机器学习绘图库Python Matplotlib.pyplot全网最全面新手教程
最近看到一个讲Matplotlib的英文教程写的很高明,兼收并蓄,简单易懂,特意翻译过来,与君共享。原网址在:http://cs231n.github.io/python-numpy-tutorial/#matplotlib 。
Matplotlib(https://matplotlib.org/)是一个用来绘图的python库,它的matplotlib.pyplot模块提供了一个与MATLAB非常类似的绘图系统。
绘图(Plotting)
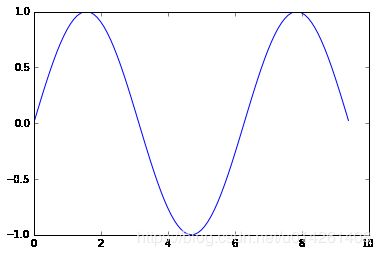
matplotlib中最重要的函数就是plot,它可以绘制二维图像,例子如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Compute the x and y coordinates for points on a sine curve
x = np.arange(0, 3 * np.pi, 0.1)
y = np.sin(x)
# Plot the points using matplotlib
plt.plot(x, y)
# 注意,必须调用plt.show(),不然图像不会显示出来
plt.show()
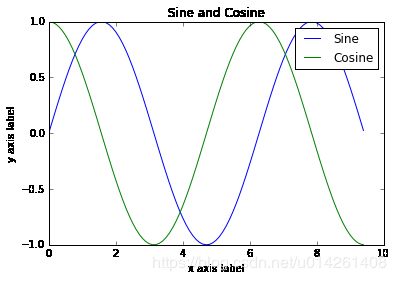
我们也可以在一幅图里绘制多条曲线,并且加上标题,图例,以及轴标签:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Compute the x and y coordinates for points on sine and cosine curves
x = np.arange(0, 3 * np.pi, 0.1)
y_sin = np.sin(x)
y_cos = np.cos(x)
# Plot the points using matplotlib
plt.plot(x, y_sin)
plt.plot(x, y_cos)
plt.xlabel('x axis label')
plt.ylabel('y axis label')
plt.title('Sine and Cosine')
plt.legend(['Sine', 'Cosine'])
plt.show()
有关plot函数更详细更全面的讲解尽在官方文档:https://matplotlib.org/api/pyplot_api.html#matplotlib.pyplot.plot 。
子图(Subplots)
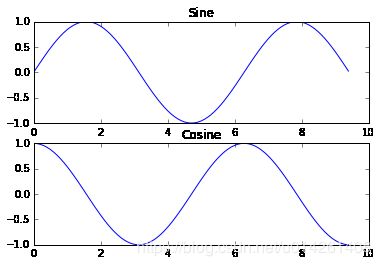
使用subplot函数,你就可以在同一个图像里绘制多个子图,栗子如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Compute the x and y coordinates for points on sine and cosine curves
x = np.arange(0, 3 * np.pi, 0.1)
y_sin = np.sin(x)
y_cos = np.cos(x)
# 我要绘制2行1列的子图,现在声明,我要绘制第1个子图啦~
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
# Make the first plot
plt.plot(x, y_sin)
plt.title('Sine')
# 现在声明我要绘制第2个子图啦~
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot(x, y_cos)
plt.title('Cosine')
# Show the figure.
plt.show()
关于subplot函数更详细的介绍尽在官方文档:https://matplotlib.org/api/pyplot_api.html#matplotlib.pyplot.subplot 。
图像(Images)
可以使用imshow函数绘制图像,栗子如下:
import numpy as np
from scipy.misc import imread, imresize
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = imread('assets/cat.jpg')
img_tinted = img * [1, 0.95, 0.9]
# Show the original image
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img)
# Show the tinted image
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
# A slight gotcha with imshow is that it might give strange results
# if presented with data that is not uint8. To work around this, we
# explicitly cast the image to uint8 before displaying it.
plt.imshow(np.uint8(img_tinted))
plt.show()