos(r)*np.cos(ang_c)+np.sin(r)*np.sin(ang_c)*np.cos(psi)
new_lati = np.abs(90-np.rad2deg(np.arccos(cos_a)))
ang_B = np.rad2deg(np.arcsin(np.sin(psi)*np.sin(r)/np.sqrt(1-cos_a**2)))
a_val = abs(np.arccos(cos_a))
new_longi = np.abs(init_lon-np.rad2deg(np.arcsin(np.sin(psi)*np.sin(r)/np.sqrt(1-cos_a**2))))
# East or west longitude
if w_e is 'W':
if (init_lon + ang_B) <= 180 and (init_lon + ang_B)>0:
new_longi = init_lon + ang_B
W_E = 'W'
elif init_lon + ang_B > 180:
new_longi = abs(init_lon + ang_B -360)
W_E = 'E'
elif init_lon + ang_B < 0:
new_longi = abs(init_lon +ang_B)
W_E = 'E'
elif w_e is 'E':
if (init_lon - ang_B) <= 180 and (init_lon - ang_B)>0:
new_longi = init_lon - ang_B
W_E = 'E'
elif init_lon - ang_B > 180:
new_longi = abs(init_lon - ang_B -360)
W_E = 'E'
elif init_lon - ang_B < 0:
new_longi = abs(init_lon - ang_B)
W_E = 'W'
# South or north latitude
if (np.pi/2 - a_val)>0:
S_N = 'N'
else: S_N = 'S'
angle_change = np.rad2deg(np.arccos((np.cos(ang_c)-cos_a*np.cos(r))/(np.sqrt(1-cos_a**2)*np.sin(r))))
angle_change = 180 - angle_change
return angle_change, new_longi, W_E, new_lati, S_N
if __name__ == "__main__":
# The unit of r is rad
# The moving step_size should be less than 90*pi/180
# # input from terminal
# init_longitude, w_e_input, init_latitude, s_n_input, move_step_size, init_included_angle = \
# map(str,input('Enter initial_longitude, latitude, moving step_size and angular separation,\n, e.g., 60 E 30 N 1 120 >>> ').split())
# init_longitude = float(init_longitude)
# init_latitude = float(init_latitude)
# move_step_size = float(move_step_size)
# init_included_angle = float(init_included_angle)
# included_angle, new_longi, w_e, new_lati, s_n = \
# point_change(init_longitude, w_e_input, init_latitude, s_n_input, move_step_size, init_included_angle)
#input from code
included_angle, new_longi, w_e, new_lati, s_n = point_change(0,'W',0,'N',60*np.pi/180,90)
print(('new angular separation = %.2f\n new position = (%.2f'+w_e+', %.2f'+s_n+')')%(included_angle, new_longi, new_lati))
比如:原来的位置为西经30度北纬60度,沿着与经线成120度方向(此程序中是逆时针方向)后,得到的与新经线的夹角为153.38度,新坐标为经度78.95度,纬度14.92度